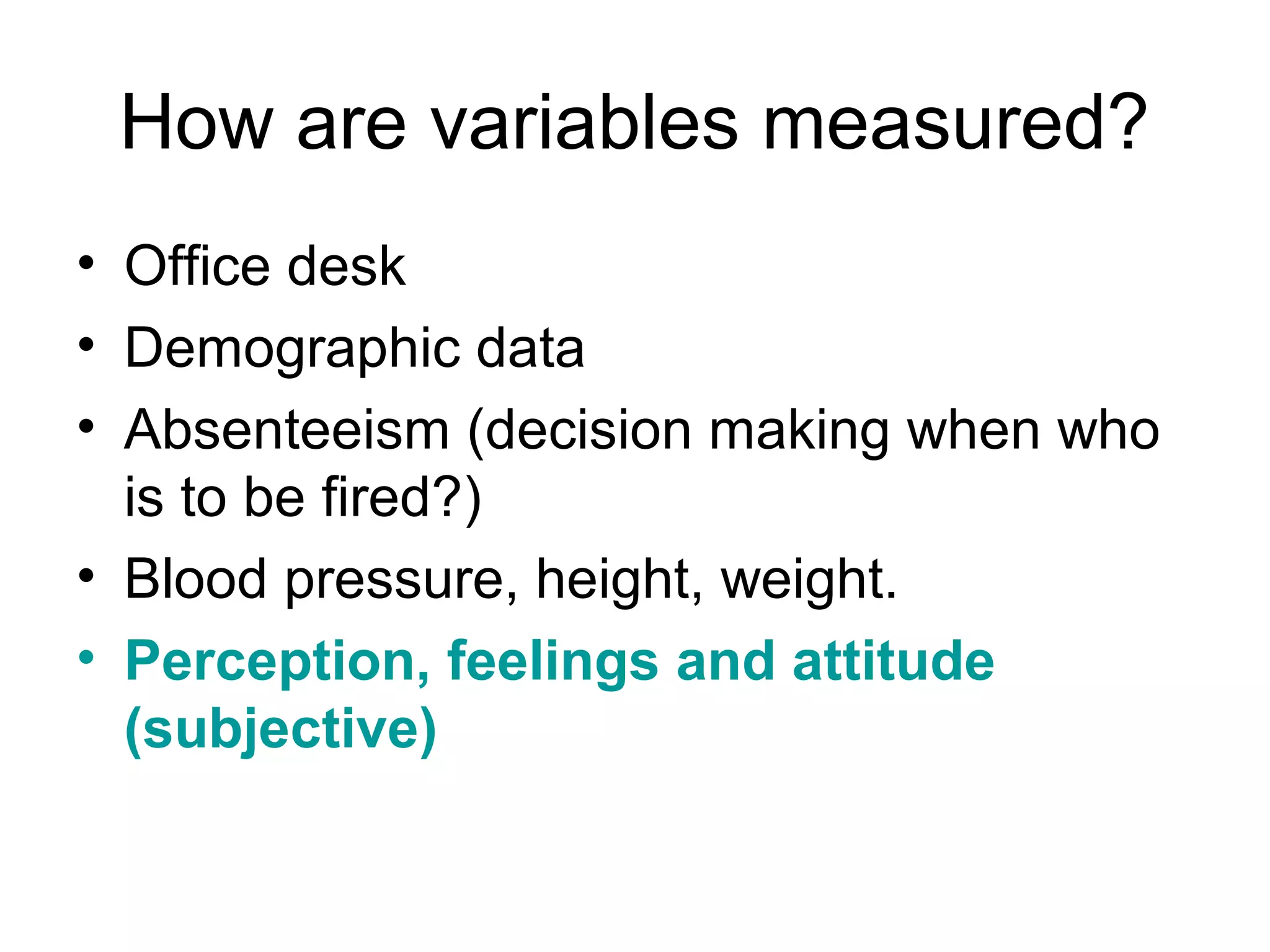
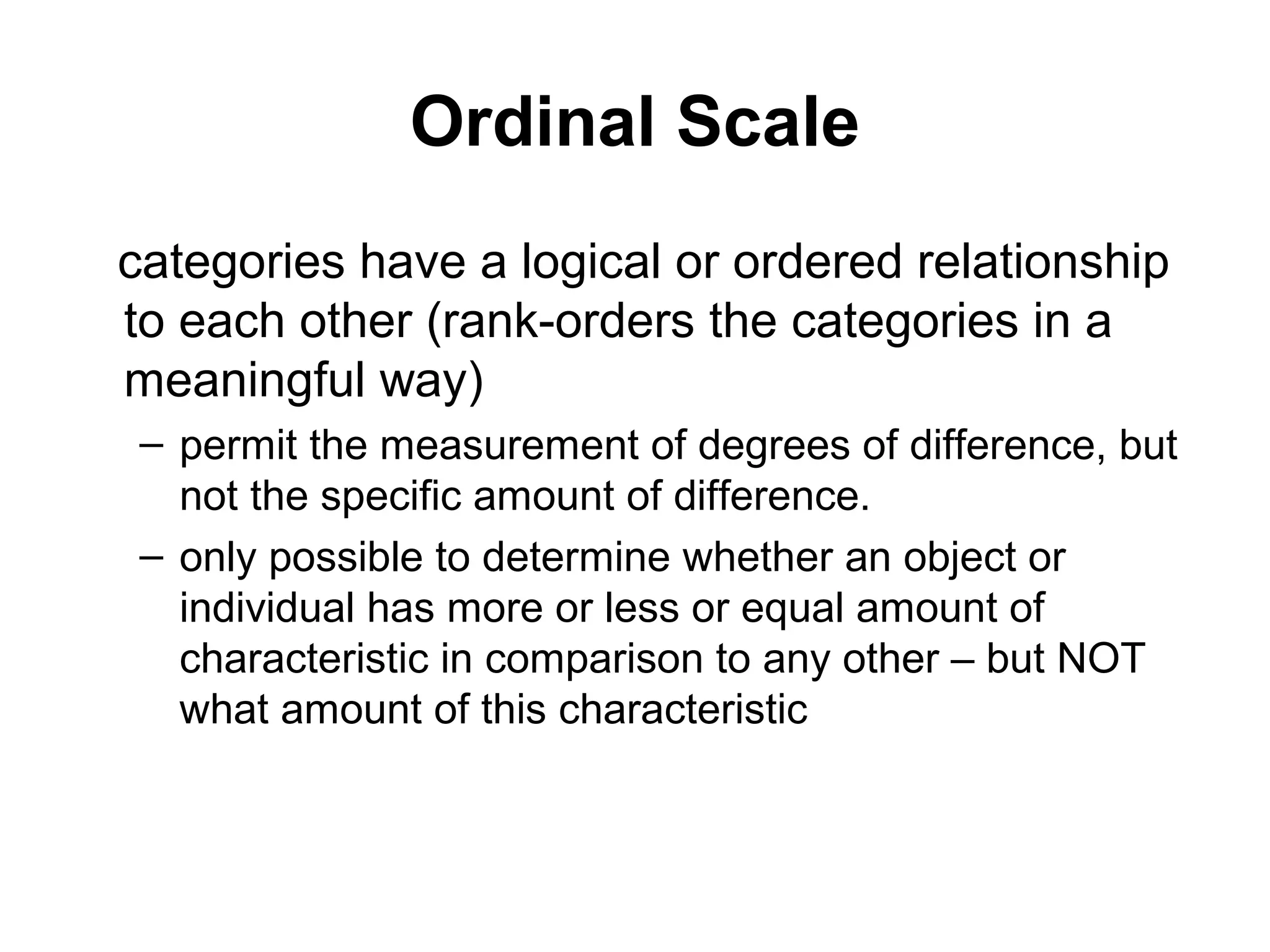
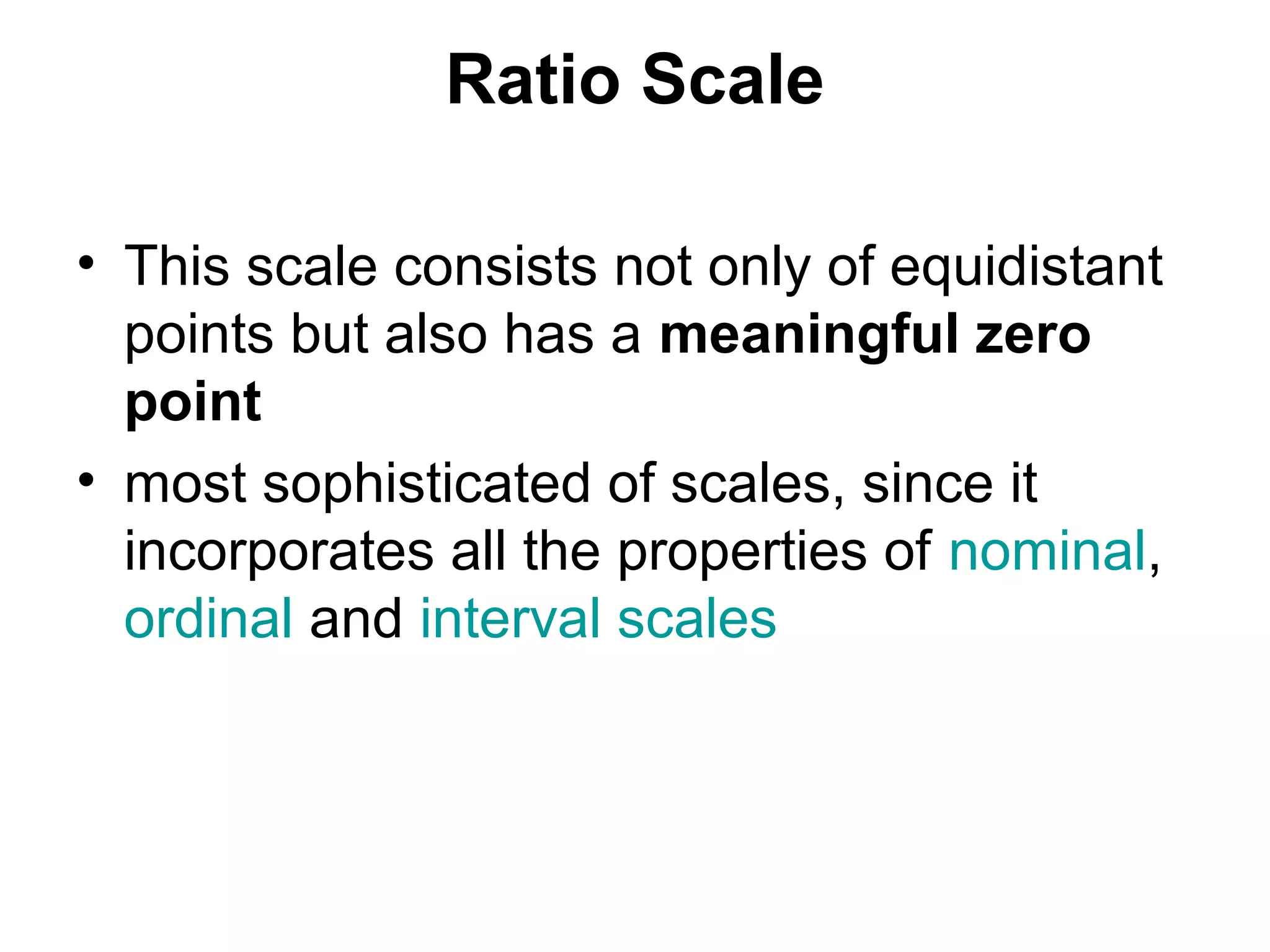
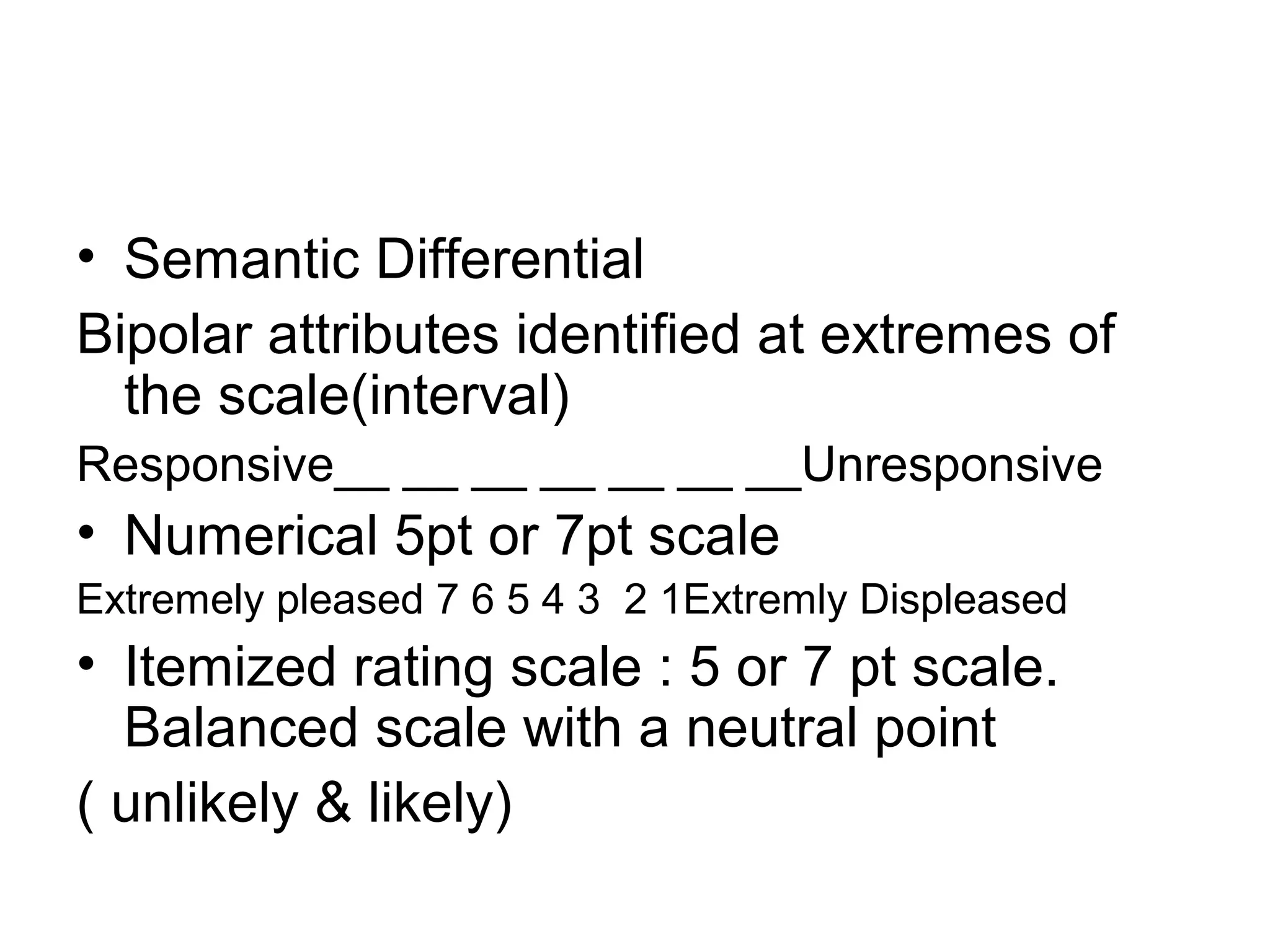
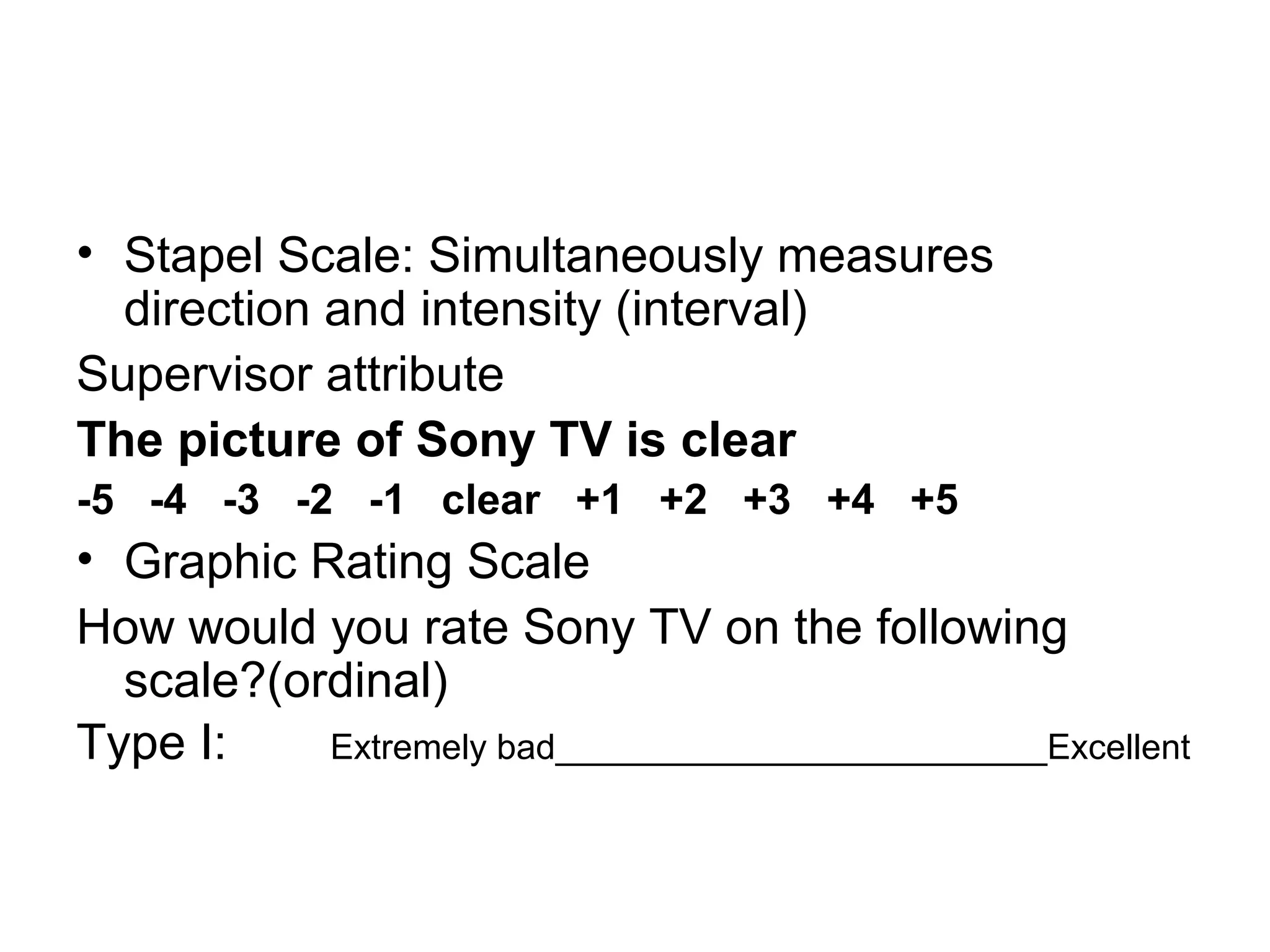
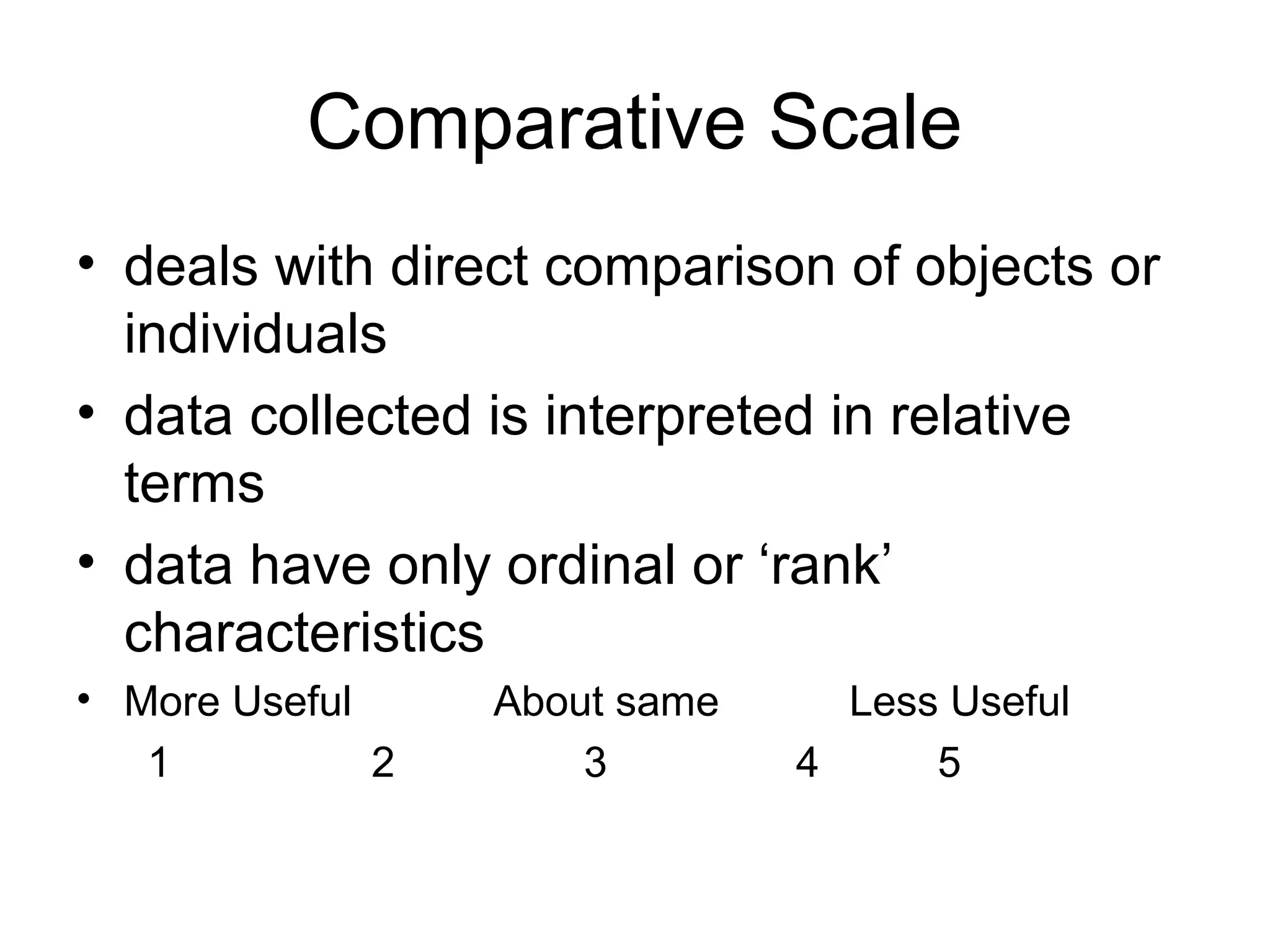
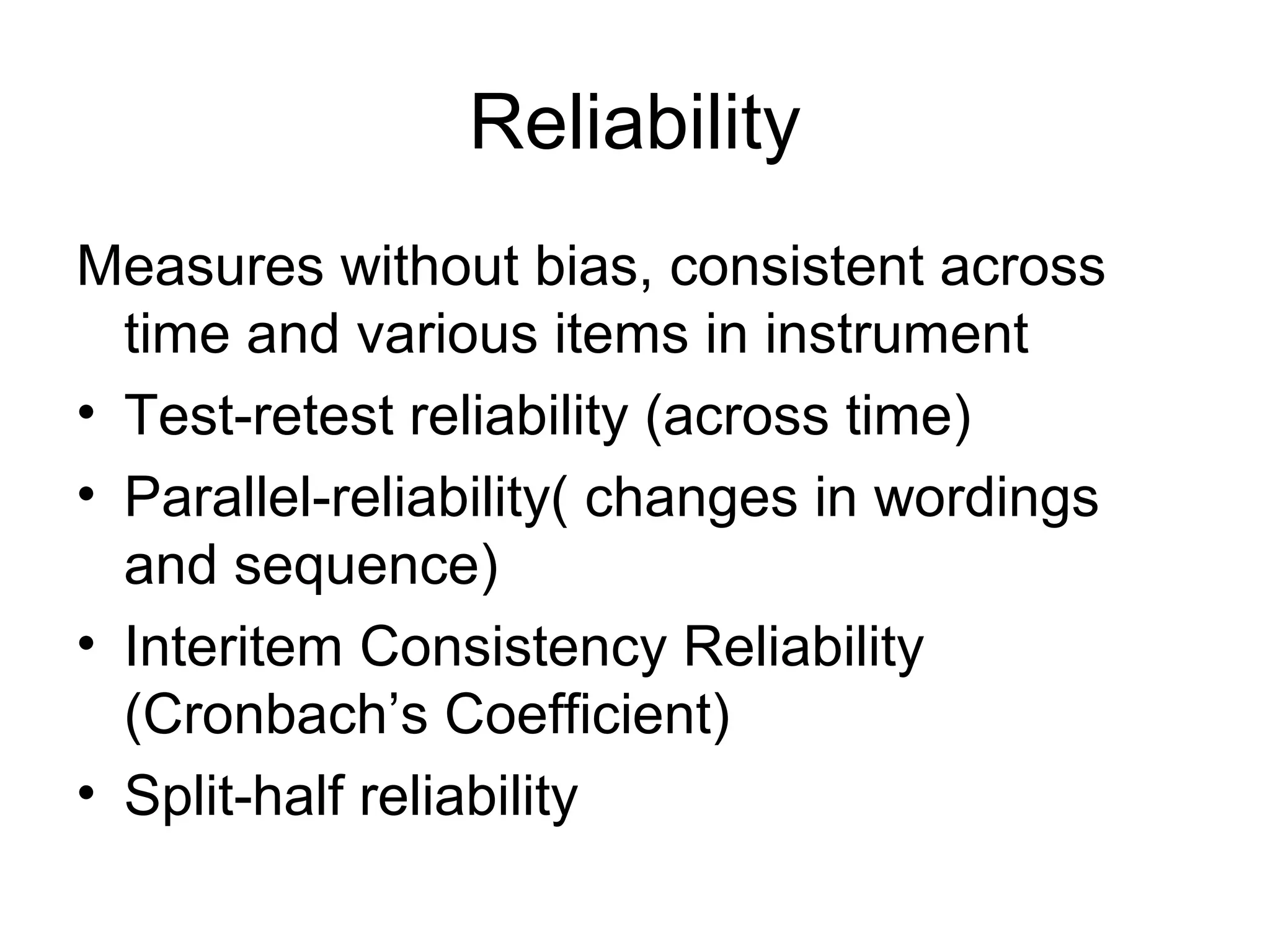
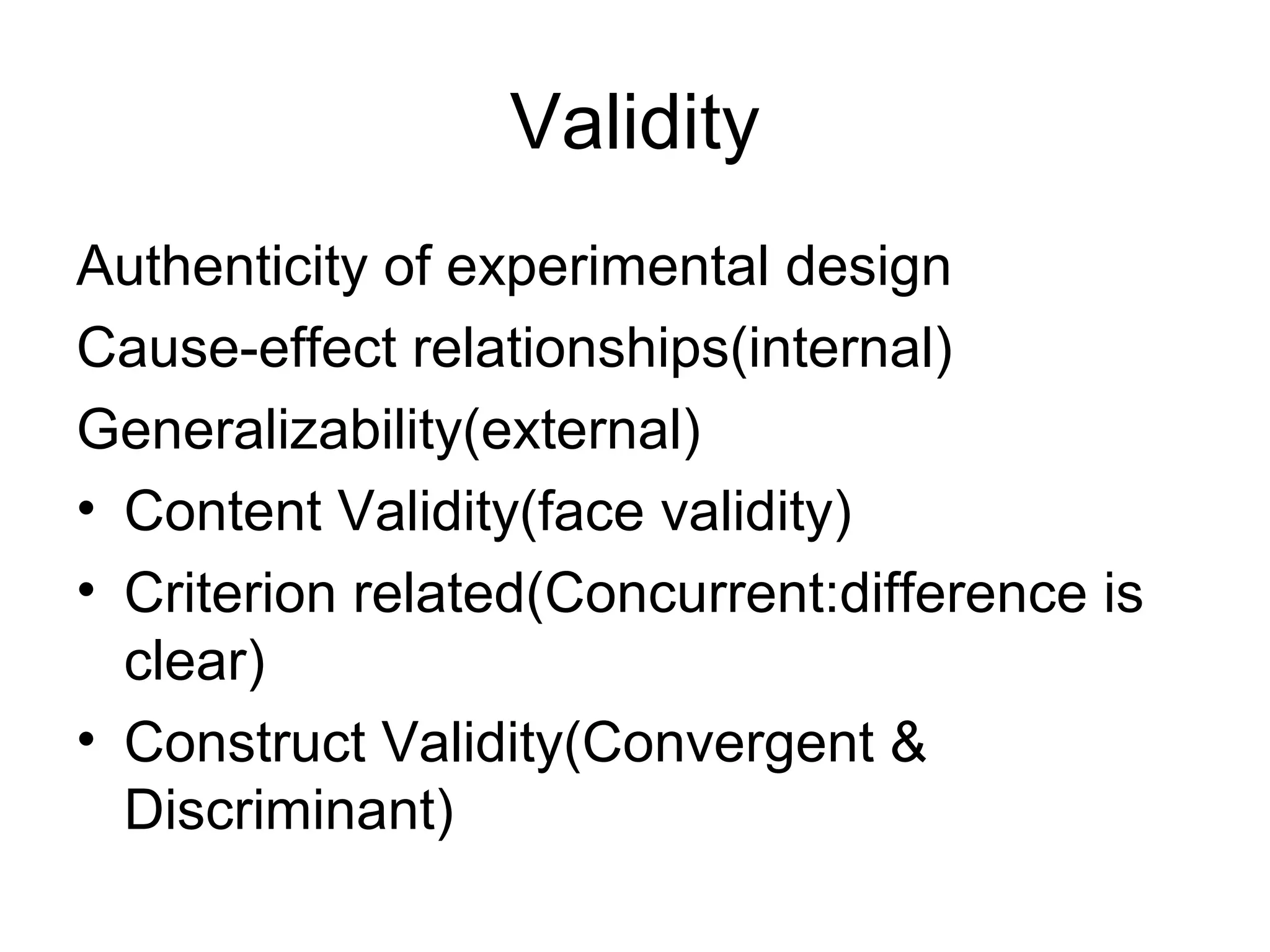
This document discusses different ways to measure variables and concepts. It describes nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales of measurement. It also discusses operational definitions and provides examples of how to operationalize abstract concepts. Finally, it outlines various rating scales that can be used to measure perceptions, attitudes, and preferences including Likert scales, semantic differentials, ranking scales, and paired comparisons.