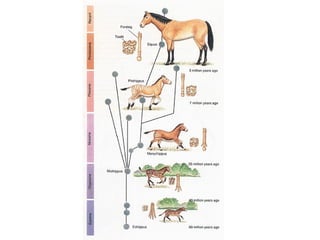
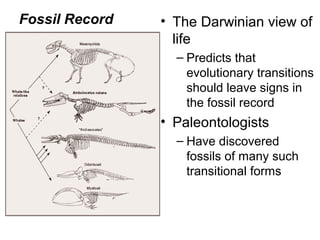
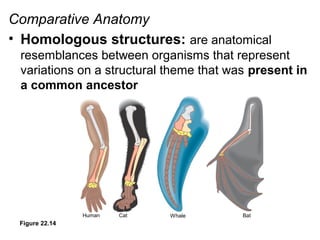
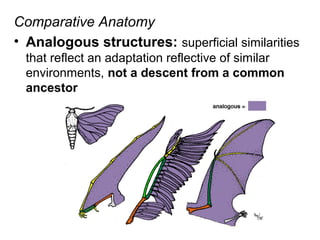
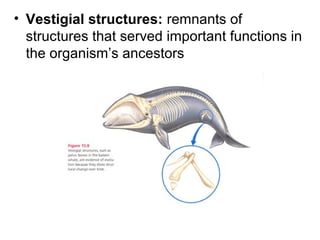
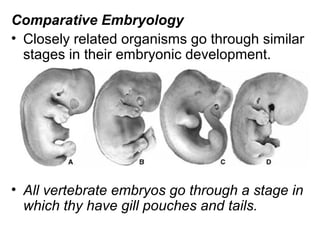
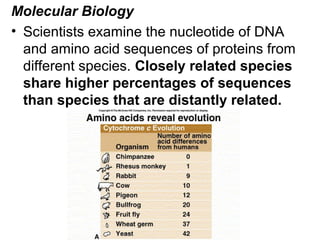
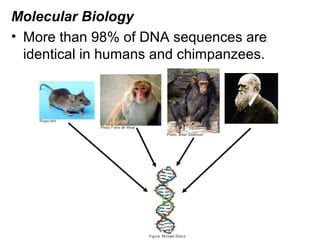
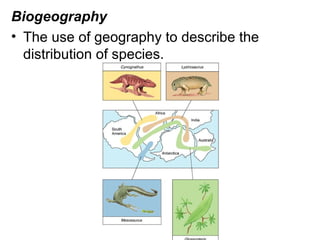
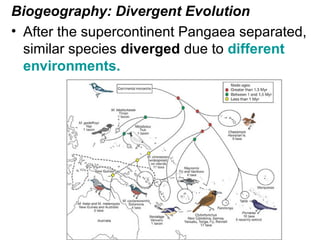
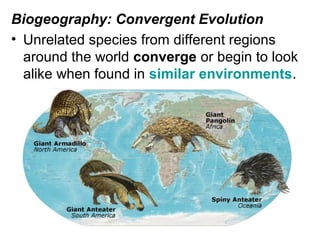
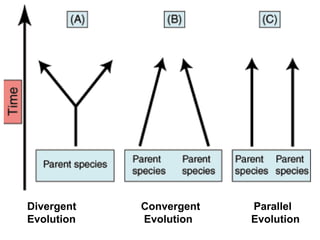
This document provides evidence for evolution from 5 areas of scientific study: the fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, molecular biology, and biogeography. Each area is summarized briefly: the fossil record shows transitional forms; comparative anatomy examines homologous, analogous, and vestigial structures; comparative embryology shows similarities in development of related species; molecular biology compares DNA/protein sequences; and biogeography looks at species distribution and examples of divergent and convergent evolution.