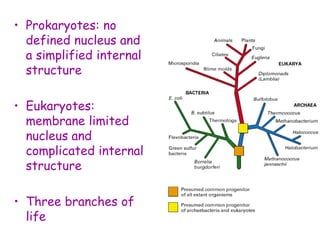
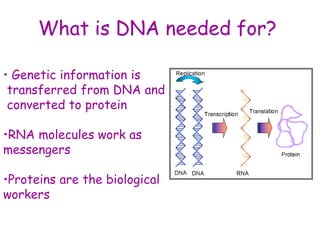
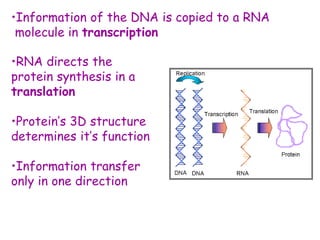
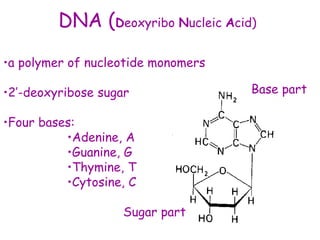
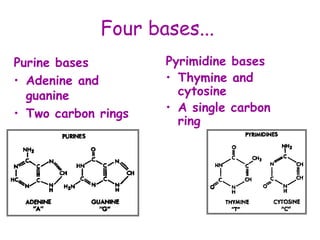
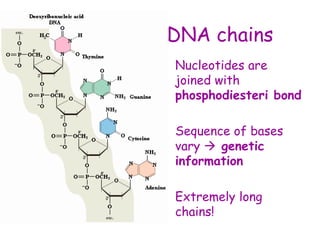
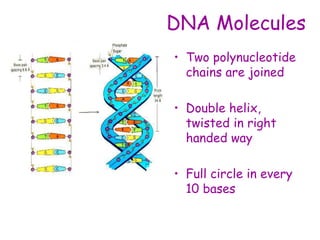
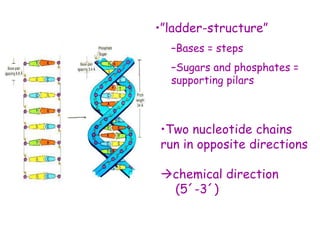
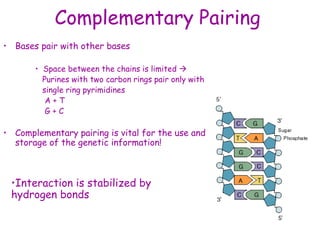
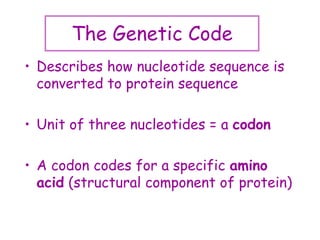
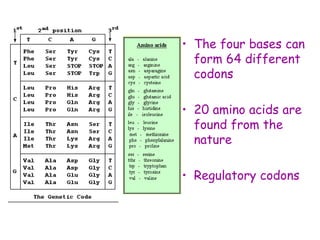
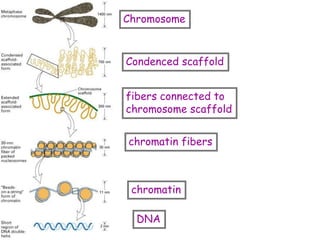
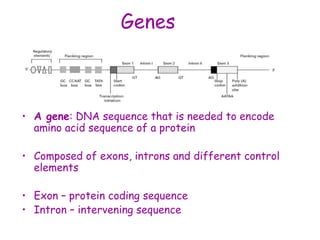
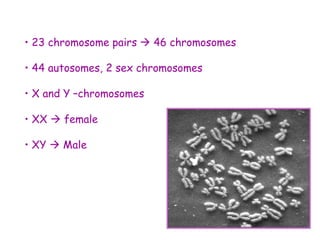
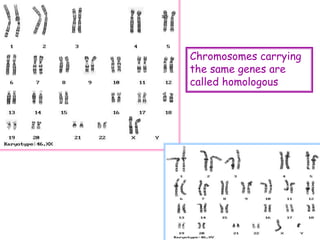
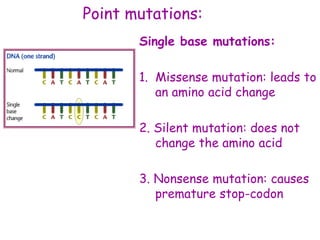
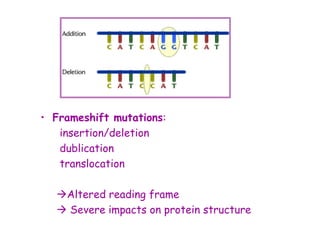
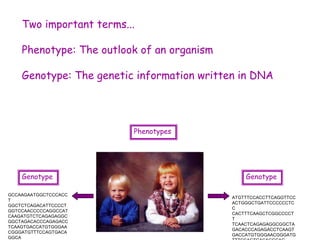
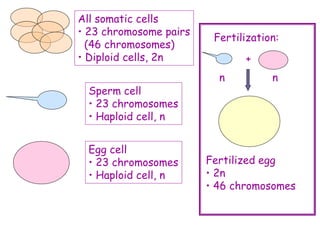
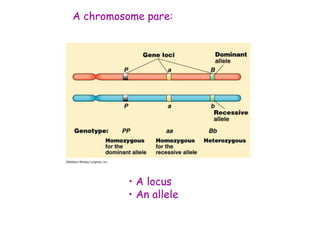
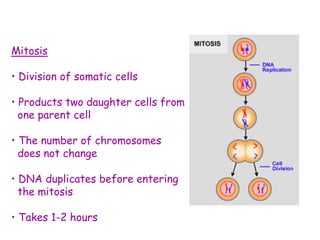
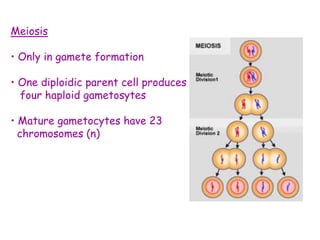
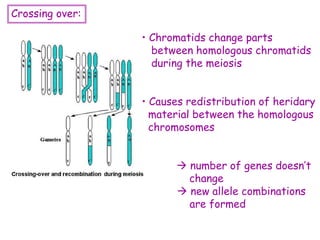
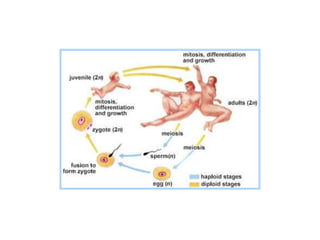
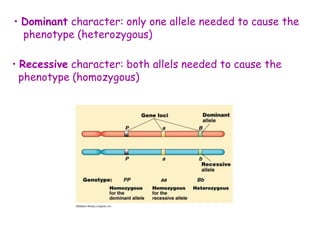
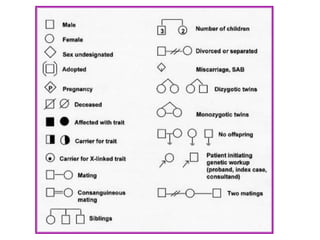
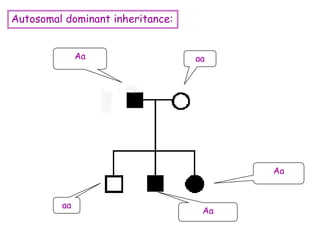
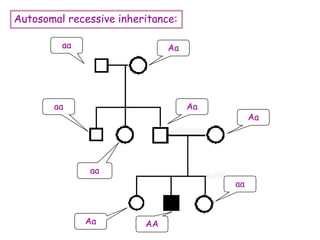
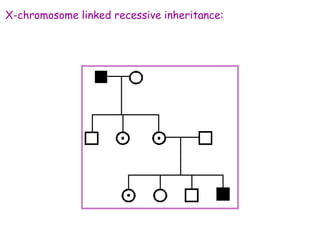
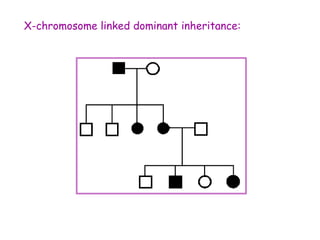
DNA contains the genetic code that determines an organism's traits. It is made up of nucleotides with four bases - adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine - that pair up in a double helix structure. Genes, located on chromosomes, are segments of DNA that encode instructions for making proteins. DNA is passed from parents to offspring, and mutations can occur that cause genetic disorders or diseases. The human genome project mapped the entire human DNA sequence, consisting of 3 billion base pairs organized into 22,000 genes on 23 chromosome pairs.