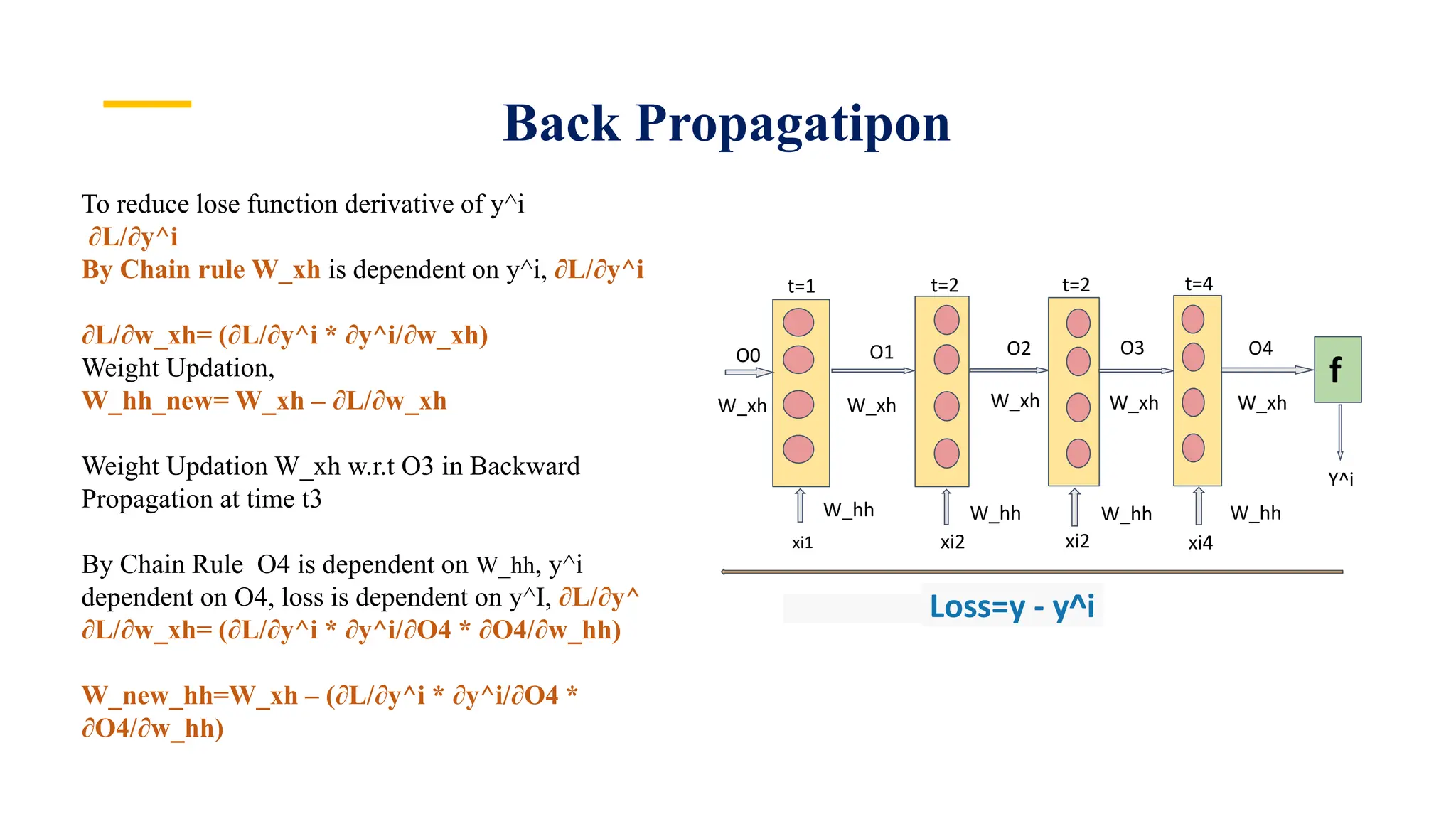
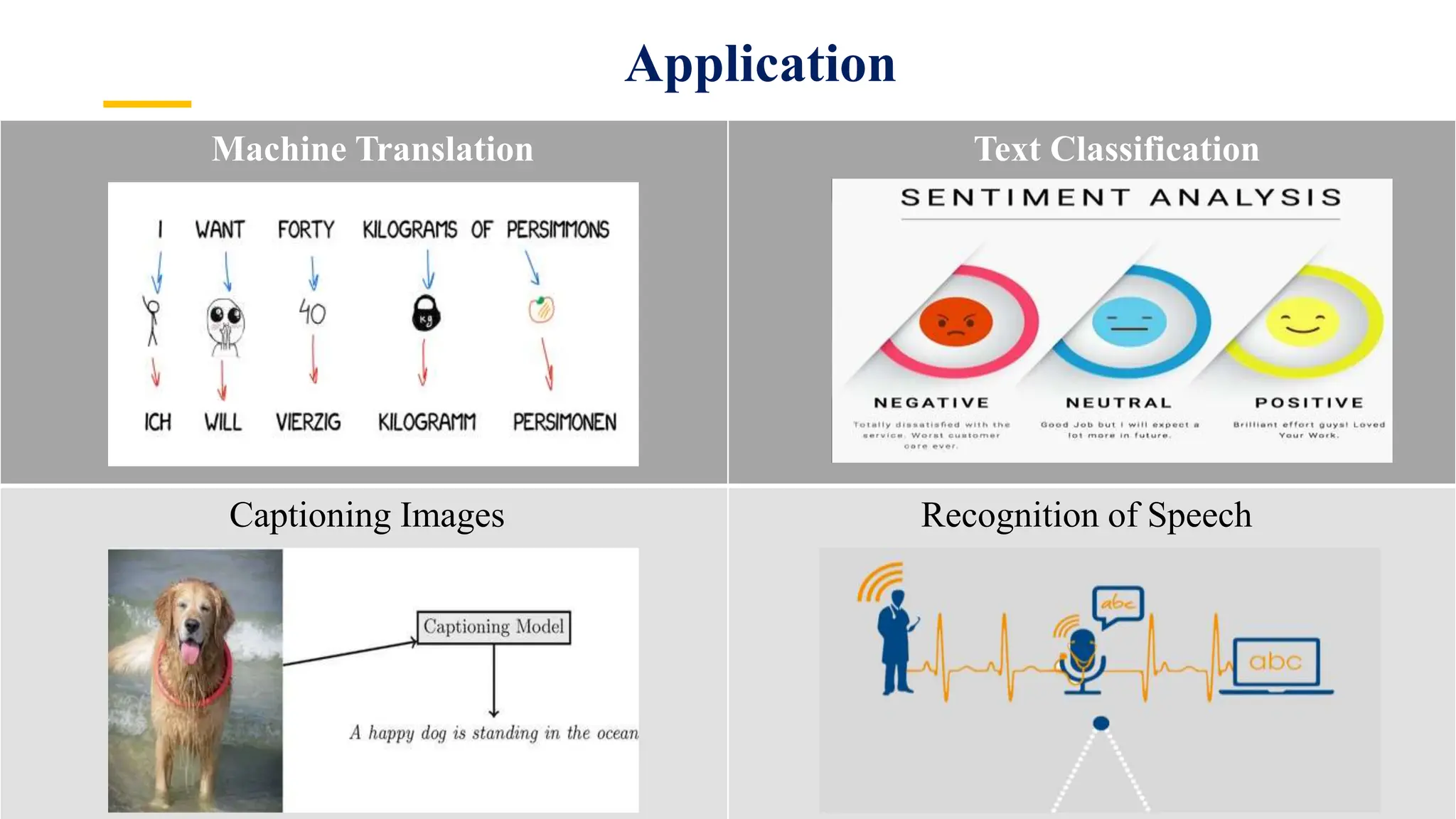
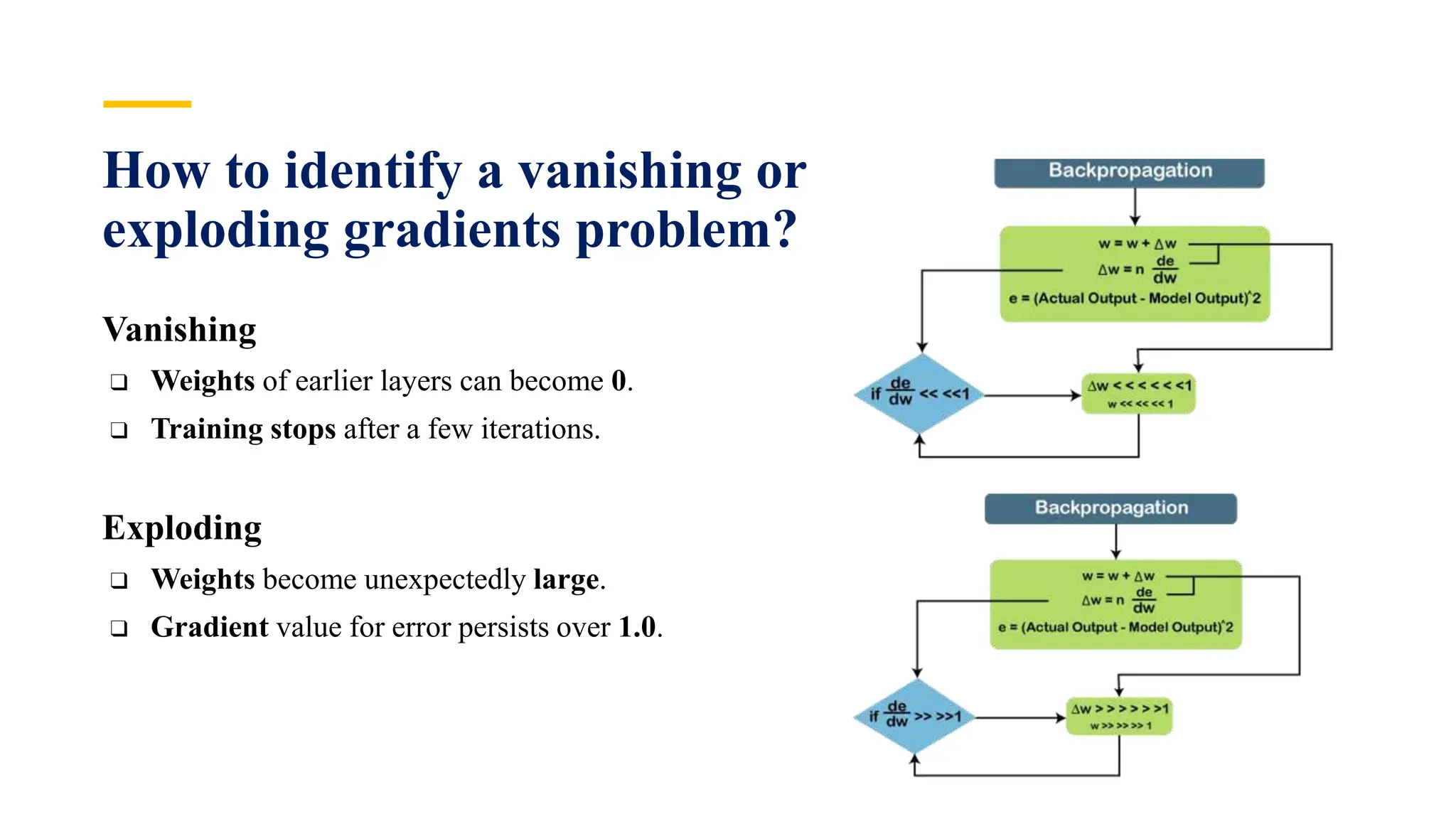
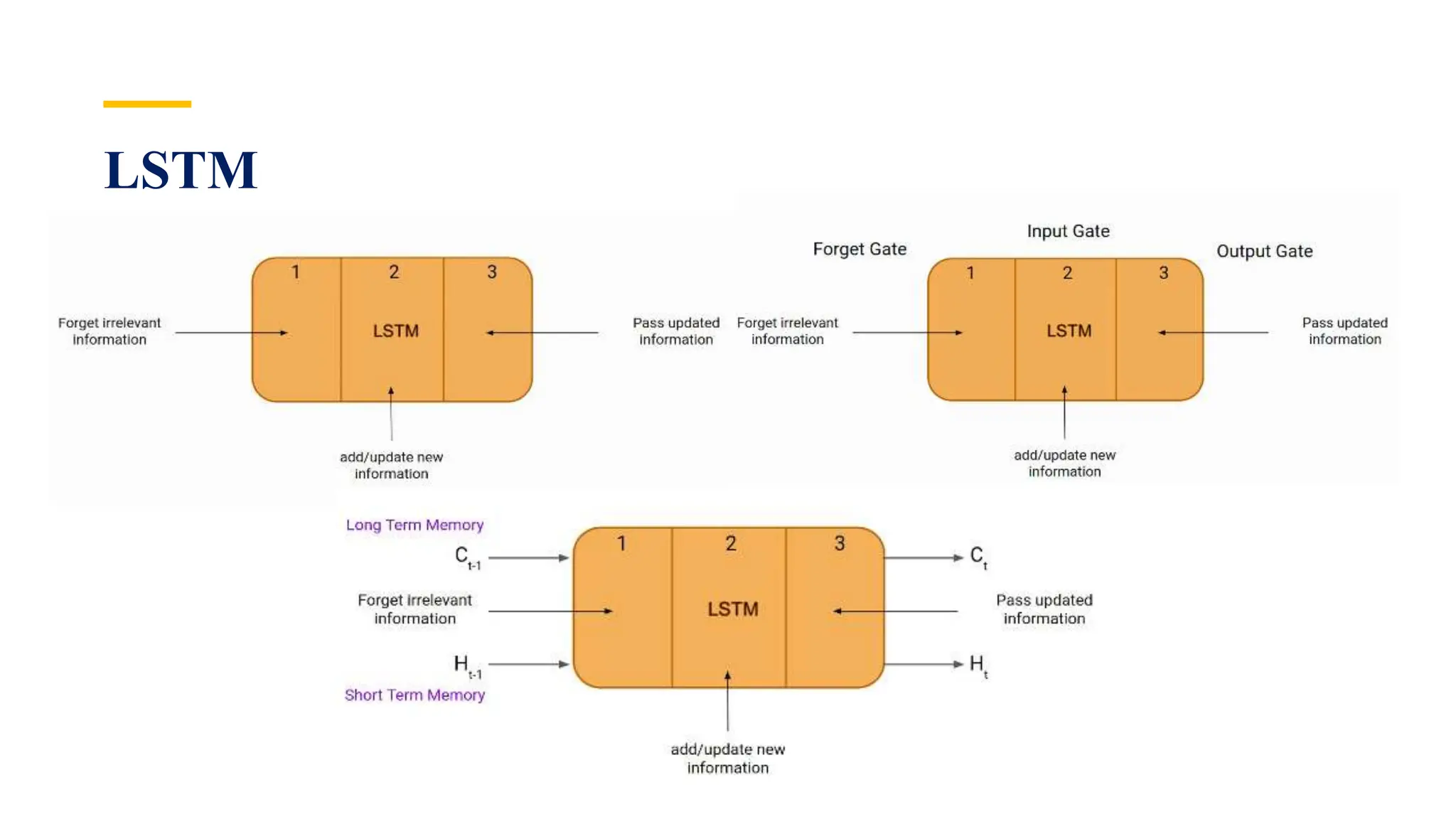
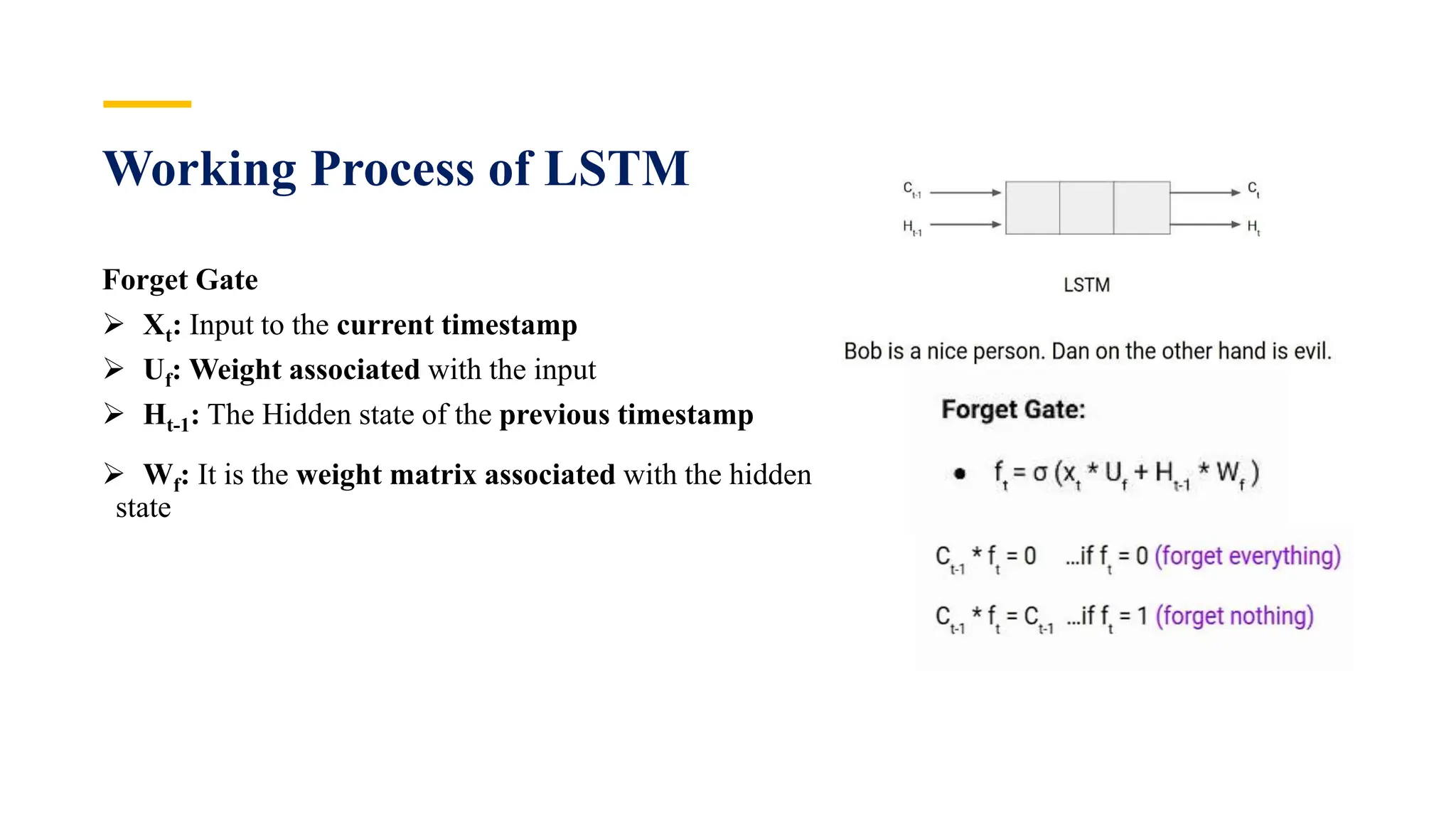
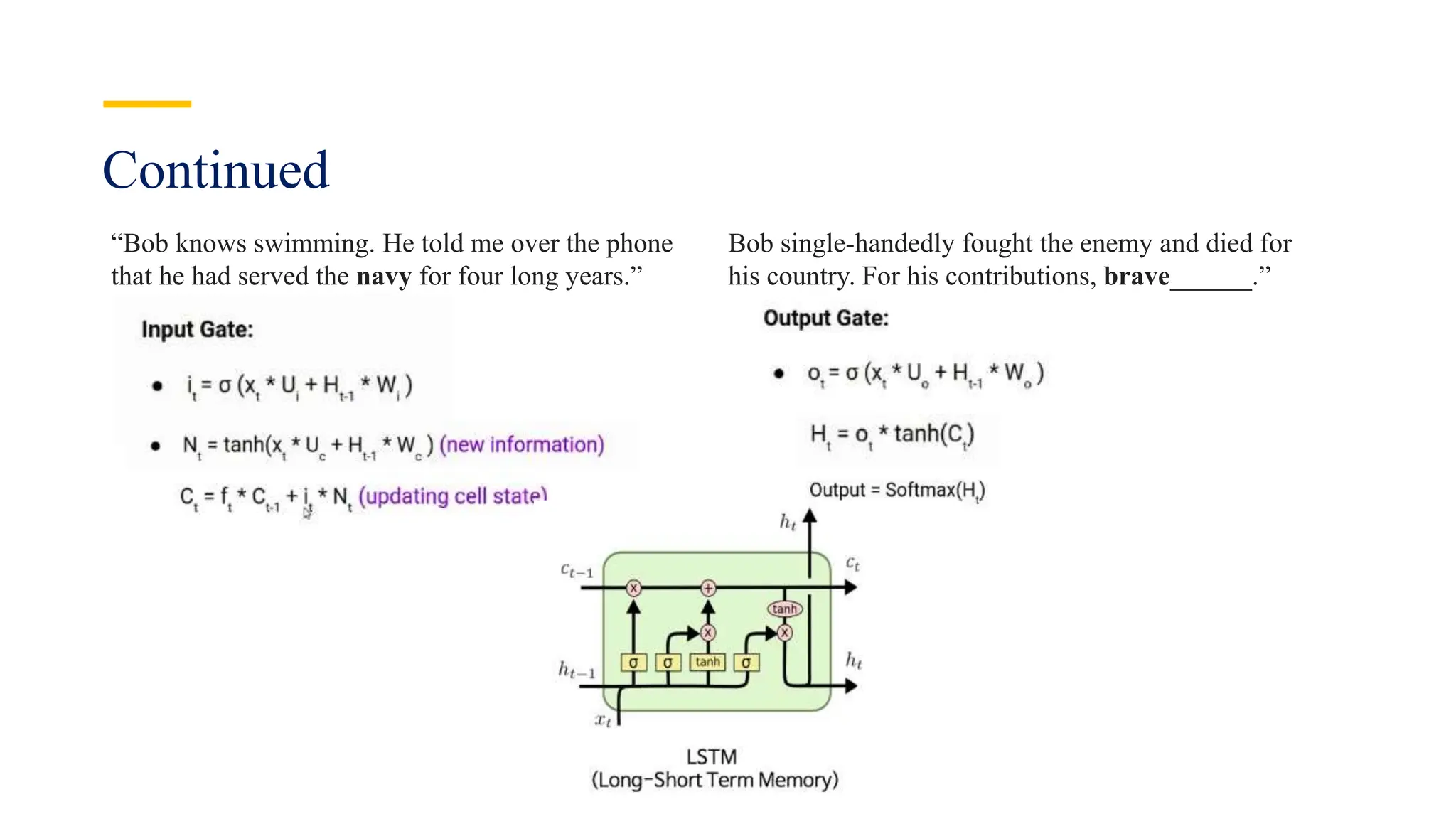
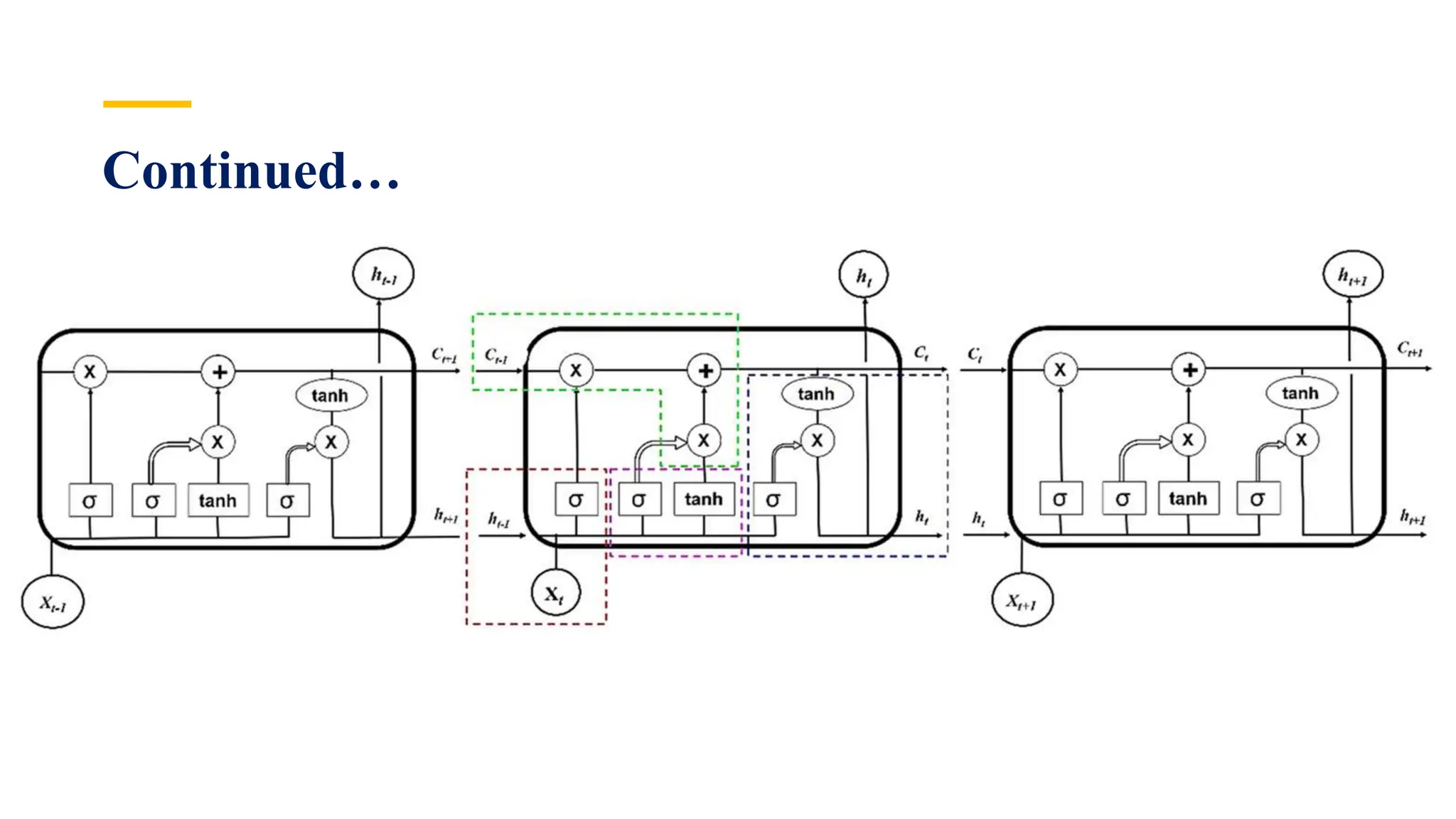
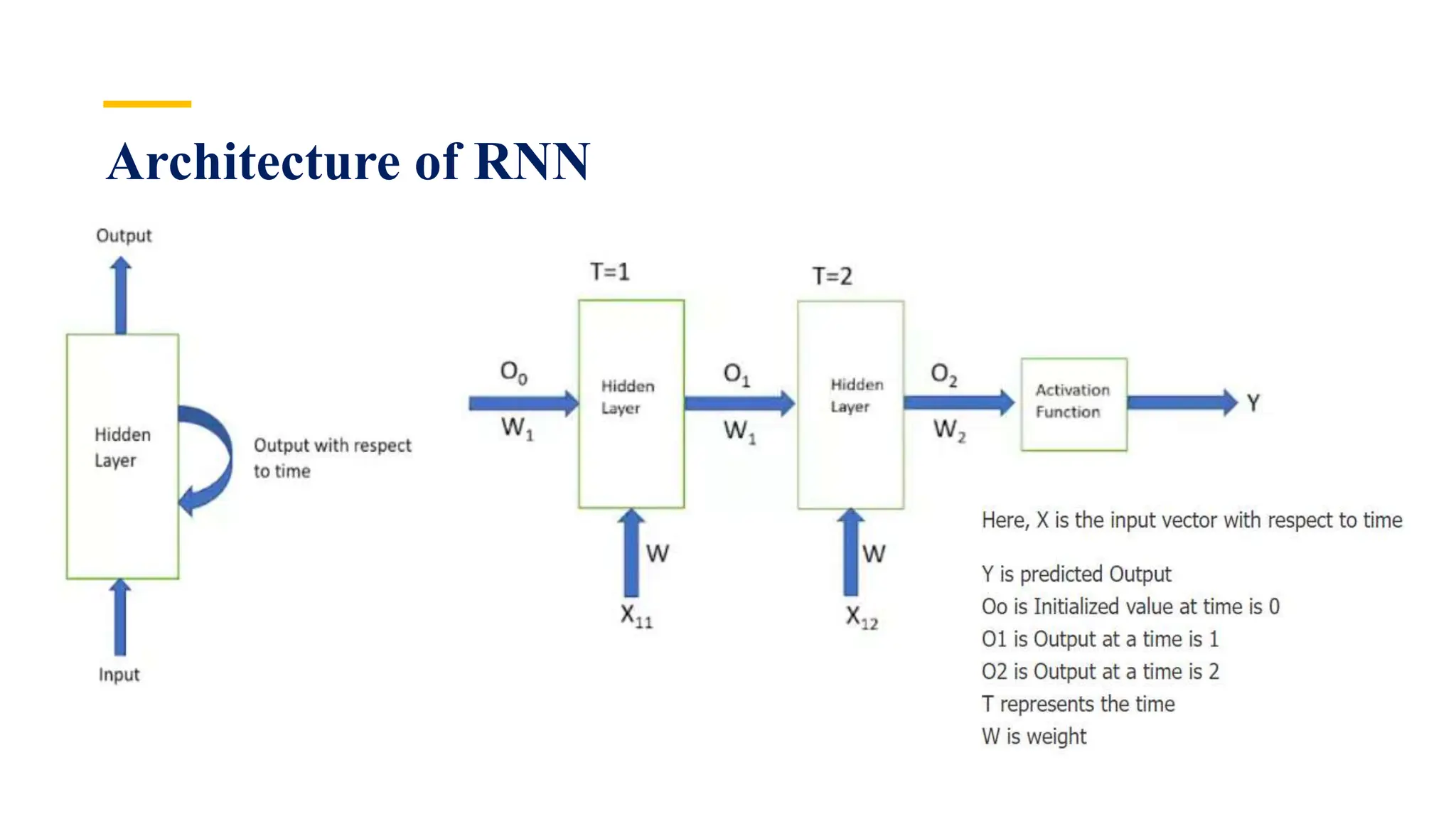
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are specialized artificial neural networks designed to process sequential or time series data, utilizing a hidden layer to retain information about past inputs. They overcome limitations of feed-forward networks by allowing for memory of previous inputs, adjusting weights through error propagation, and can be trained using backpropagation. Despite their advantages in handling sequences of varying lengths, RNNs face challenges such as vanishing and exploding gradients, which can complicate training and computation.





![Example: Character-level Language Model
Vocabulary: [h,e,l,o]
Example training sequence: “hello”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recurrentneuralnetworksrnns-231215173615-4ae834ff/75/Recurrent-Neural-Networks-RNNs-8-2048.jpg)
![Continued…
Vocabulary: [h,e,l,o]
At test-time sample characters
one at a time,
feed back to model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recurrentneuralnetworksrnns-231215173615-4ae834ff/75/Recurrent-Neural-Networks-RNNs-9-2048.jpg)