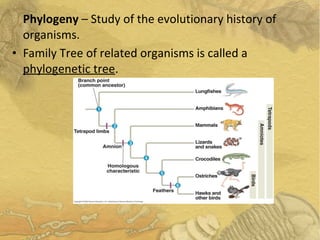
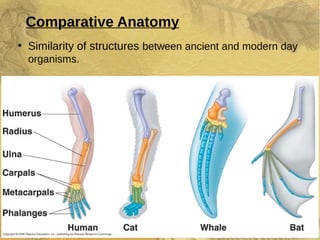
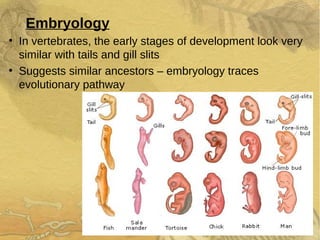
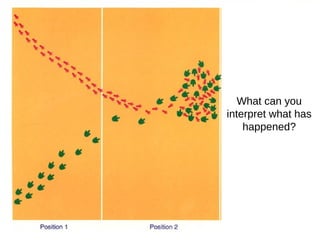
Evolution occurs over many generations as organisms adapt to changing environments through natural selection. The fossil record provides evidence of how ancient organisms differed from modern ones and how life has changed over time. Fossils, comparative anatomy, embryology, and DNA evidence all support the theory of evolution by indicating shared ancestry among groups of organisms.