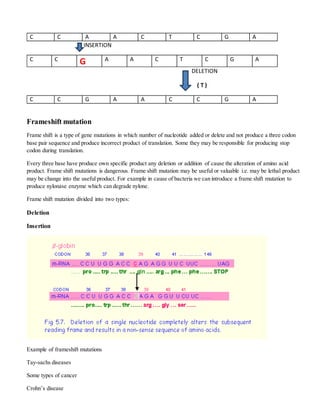
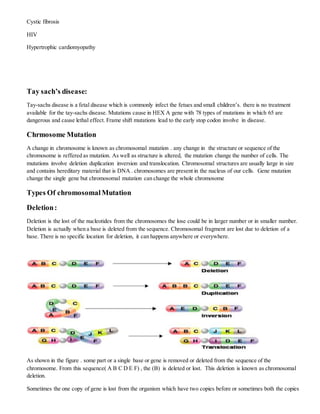
Mutations are changes in DNA sequences that can occur in genes, chromosomes, or the genome. There are several types of mutations including substitutions, insertions, deletions, and frameshifts. Mutations can be caused by errors during DNA replication or by exposure to mutagens like radiation. While some mutations are harmful and cause genetic disorders, others can be beneficial and lead to evolution. Researchers have studied mutations that occurred early in human development by analyzing DNA sequences from adult tissues to gain insights into embryology.