Embed presentation



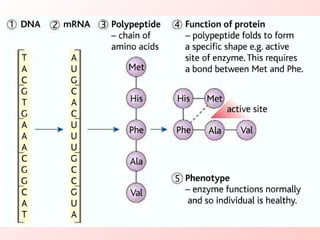
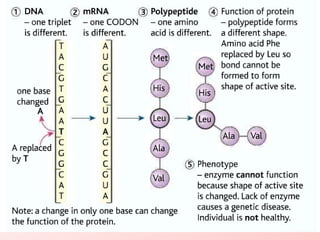
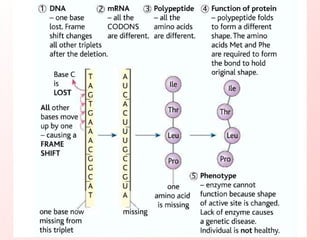
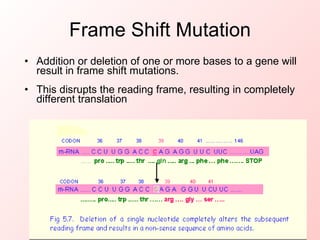


Mutations occur naturally or through mutagens and create genetic variation; deleterious mutations are removed by natural selection while beneficial mutations accumulate, resulting in evolution. A gene is a segment of DNA defined by its base sequence; any change by addition, deletion, or substitution of bases disrupts the gene's function. Frameshift mutations from inserting or removing bases change a gene's reading frame, altering its translation entirely. Substitution mutations substitute one base for another within a gene.








