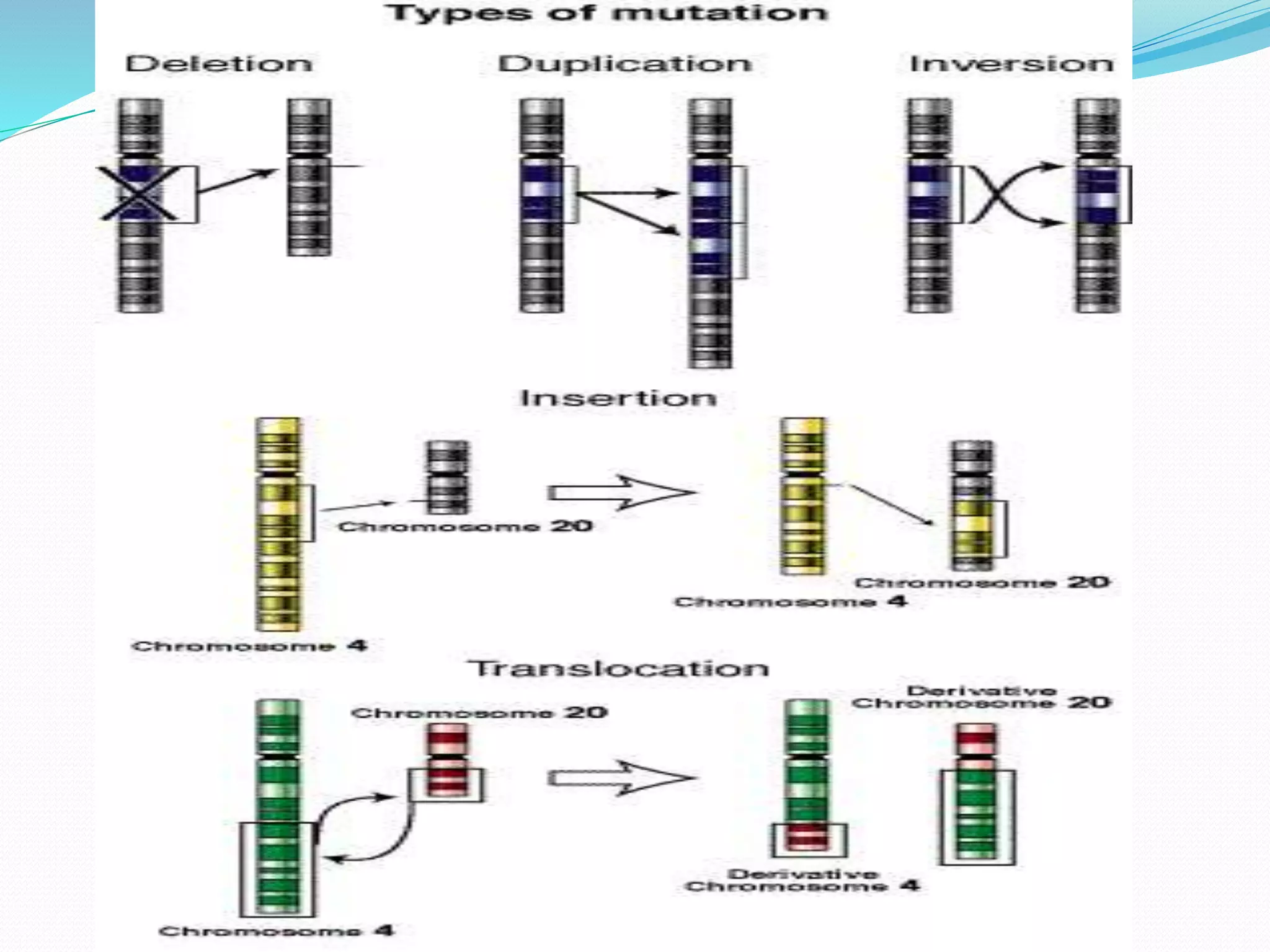
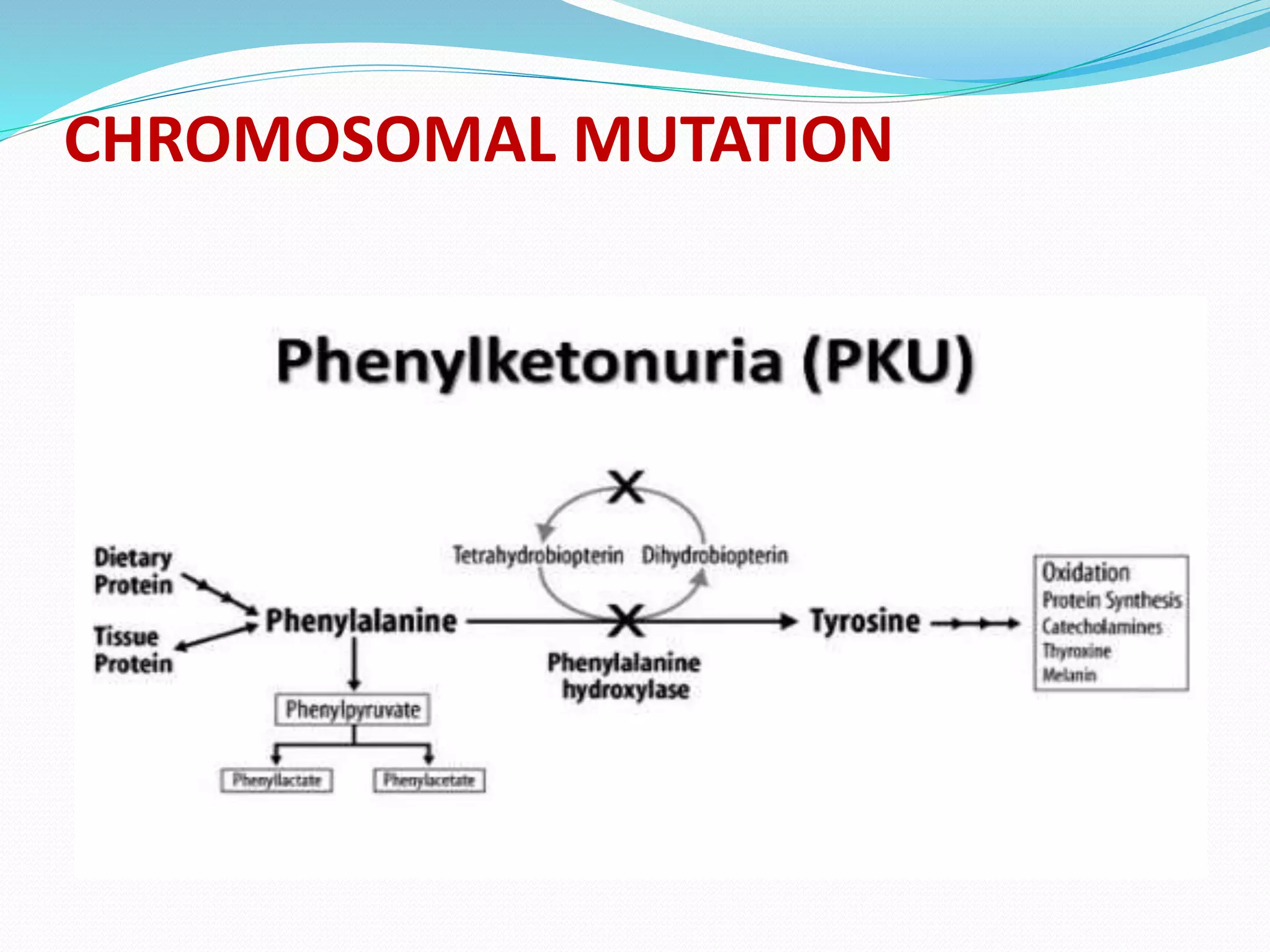
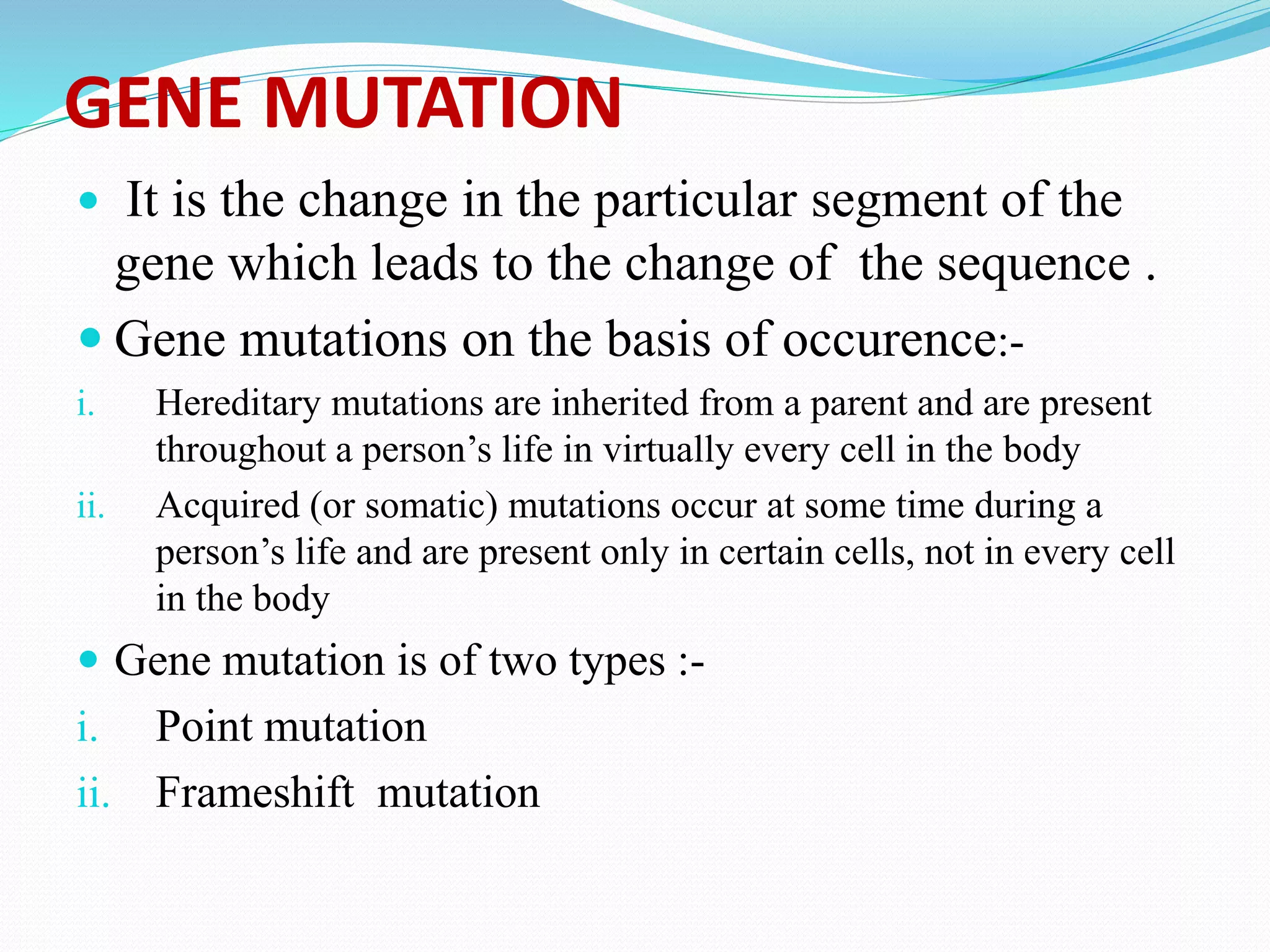
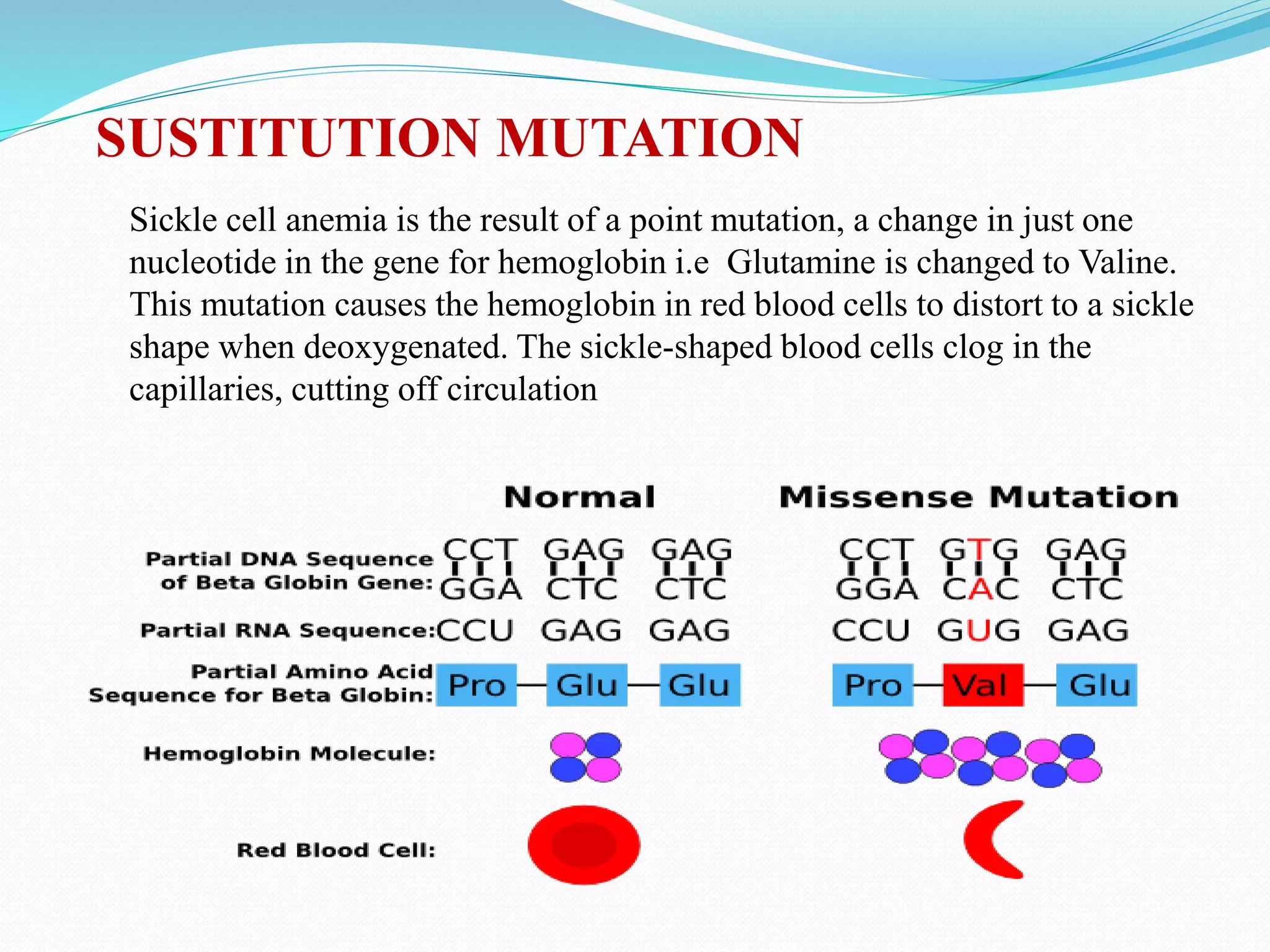
Mutations are changes in genetic material that alter the DNA sequence. There are two main types of mutations: chromosomal mutations, which involve changes to entire chromosomes, and gene mutations, which affect specific genes. Gene mutations can be further classified as point mutations, which involve a single nucleotide change, or frameshift mutations, caused by insertions or deletions of DNA bases. Mutations can be harmful, neutral, or beneficial, and are an important source of genetic variation driving evolution. Common genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy are caused by specific mutations.