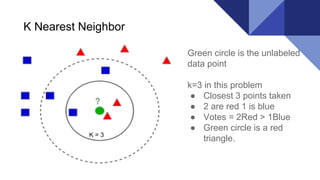
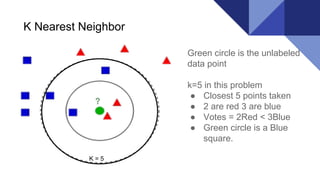
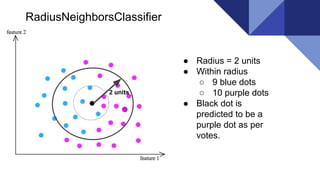
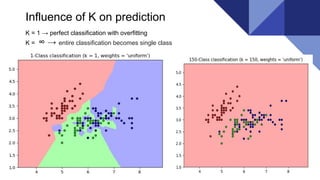
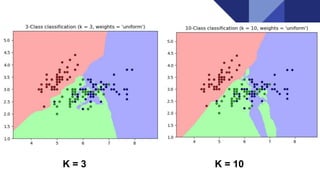
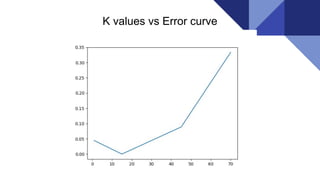
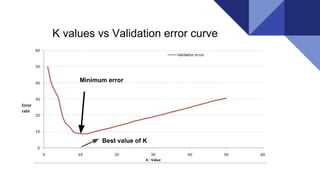
The document discusses the k-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm, a lazy learning method used for classification and regression in both supervised and unsupervised learning. It explains how KNN works by making predictions based on the majority vote of the 'k' closest points to an unlabeled data point, while using distance metrics like Euclidean and Hamming distance. The text also highlights the influence of the 'k' value on model performance, its advantages and disadvantages, and various applications in fields such as finance and medicine.