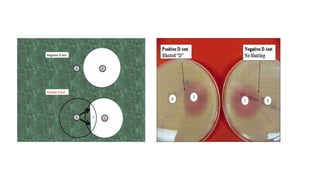
The document discusses the inducible clindamycin resistance test (D test) which is recommended to test for inducible resistance in staphylococci, streptococcus pneumoniae, and beta-hemolytic streptococci that are erythromycin resistant but clindamycin susceptible. The D test detects resistance by observing whether the zone of inhibition around a clindamycin disk is flattened near an erythromycin disk. A positive result indicates inducible resistance and that clindamycin treatment may fail in vivo due to selection of resistant mutants. The procedure and interpretation of the D test is described along with its limitations and clinical significance when evaluating clindamycin susceptibility.