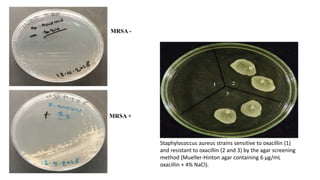
This document discusses methods for detecting Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). MRSA is any strain of S. aureus that is resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics due to the mecA gene. Rapid detection of MRSA is important for optimal treatment and reducing costs. The document describes several screening methods, focusing on the oxacillin salt agar screening test which involves growing bacterial samples on agar containing oxacillin and 4% NaCl. Growth of more than one colony indicates oxacillin resistance and identifies the strain as MRSA.