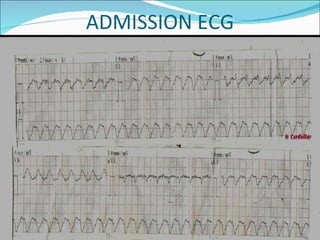
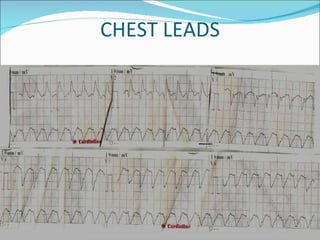
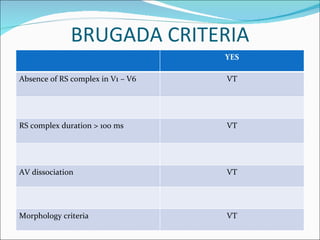
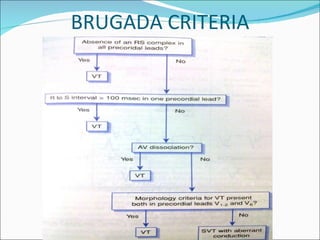
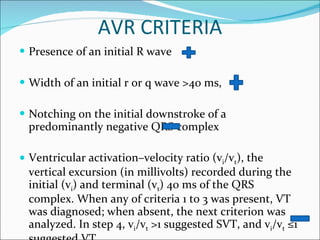
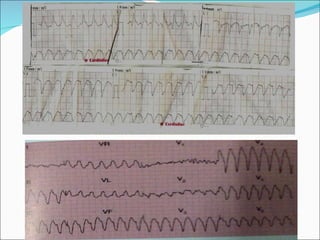
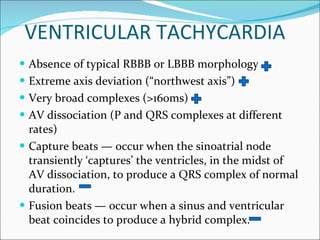
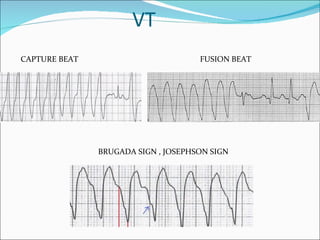
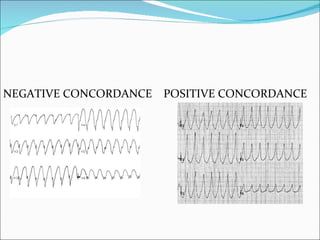
A 22-year-old male presented with acute onset breathlessness, palpitations, and profuse sweating. His ECG showed tachycardia at a rate of 200 bpm with a right bundle branch block pattern. This wide complex tachycardia was determined to be ventricular tachycardia based on Brugada criteria and AVR criteria, including the absence of an RS complex in leads V1-V6, a QRS duration greater than 100 ms, and a ventricular activation-velocity ratio greater than 1. The patient was diagnosed with ventricular tachycardia based on the ECG findings and treated accordingly.