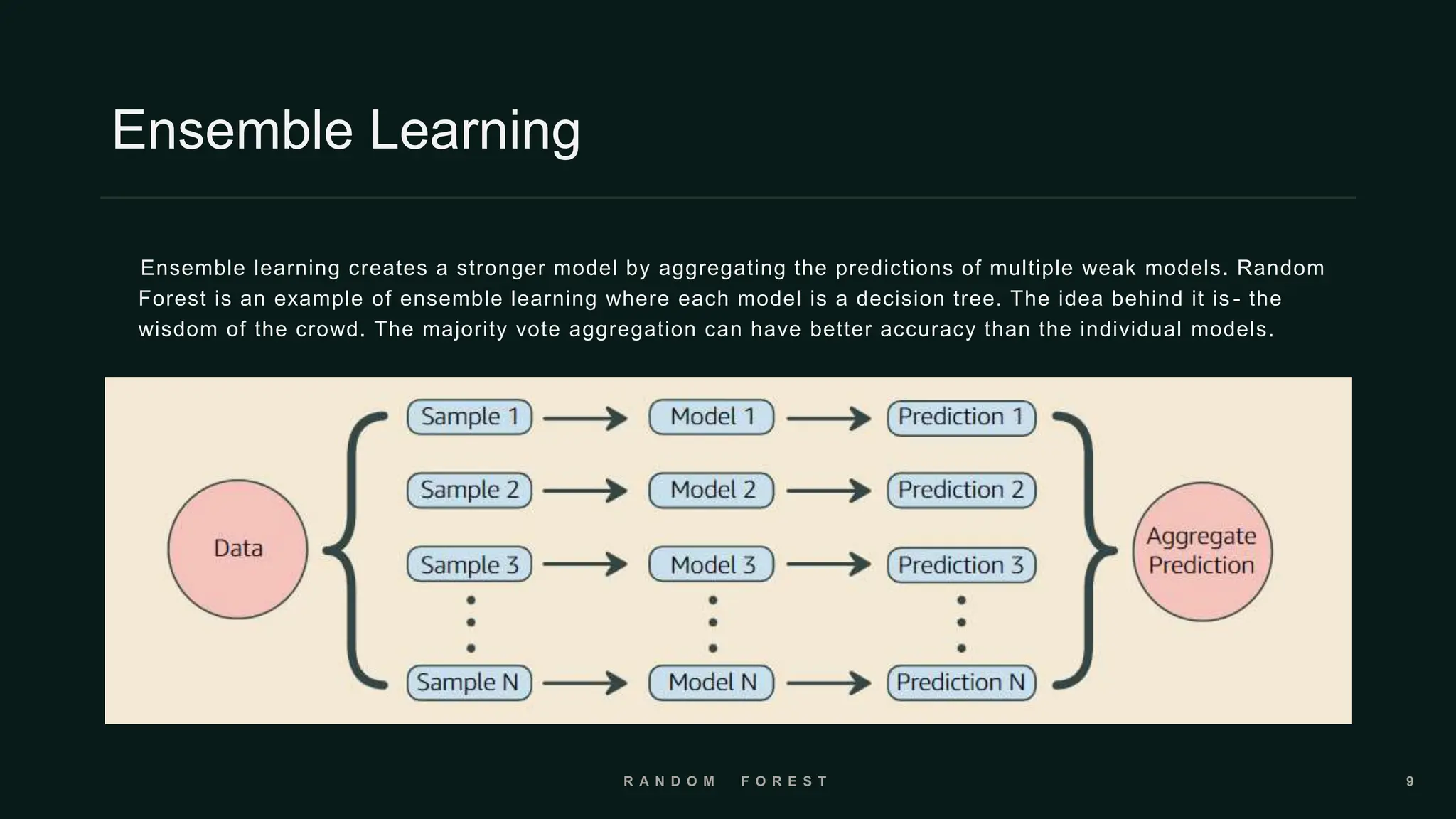
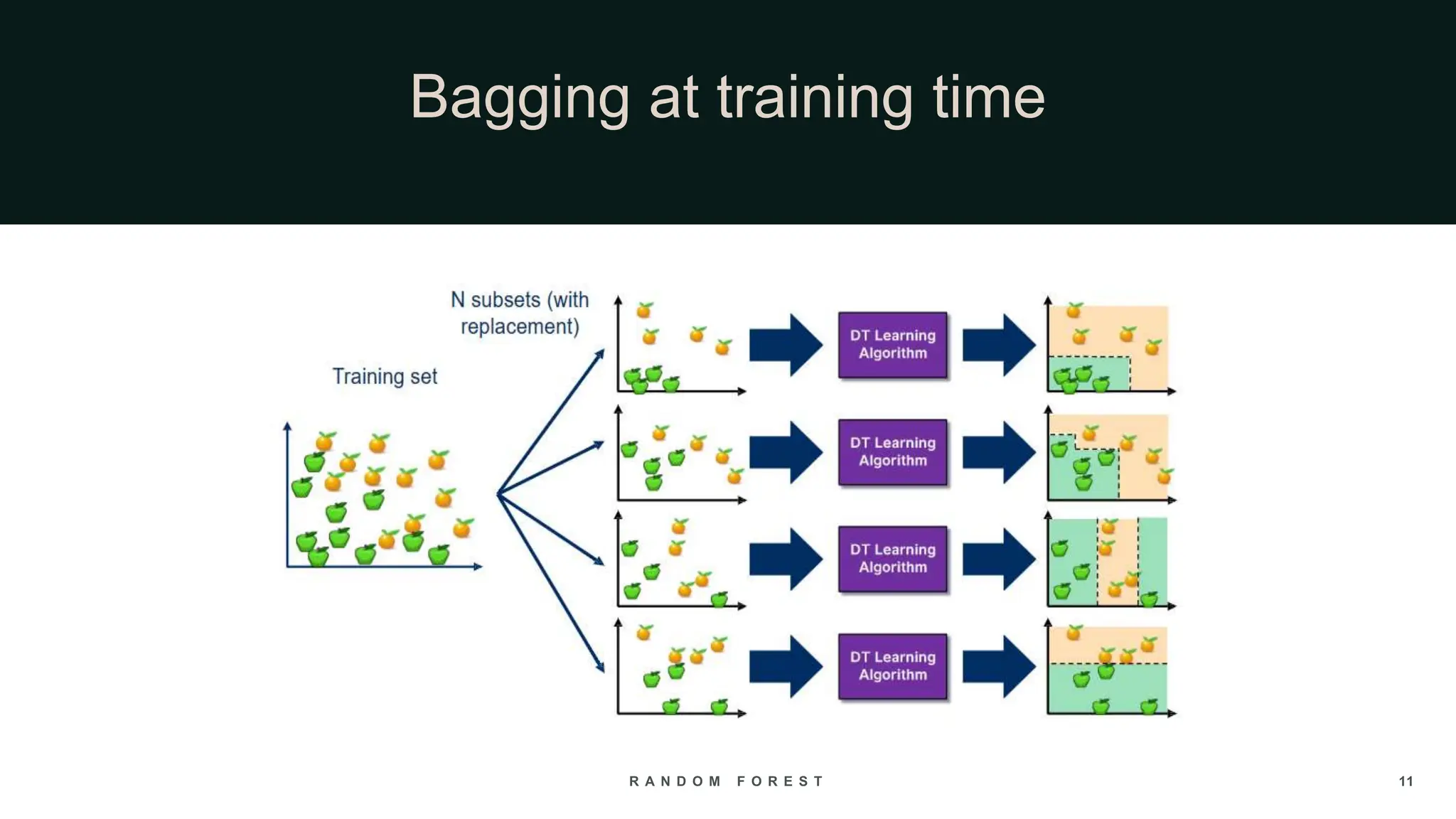
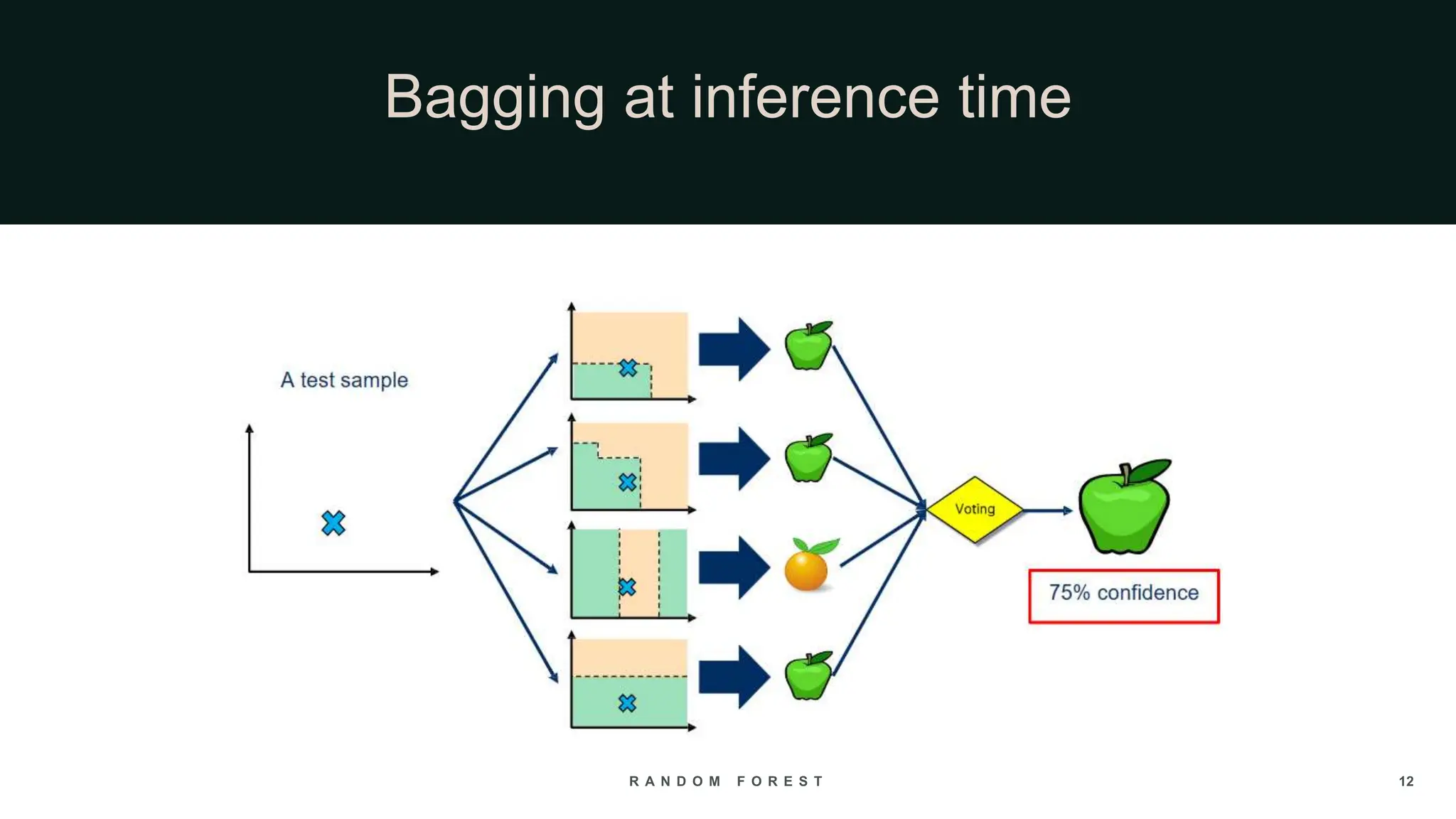
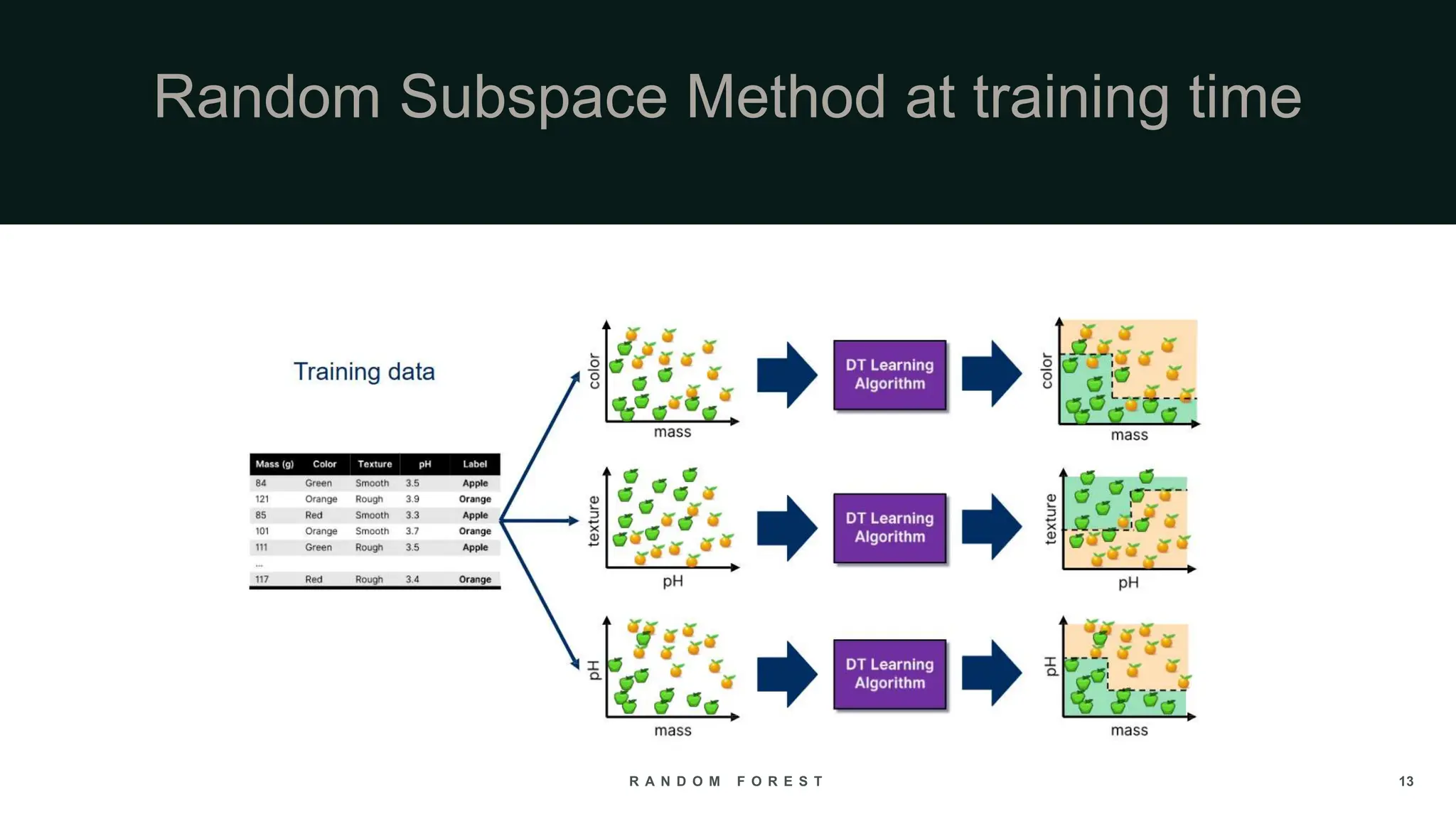
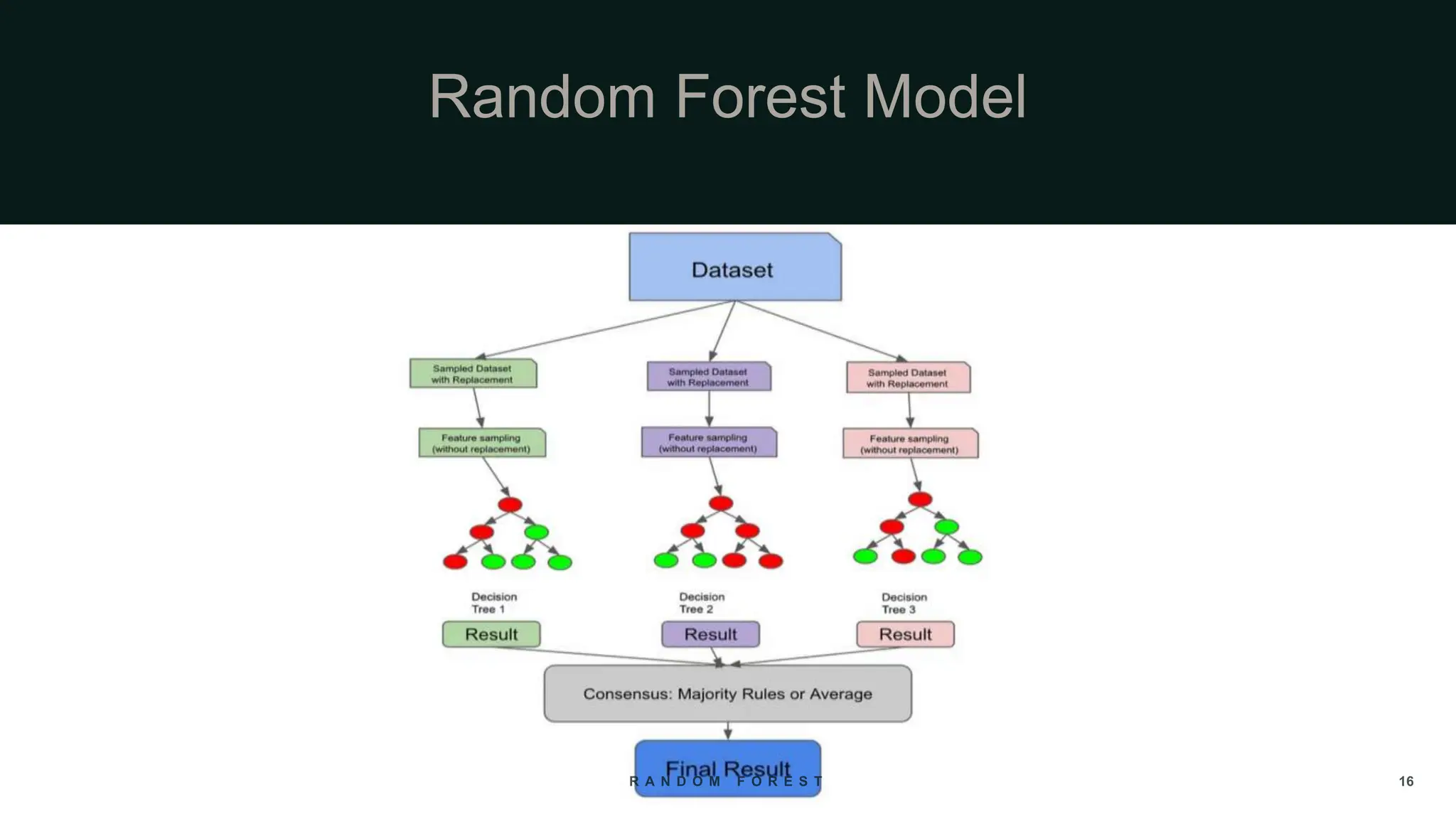
The document provides an overview of the Random Forest algorithm, a supervised machine learning method that utilizes decision trees to improve prediction accuracy through ensemble learning. It details the history, operational principles, dataset preparation methods, advantages, and disadvantages of the random forest model, along with its applications in various fields. Key concepts discussed include supervised learning, bagging, and the importance of aggregating results from multiple models.