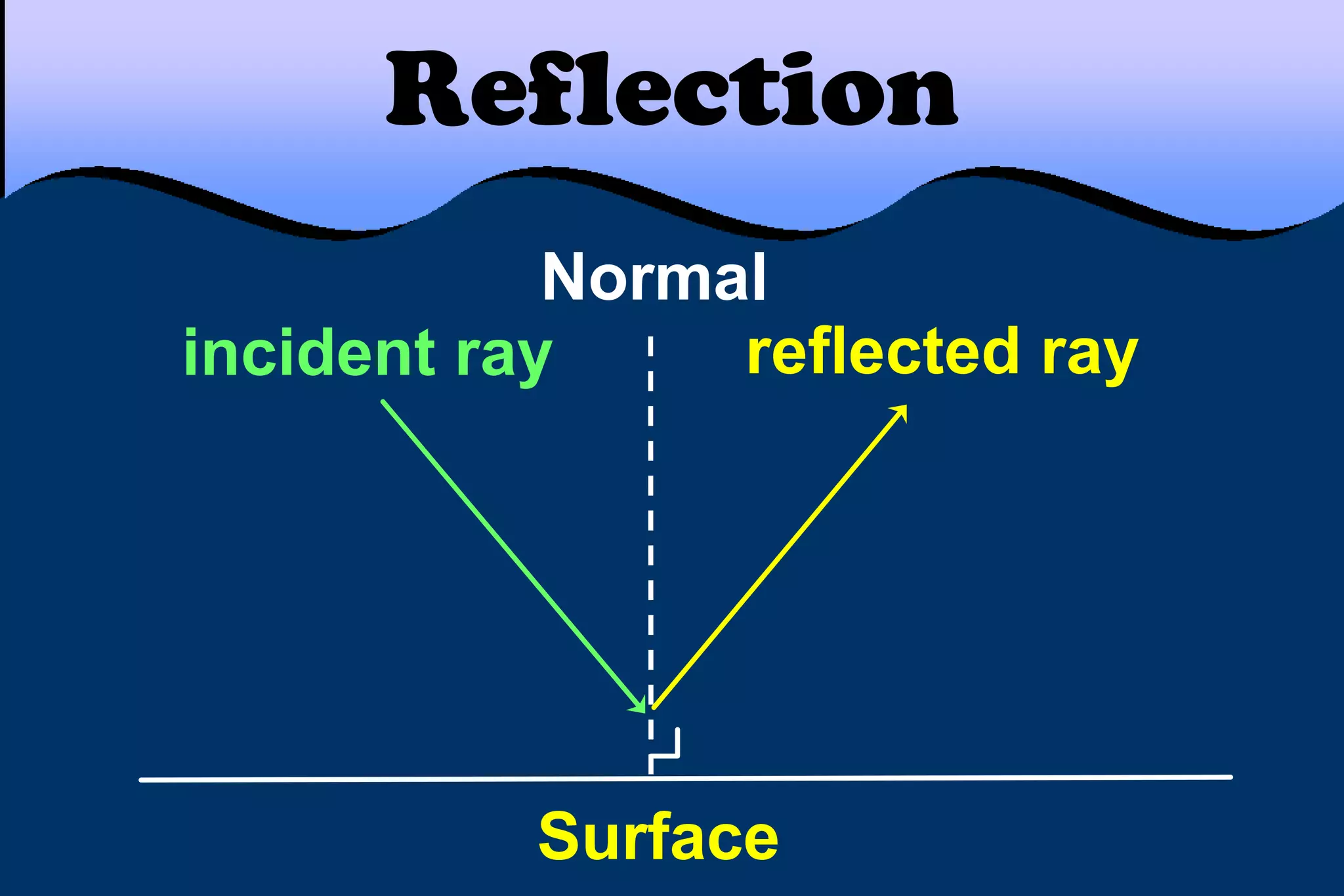
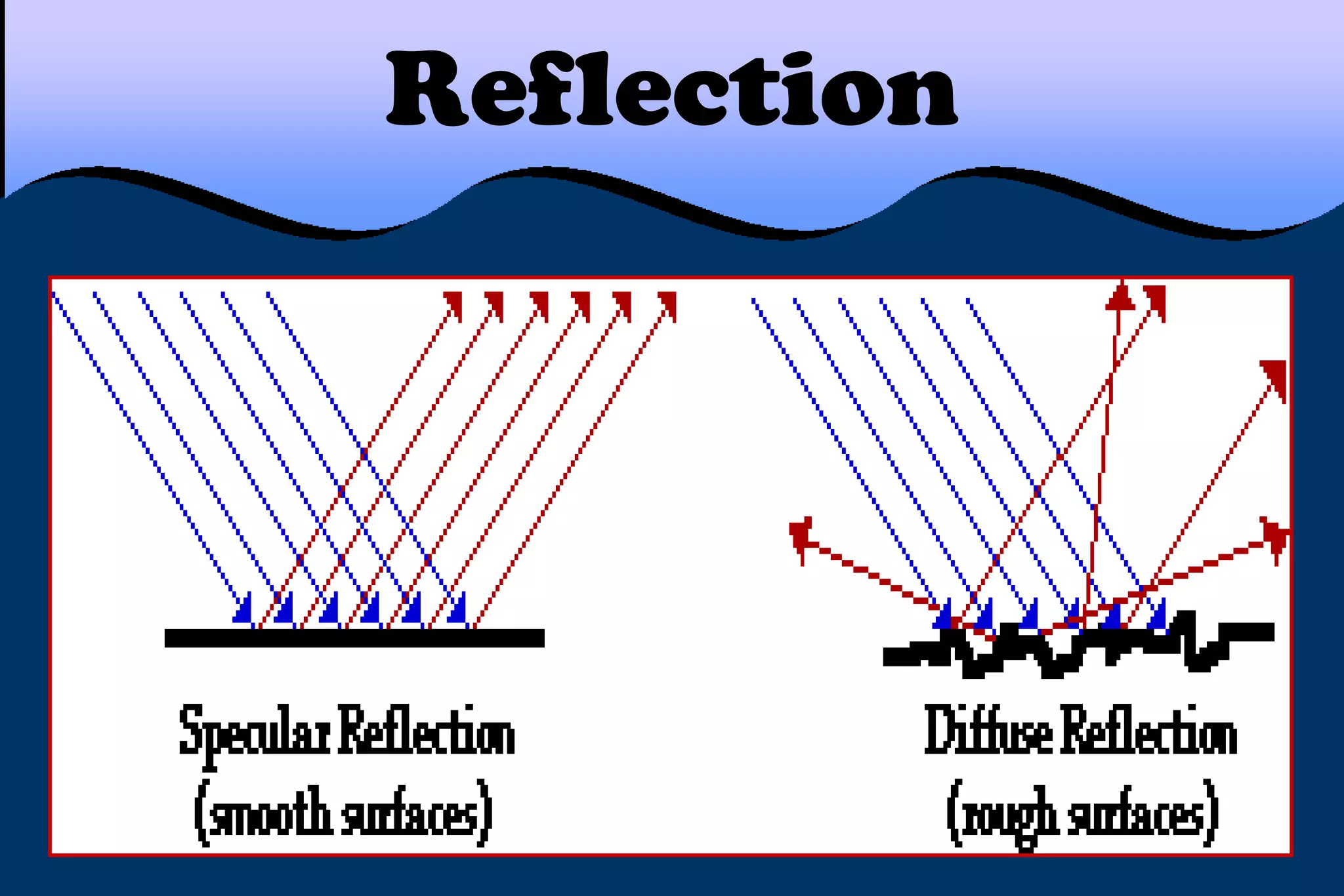
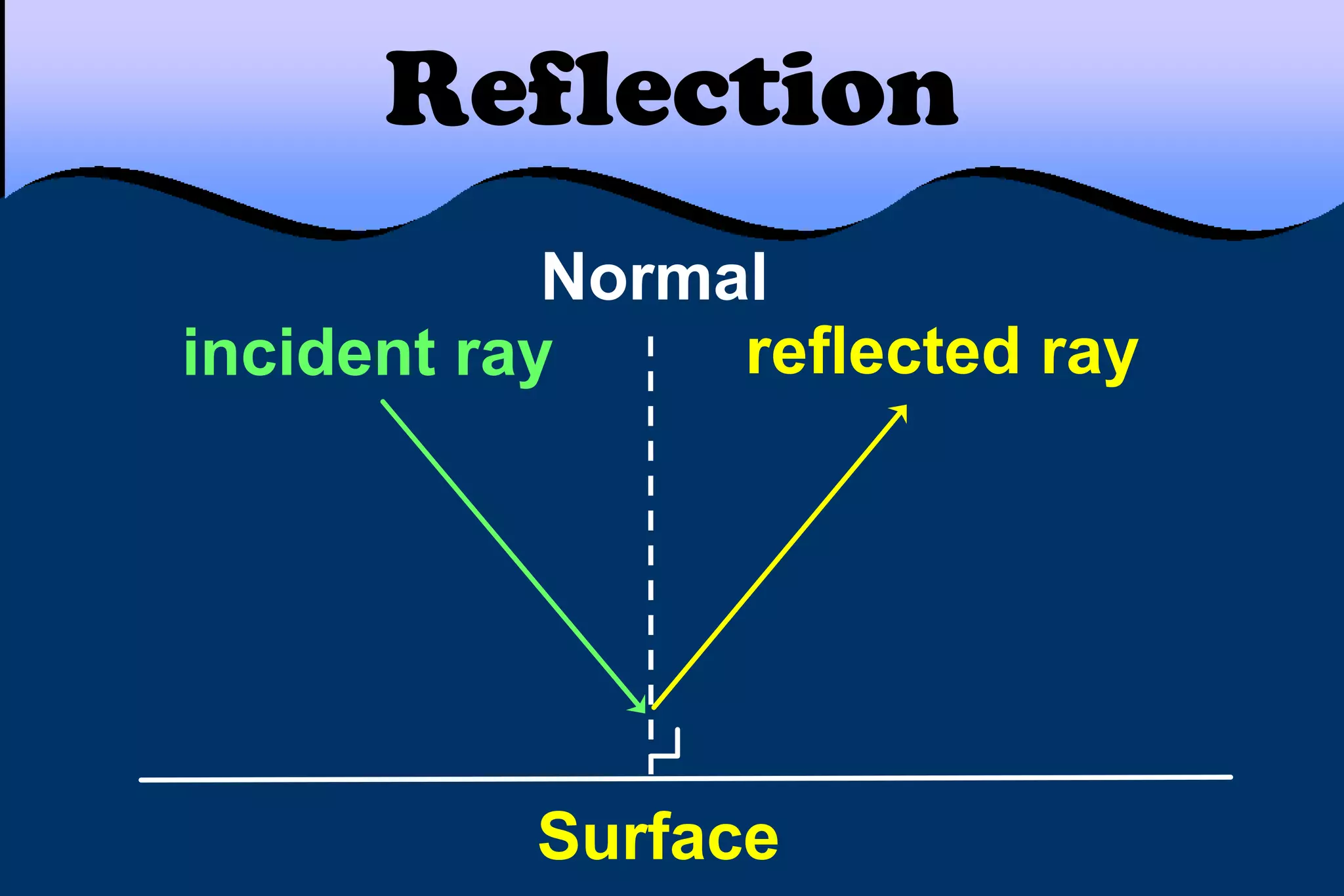
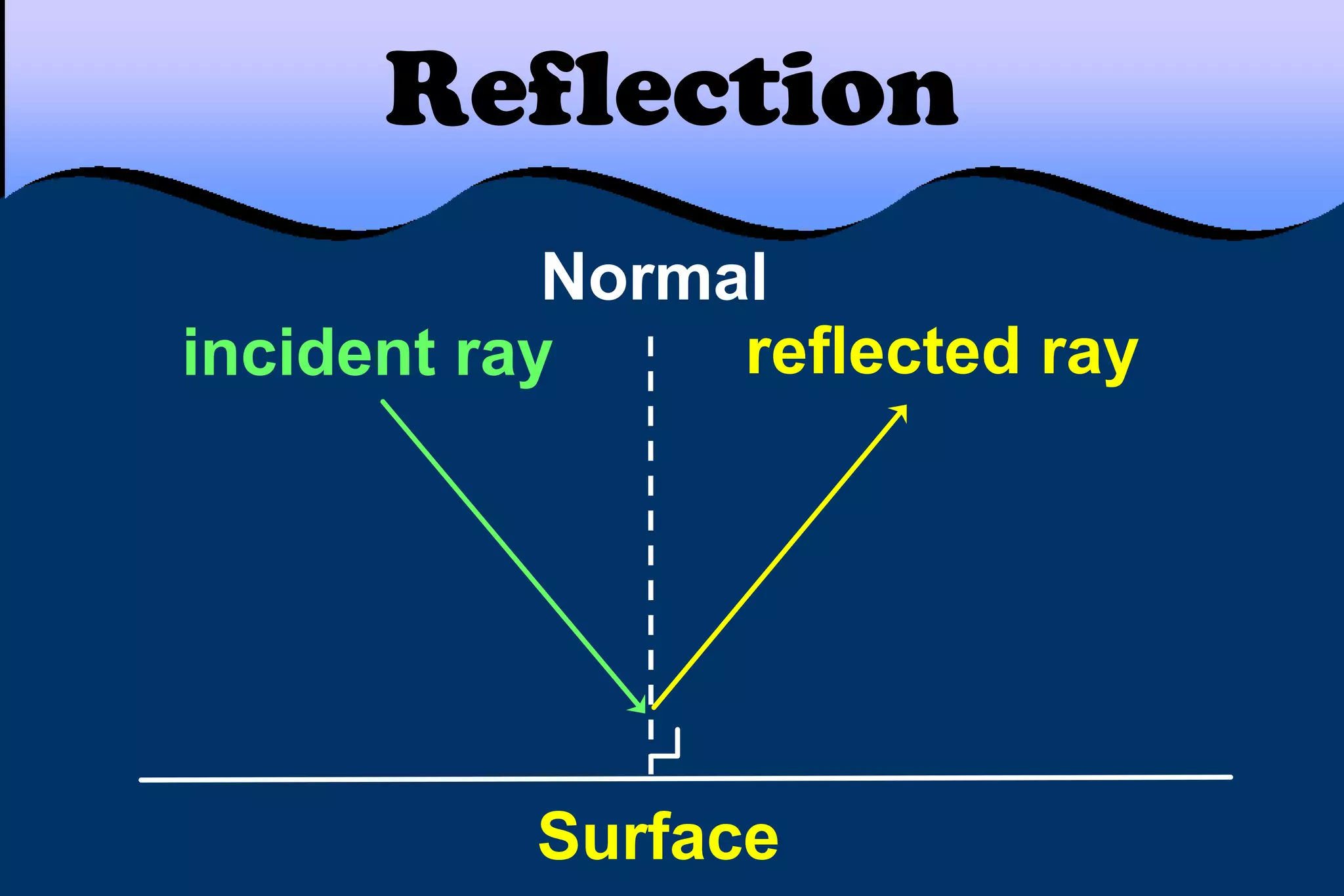
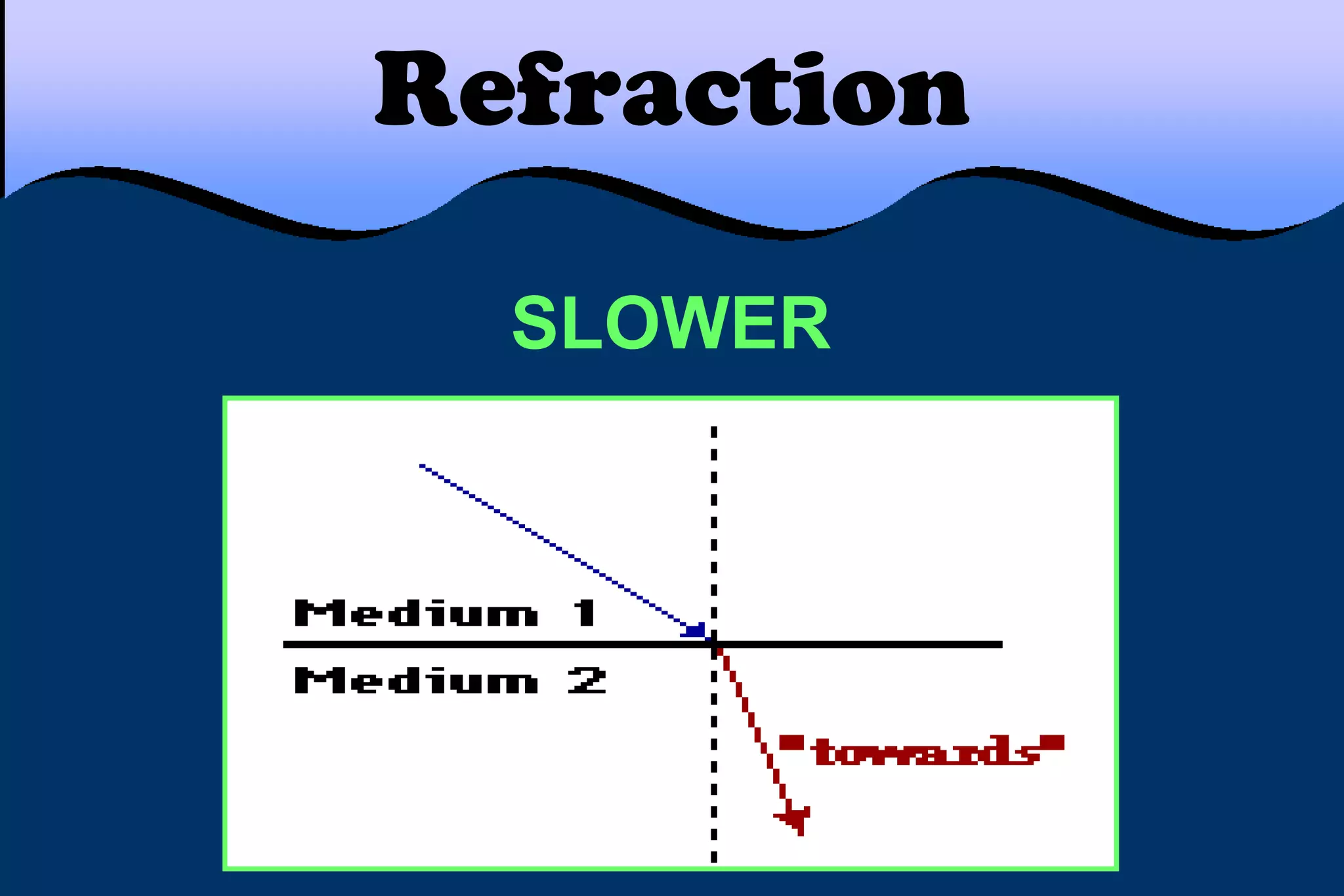
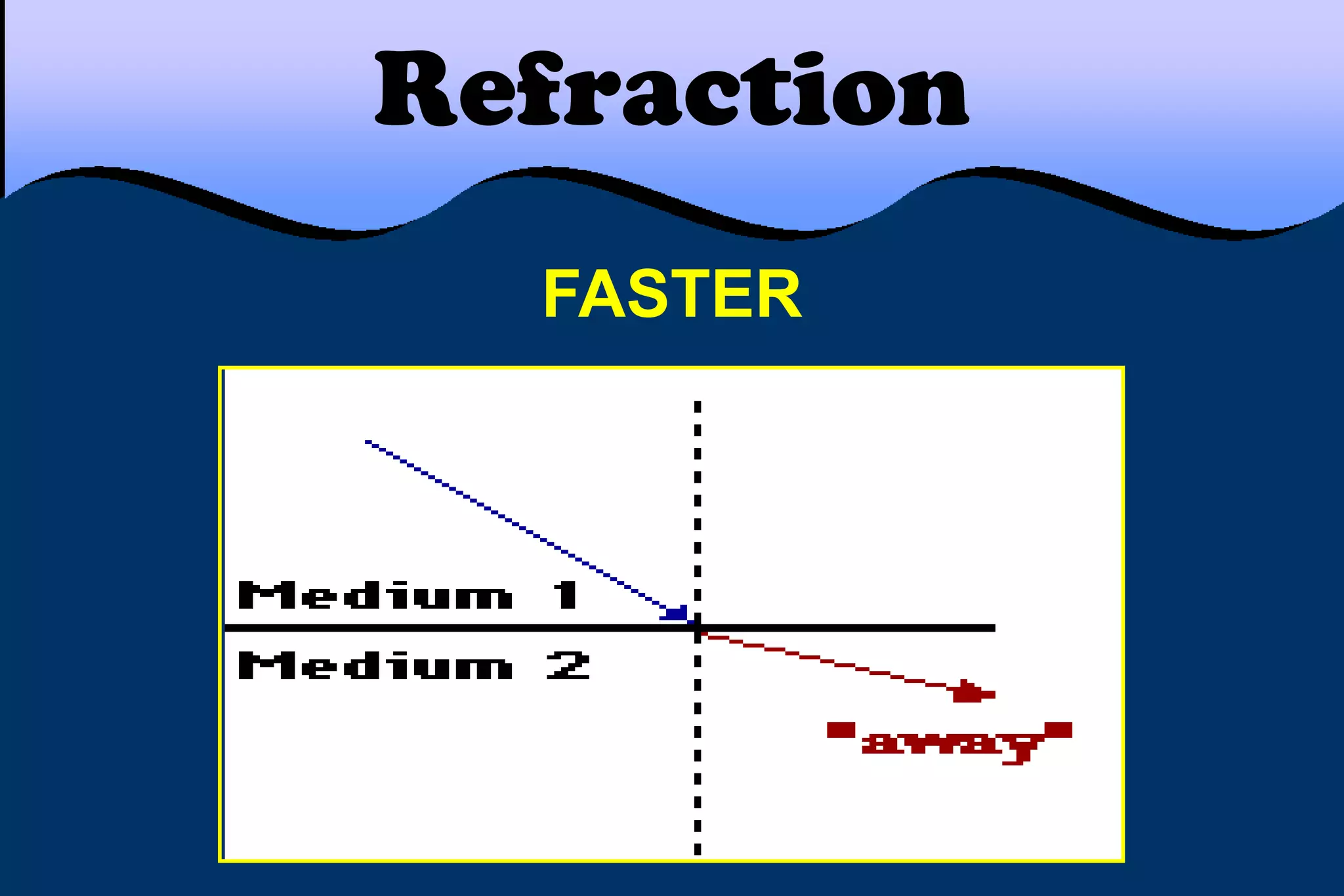
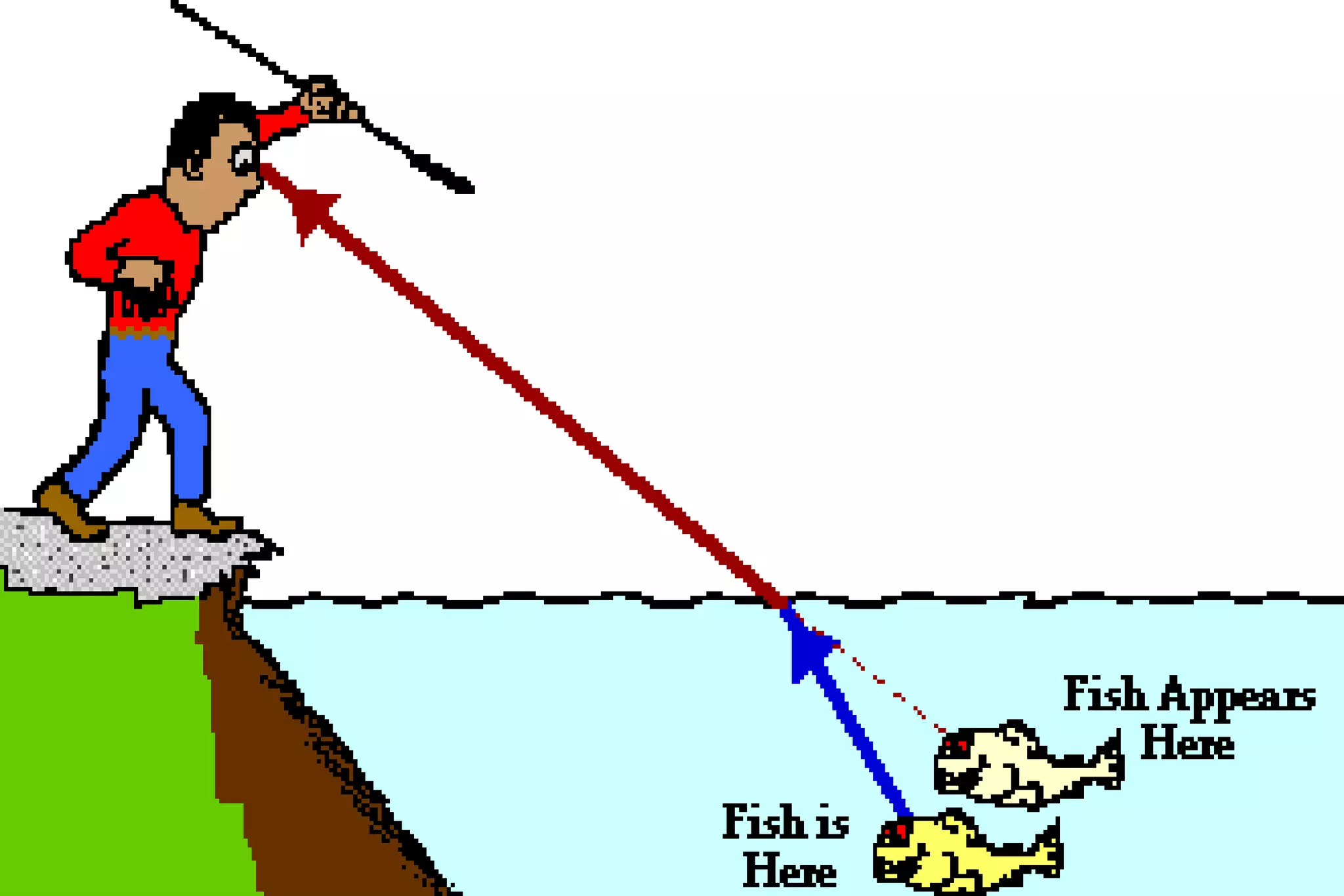
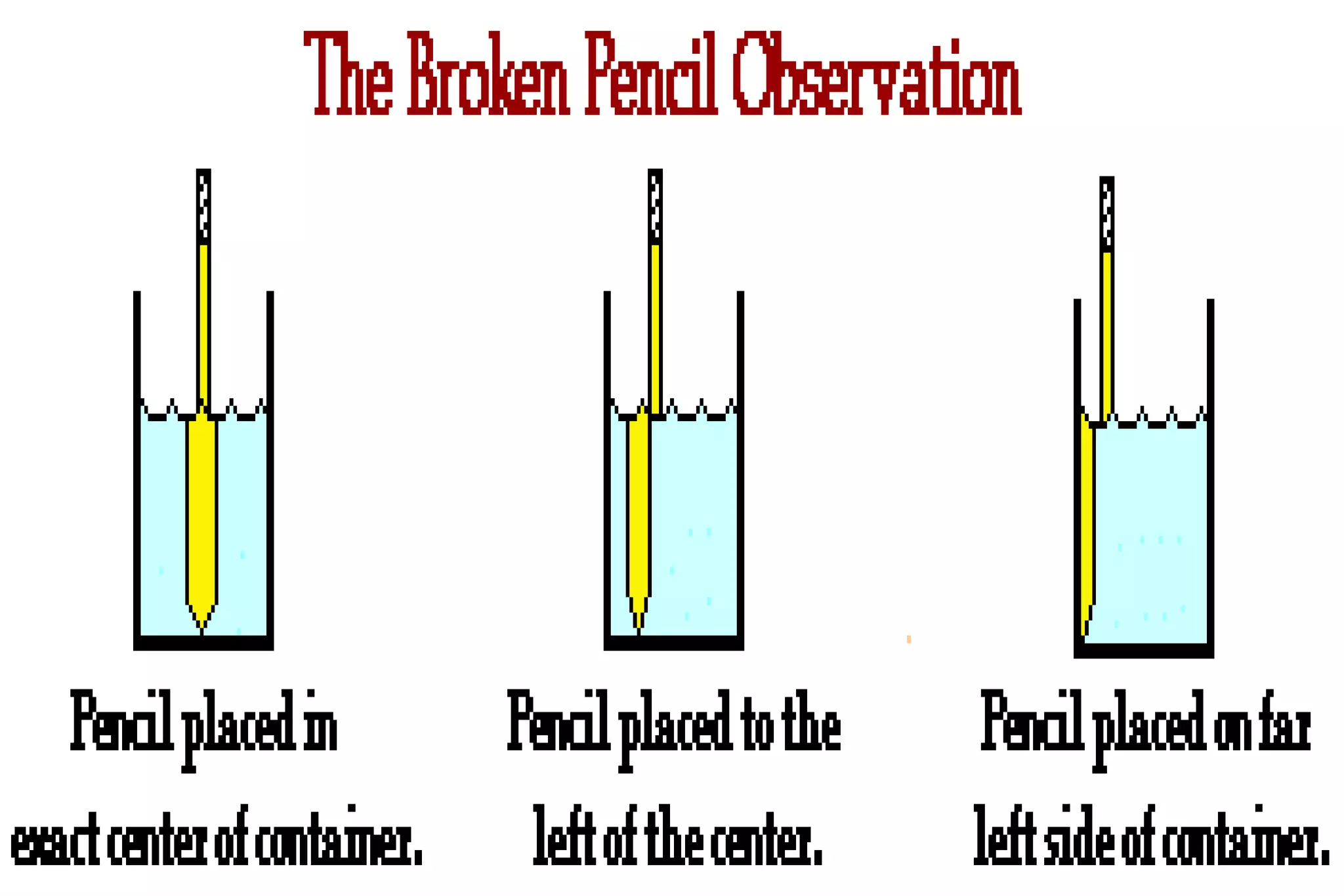
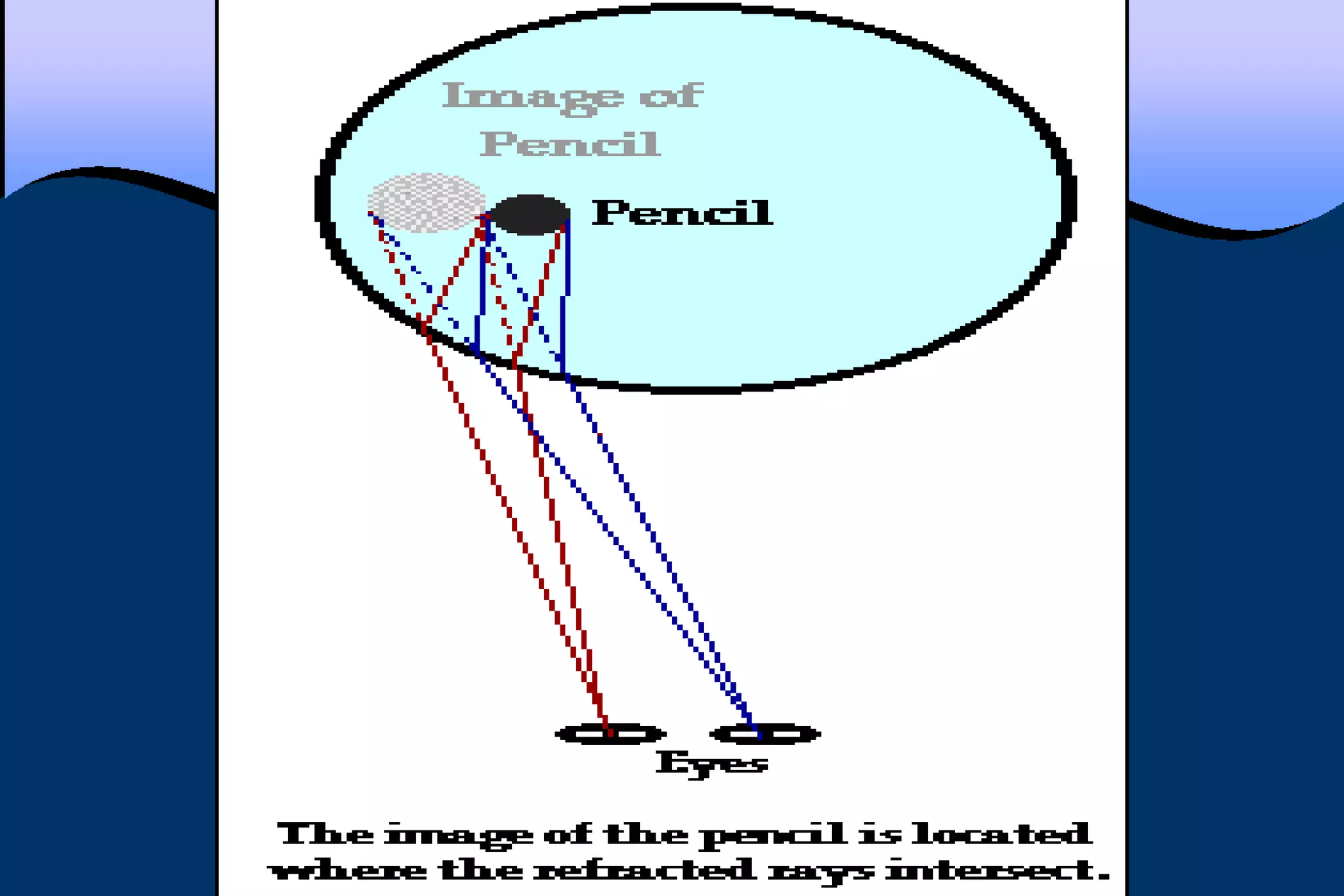
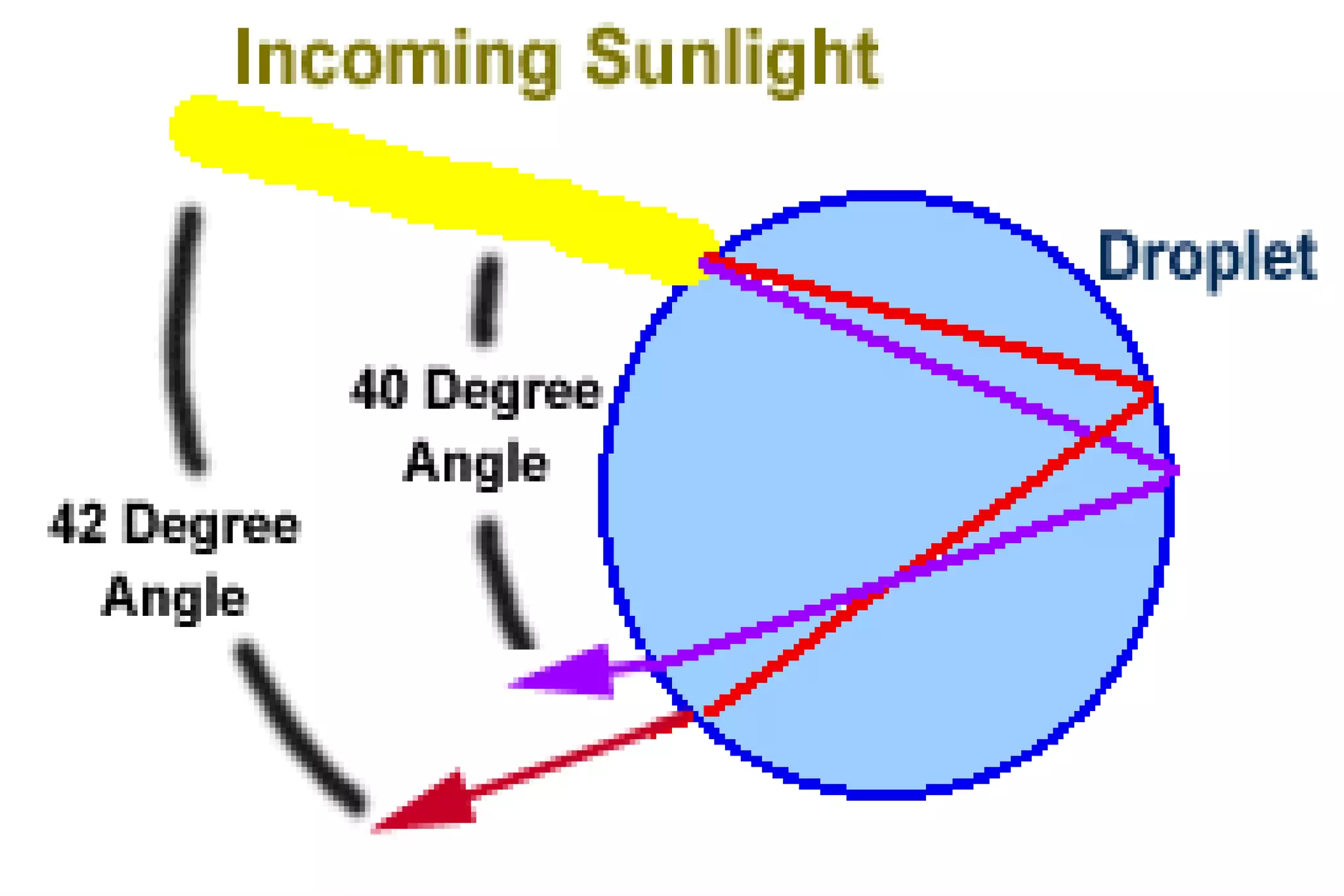
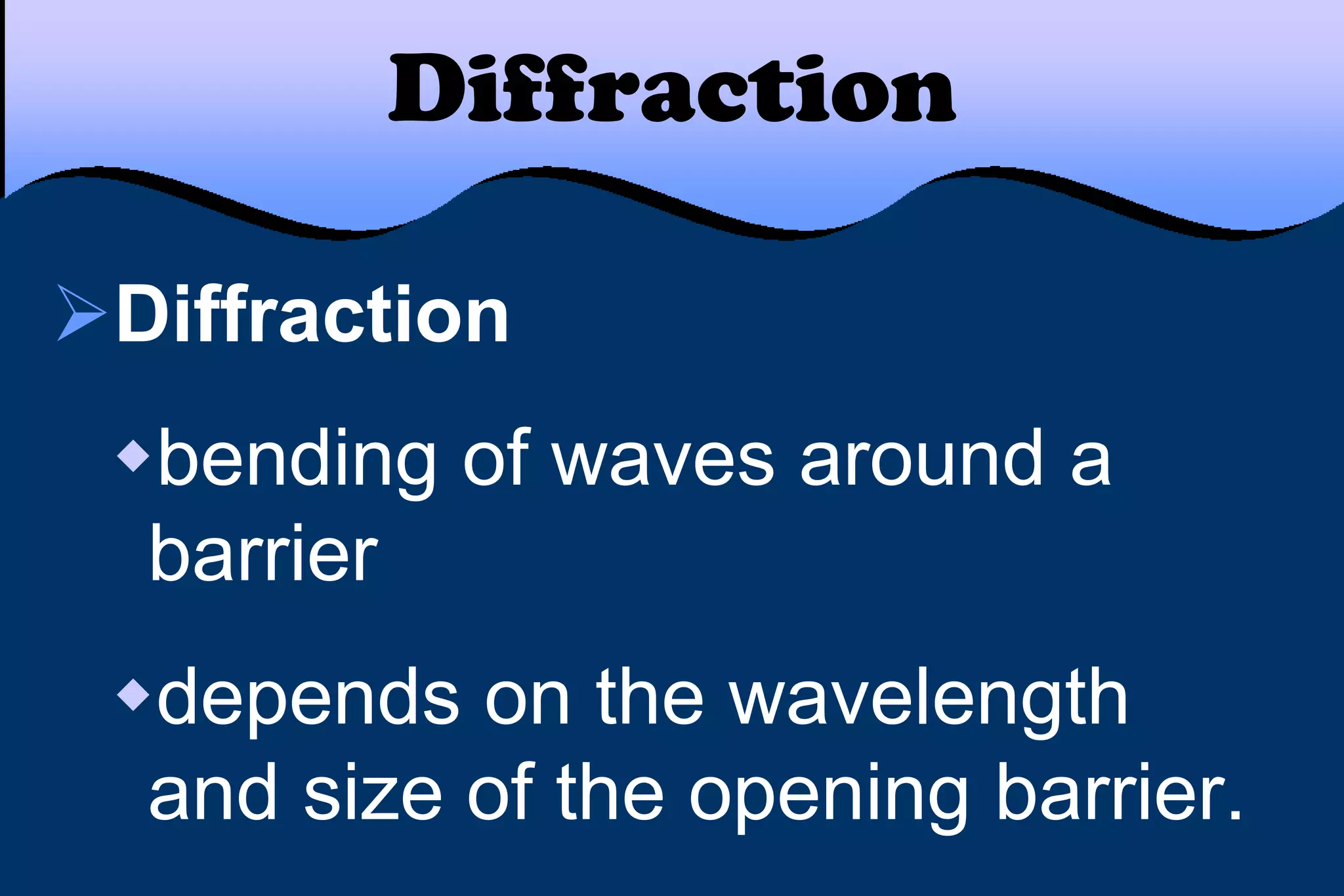
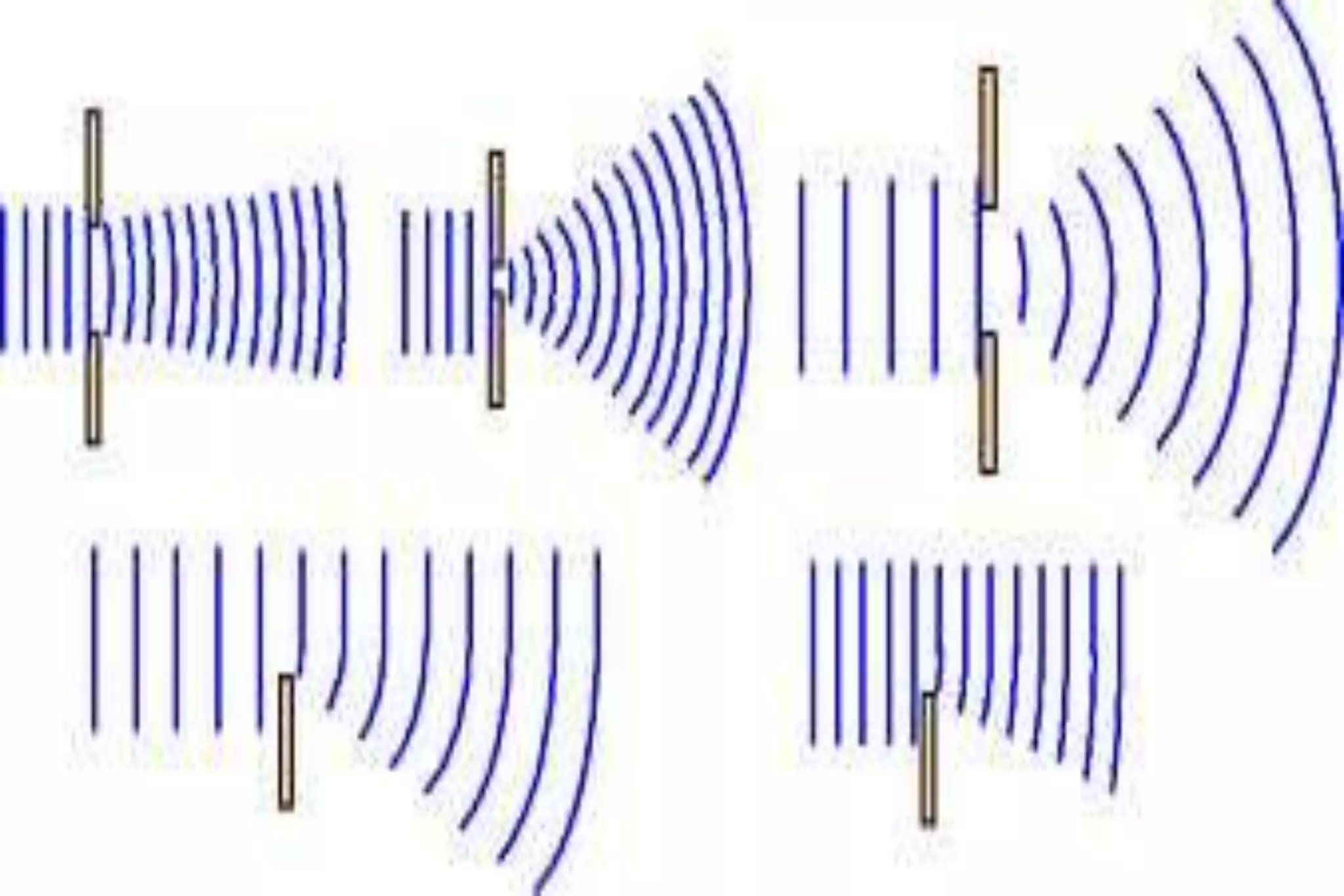
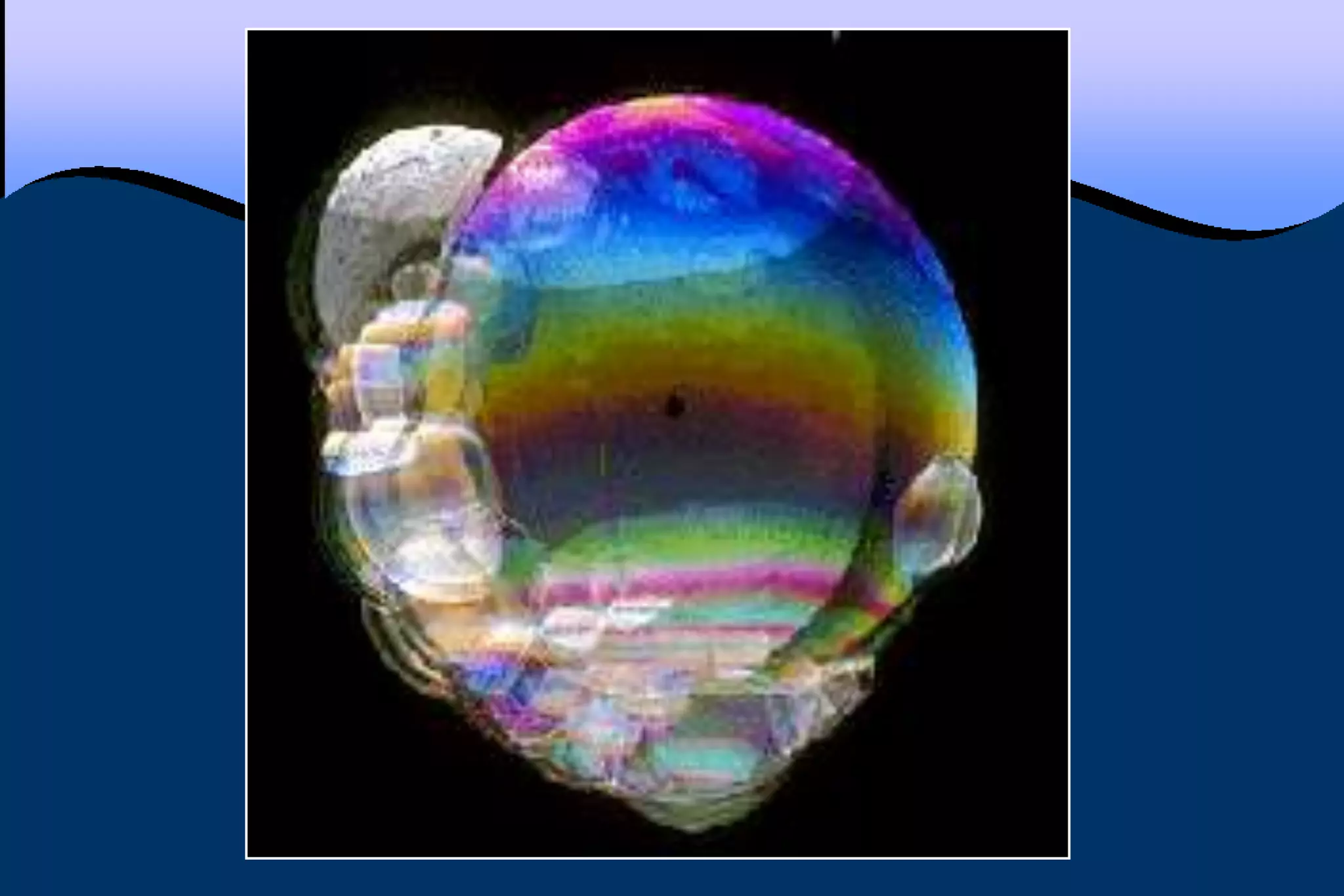
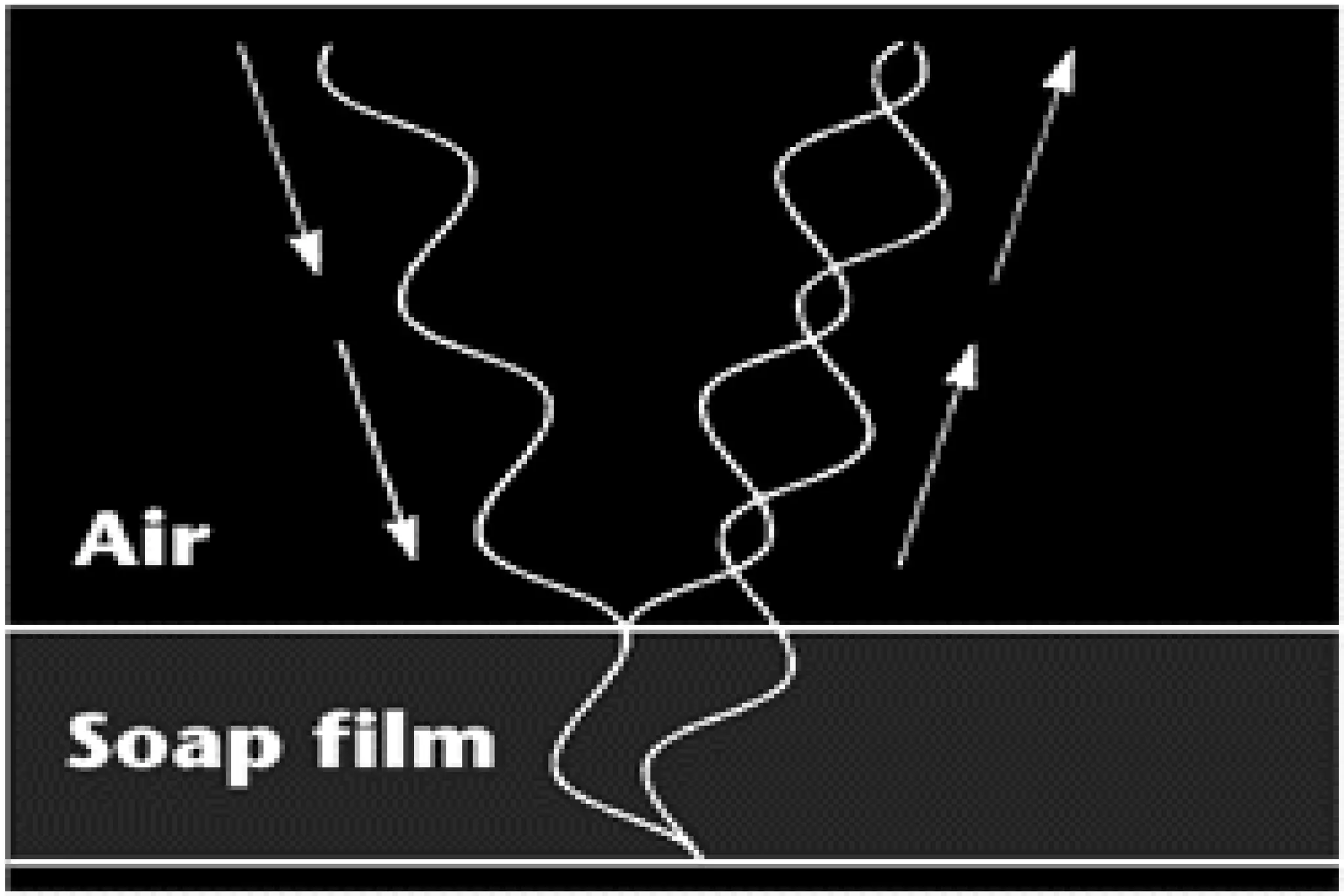
This document discusses key properties of light including reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface, following the law that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Refraction is the bending of light when passing from one medium to another at different speeds. Diffraction causes light to bend around barriers depending on the wavelength and barrier size. Interference results from the interaction of crests and troughs of light waves, producing constructive or destructive interference.