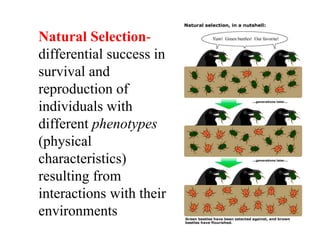
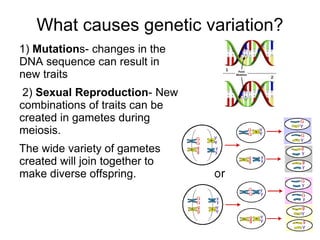
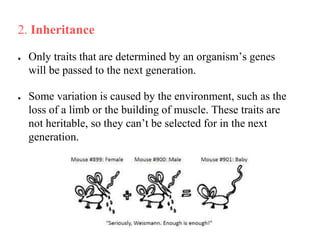
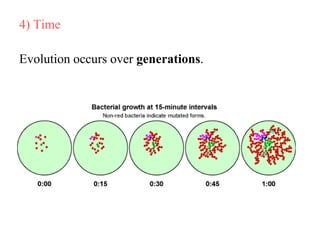
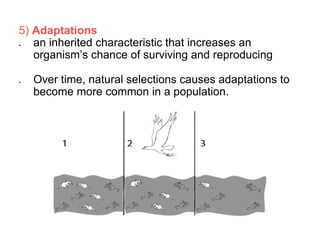
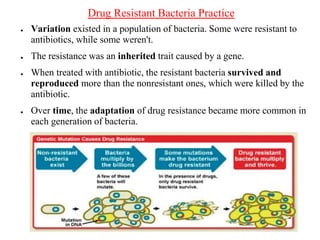
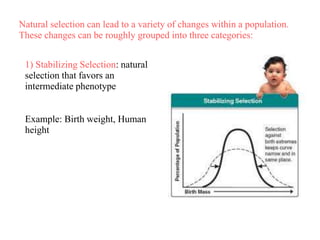
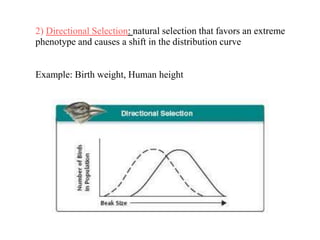
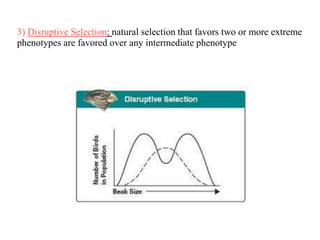
Charles Darwin first proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection. Natural selection is the process by which organisms with traits better suited to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more, passing on those favorable traits. For natural selection to occur there must be genetic variation within a population, the variations must be heritable, individuals must compete for limited resources, and favorable traits must increase reproductive success over time. These conditions lead to adaptations becoming more common and populations changing.