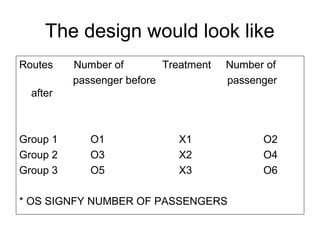
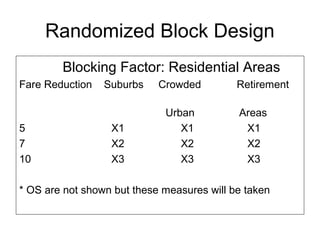
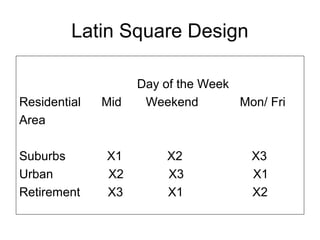
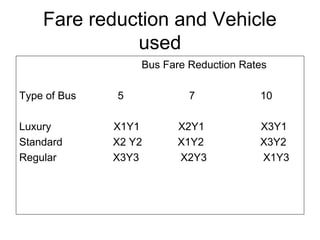
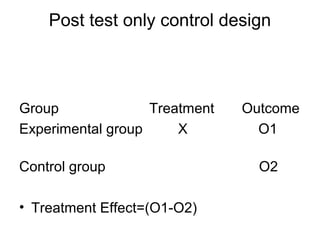
Experimental research designs involve examining potential cause-and-effect relationships between variables through experiments. There are various types of experimental designs including informal designs like quasi-experiments and pre-test/post-test designs, as well as formal designs like completely randomized designs, randomized block designs, Latin square designs, and factorial designs. These designs allow researchers to systematically test and compare the effects of independent variables or treatments on a dependent variable while controlling for other possible influences.








![Pretest posttest experimental and
control group design
Group Pretest Treatment Posttest
Experimental group O1 X O2
Control group O3 O4
Treatment Effect=[(O2-O1)-(O4-O3)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentaldesign-130401113710-phpapp02/85/Experimental-design-10-320.jpg)
![Solomon Four-Group Design
Group Pretest Treatment Posttest
Experimental O1 X O2
Control O3 O4
Experimental X O5
Control O6
Treatment Effect E=O2-O1
=O2-O4
=O5-O6
=O5-O3
=[(O2-O1)-(O4-O3)]
* all Es are similar if cause and effect is highly valid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/experimentaldesign-130401113710-phpapp02/85/Experimental-design-11-320.jpg)