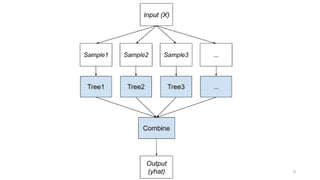
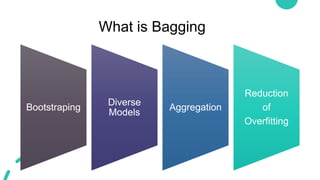
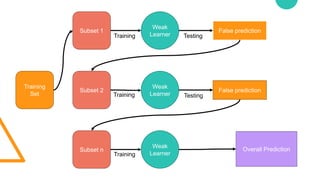
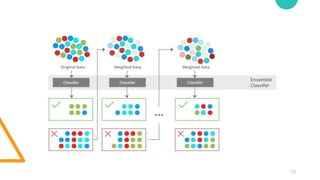
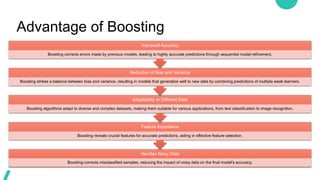
Ensemble learning in machine learning combines predictions from multiple models to enhance performance and accuracy, primarily through methods like bagging and boosting. Bagging reduces overfitting by aggregating diverse models independently, while boosting sequentially improves model accuracy by focusing on misclassified data. Both techniques offer enhanced robustness, stability, and adaptability to various applications, such as text classification and medical diagnosis.