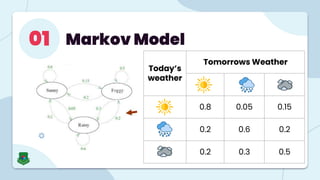
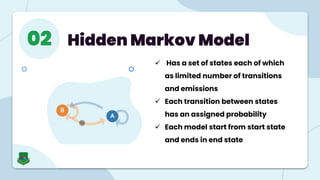
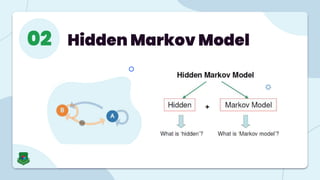
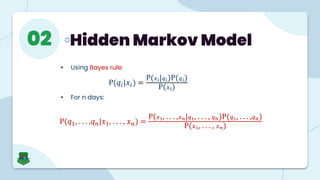
The document provides an overview of Markov Models and Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), detailing their definitions, applications, and problems associated with them. Markov Models are stochastic processes where future states depend only on the current state, while HMMs involve hidden states and observable symbols, with specific algorithms like Baum-Welch and Viterbi used for evaluation, decoding, and learning. Applications of HMMs span various fields, including speech recognition, financial modeling, and time series analysis.