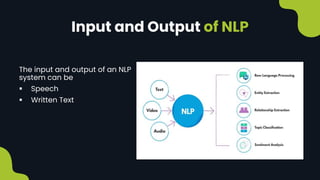
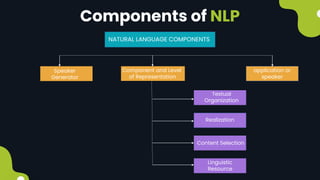
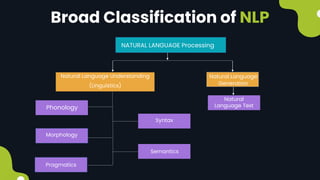
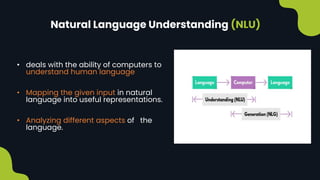
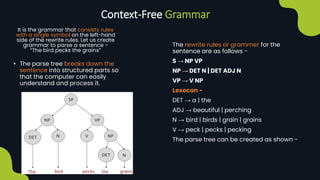
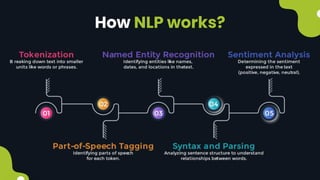
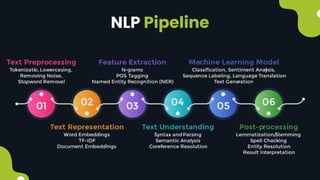
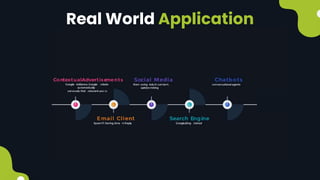
Natural language processing (NLP) enables computers to understand and interpret human language, encompassing tasks like translation and sentiment analysis. It includes components such as natural language understanding (NLU), which interprets language, and natural language generation (NLG), which produces text. The challenges in NLP are significant due to linguistic complexities, yet its applications can vastly improve human-computer interaction.