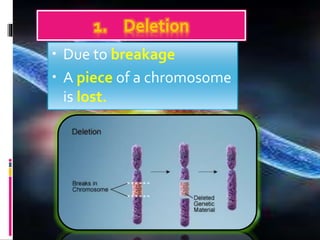
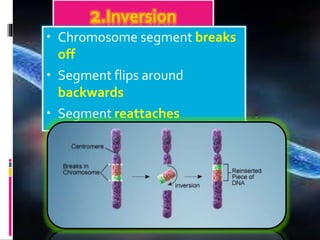
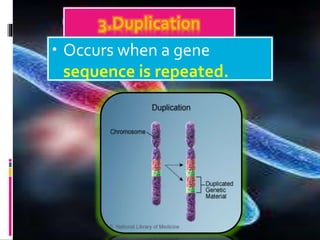
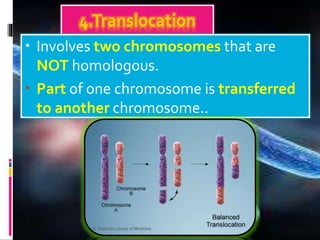
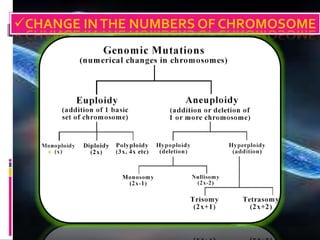
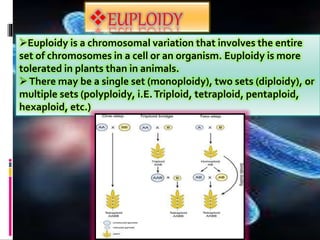
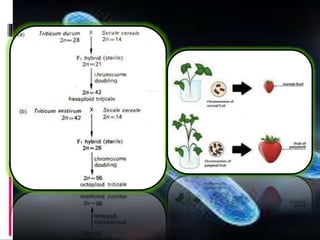
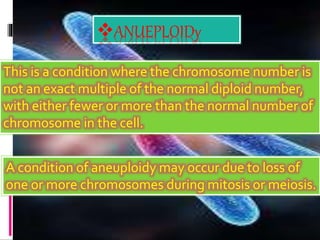
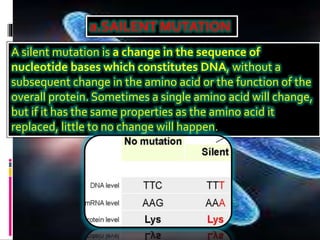
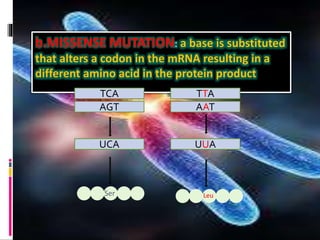
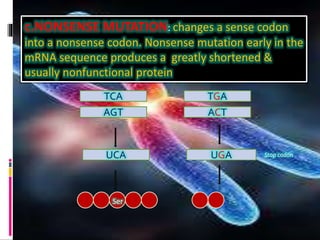
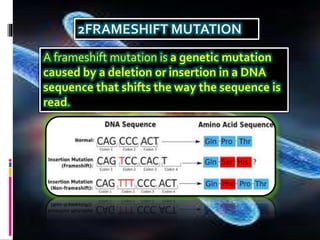
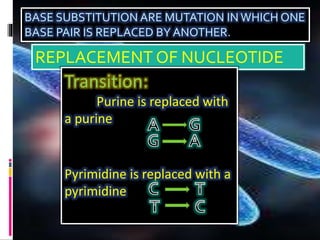
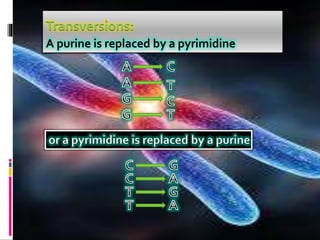
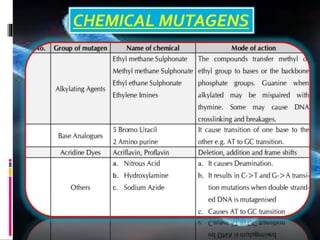
Mutations are changes to an organism's genetic material. There are several types of mutations, including changes to DNA sequences, chromosomes, and chromosome numbers. Point mutations alter single nucleotide base pairs and can be silent, missense, or nonsense. Chromosome mutations include deletions, inversions, duplications, and translocations. Changes in chromosome number include euploidy (having normal or multiple sets) and aneuploidy (having extra or missing chromosomes). Mutations can occur spontaneously or be induced by mutagens like radiation or chemicals. They provide genetic variation and are an important source of evolution.