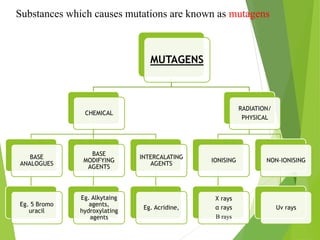
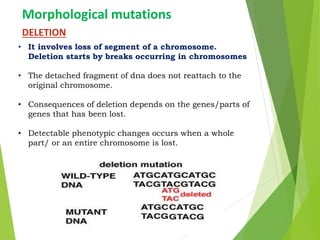
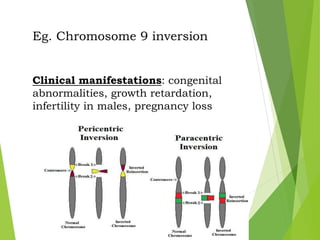
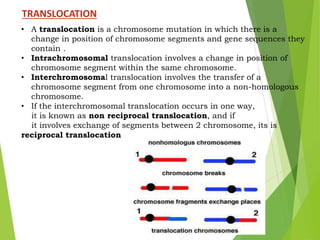
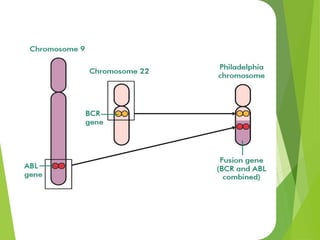
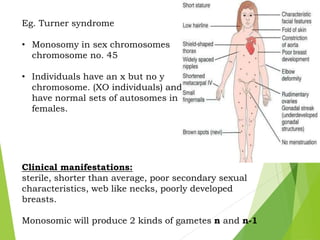
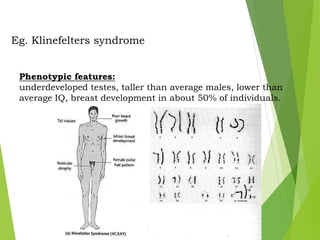
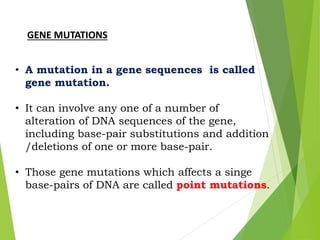
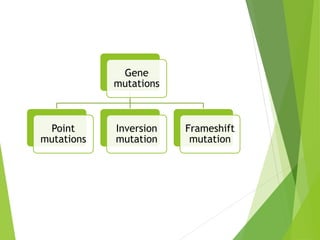
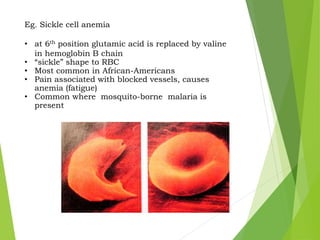
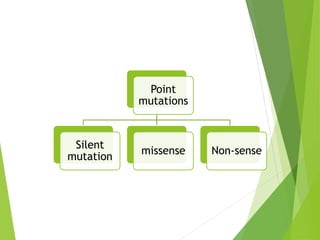
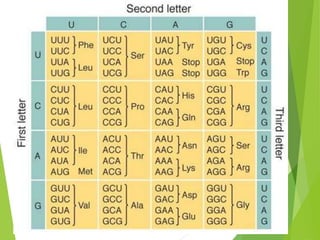
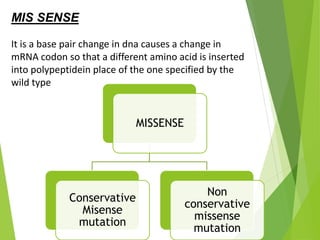
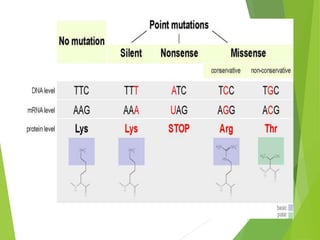
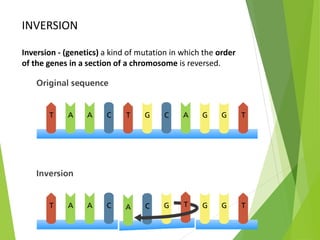
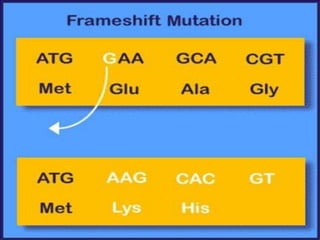
Mutations are sudden changes in the genetic material of an organism that can be caused by mutagens like chemicals, radiation, or errors in DNA replication. There are two main types of mutations: gene mutations, which alter the DNA sequence of a gene, and chromosomal mutations, which involve changes to chromosomes like deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations of DNA segments. Gene mutations can be point mutations, which substitute a single nucleotide, or frameshift mutations, which insert or delete nucleotides and alter the reading frame. Chromosomal mutations can cause diseases like Down syndrome, which results from trisomy of chromosome 21.