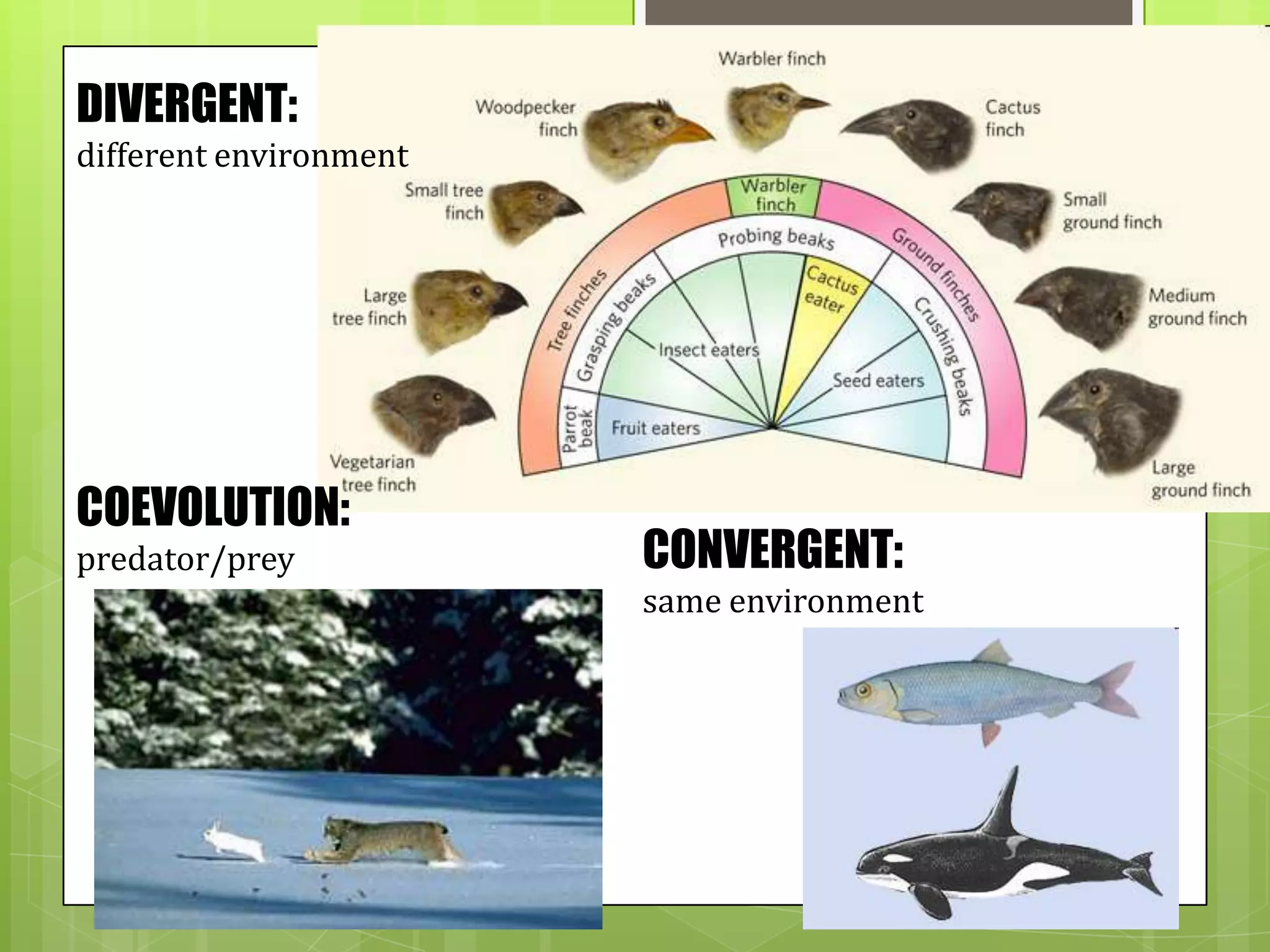
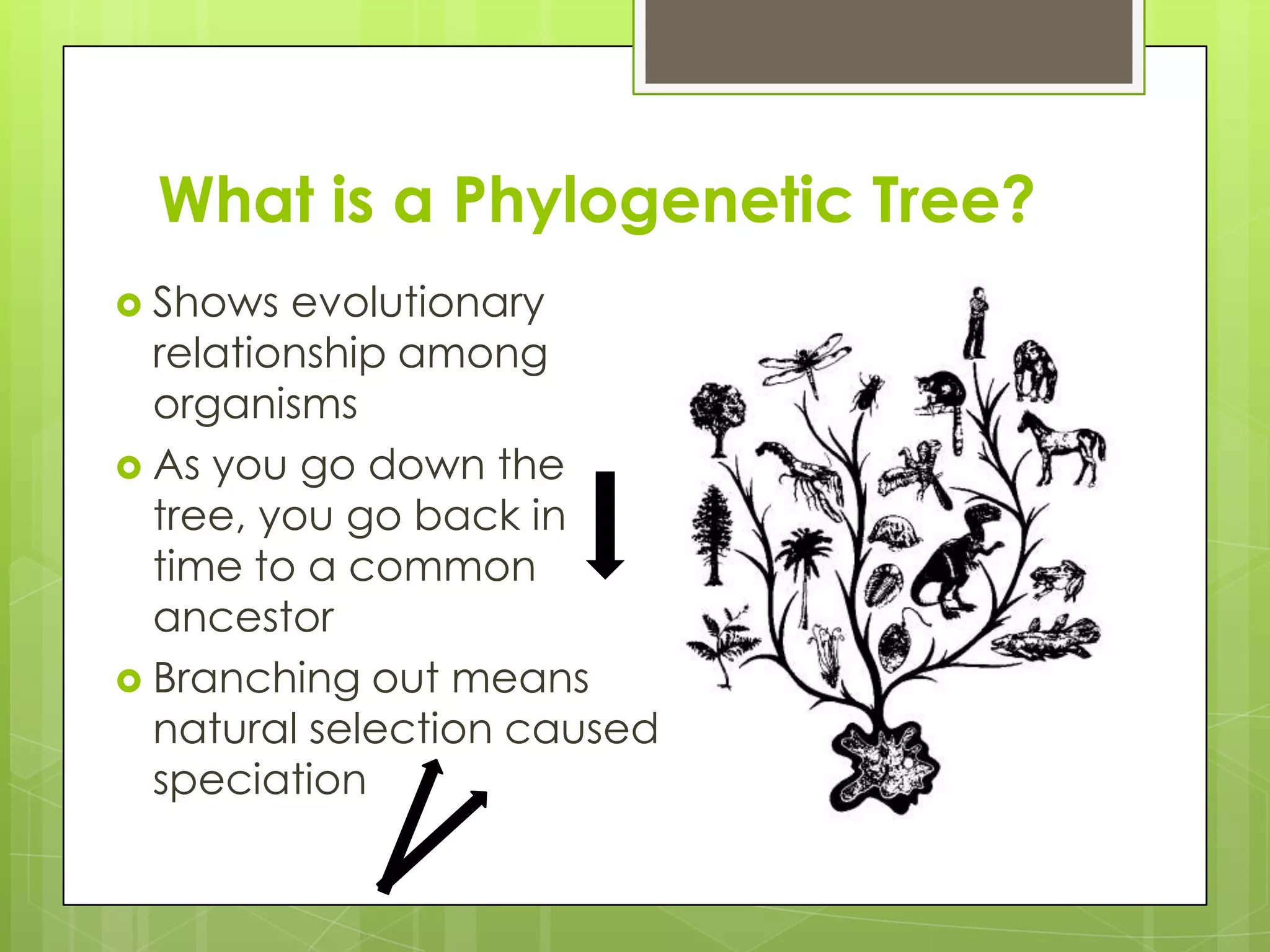
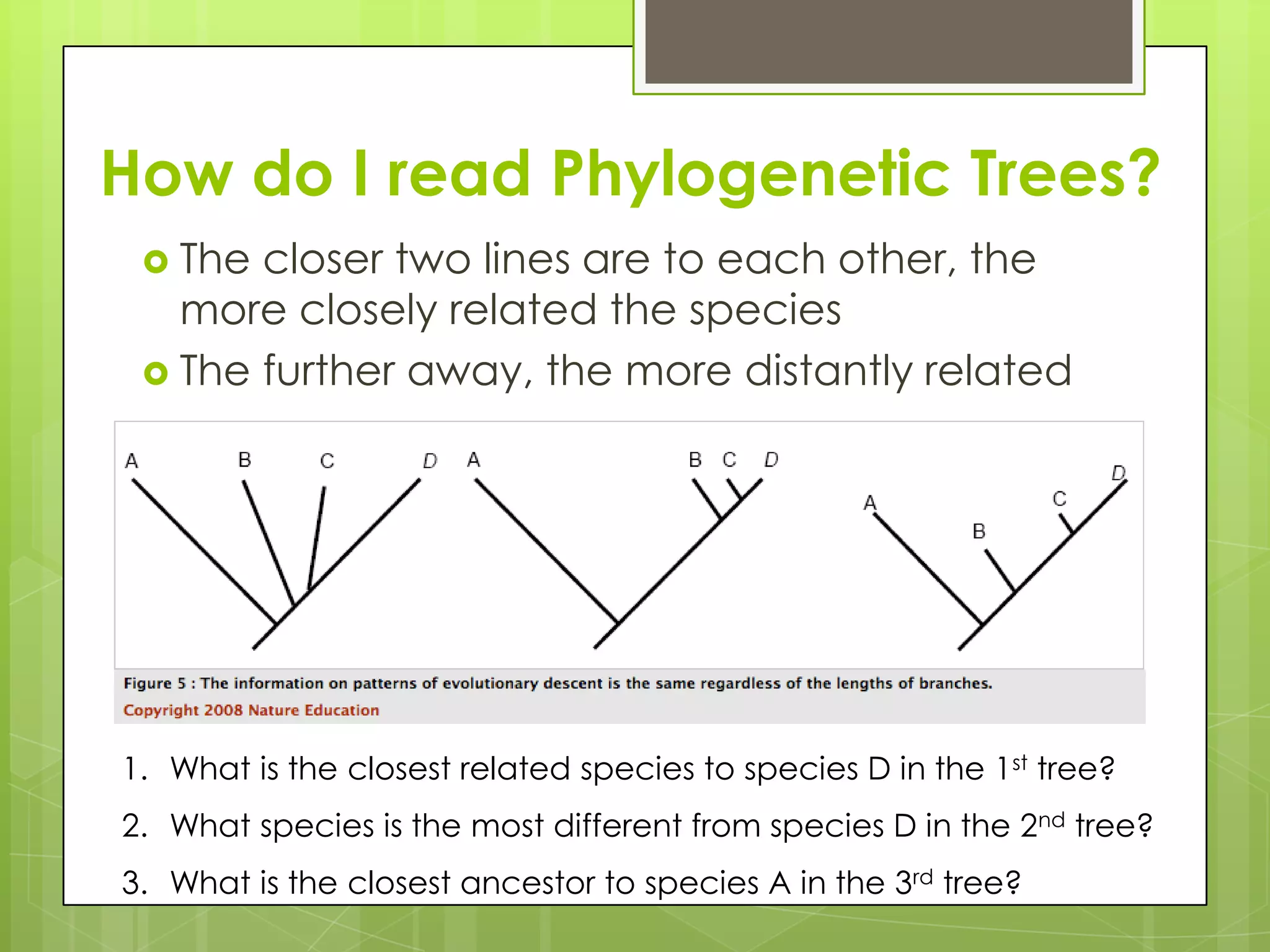
There are three main types of evolution:
1. Coevolution occurs when two species evolve together due to their close relationship, such as flowers and pollinating insects.
2. Divergent evolution happens when species with a common ancestor become more different and evolve into separate species, often in different environments like the finches of the Galapagos Islands.
3. Convergent evolution is when species with different ancestors evolve similar traits for the same environment, like dolphins and fish developing flippers for swimming.