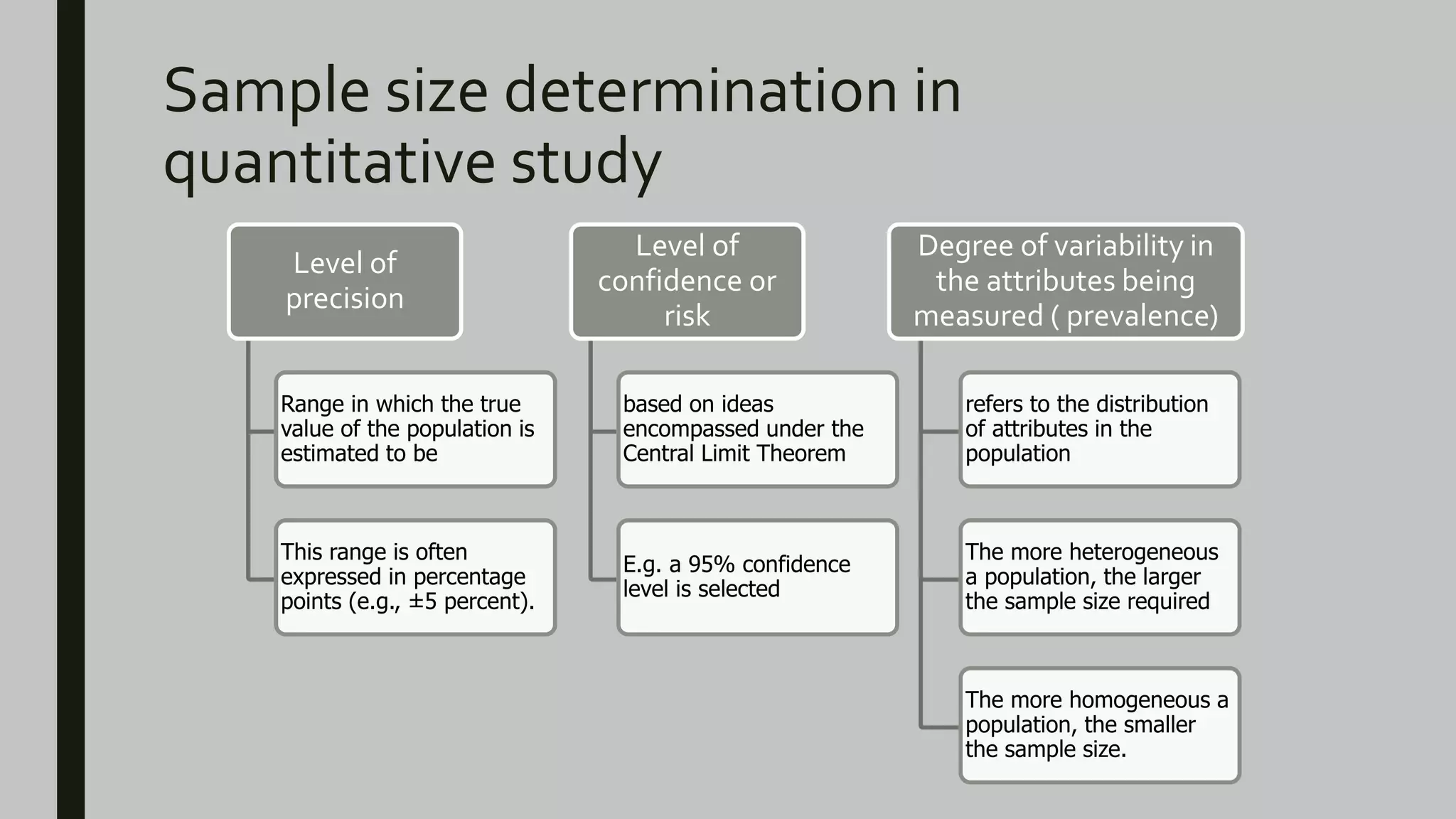
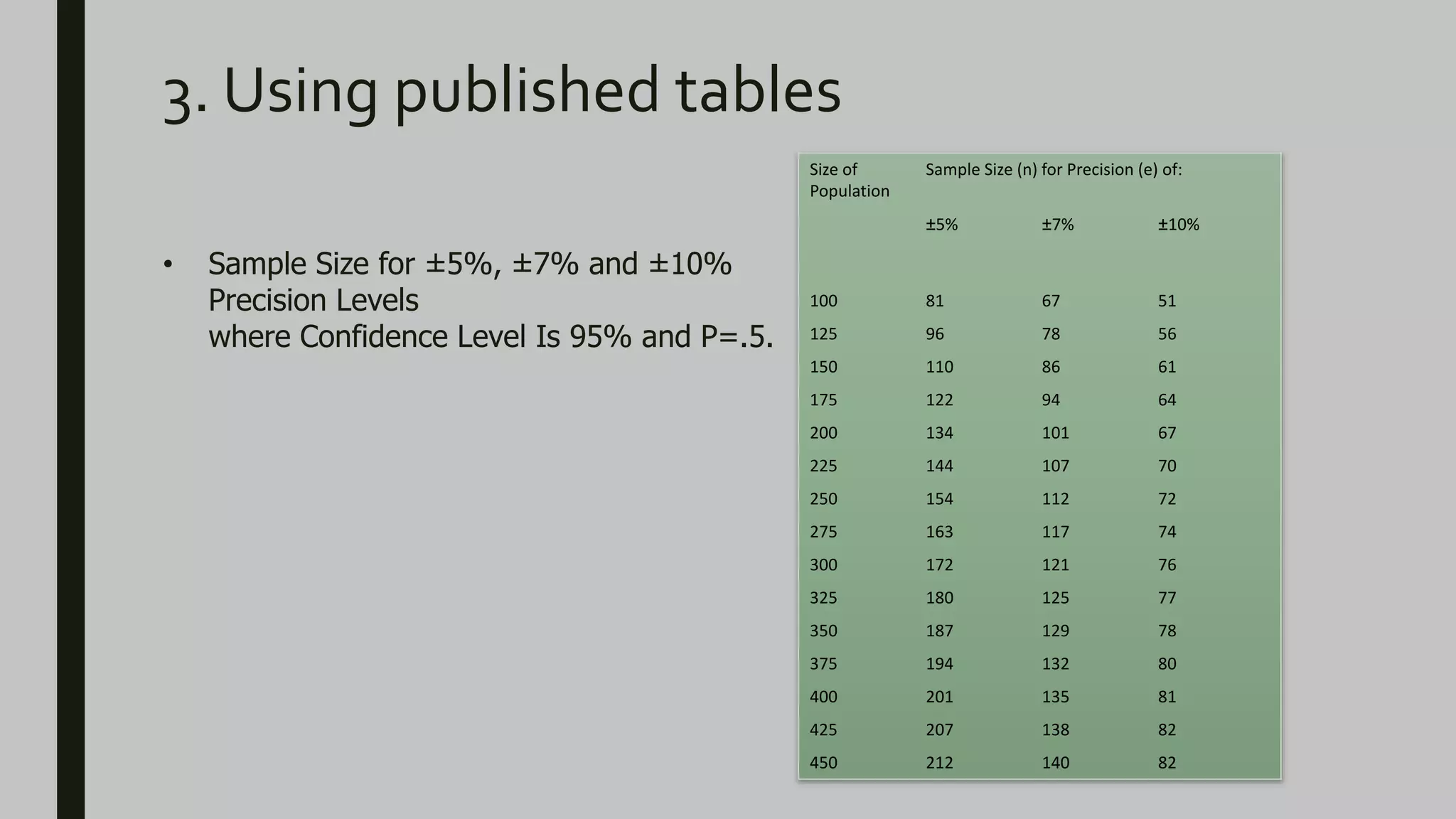
This document discusses sample size determination and sampling techniques. It covers the differences between qualitative and quantitative studies. For qualitative studies, the sample size is usually small until the point of theoretical saturation is reached. The sample should represent key characteristics of the population. For quantitative studies, sample size is determined based on the desired level of precision, confidence level, population size, and variability in attributes. Several strategies for determining sample size are presented, including using published tables, formulas like the Cochran equation, and imitating similar study sample sizes. Stratified sampling techniques like proportional and optimum allocation of samples across strata are also summarized.