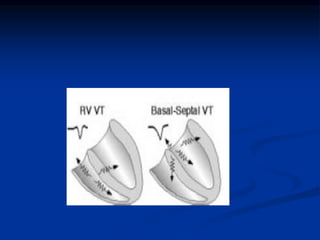
This document provides information on differentiating between ventricular tachycardia (VT) and supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) with aberrancy using electrocardiogram (ECG) criteria. It discusses:
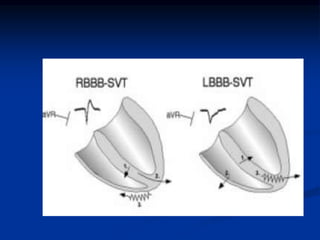
- Definitions of wide complex tachycardia, VT, SVT, LBBB and RBBB morphology
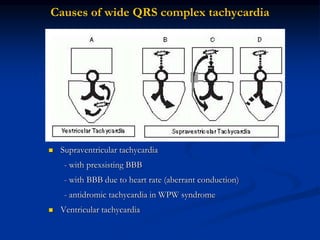
- Causes of wide QRS complexes
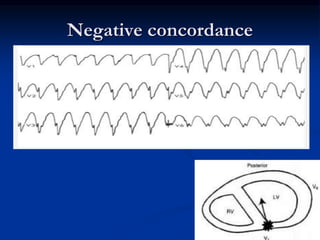
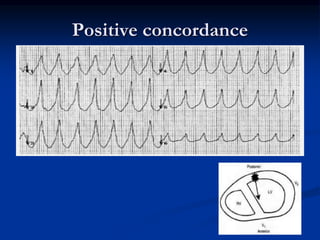
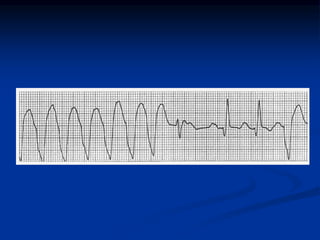
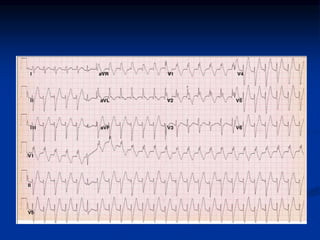
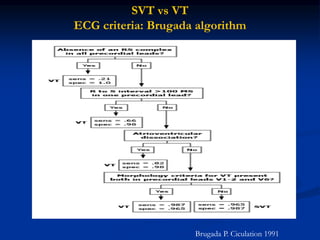
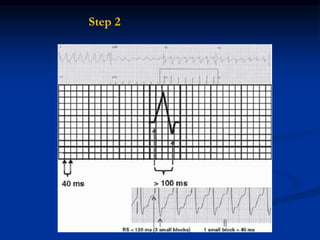
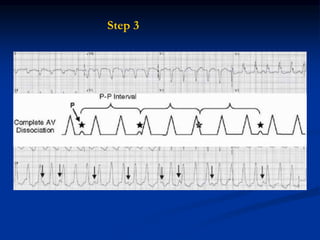
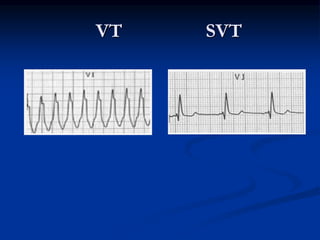
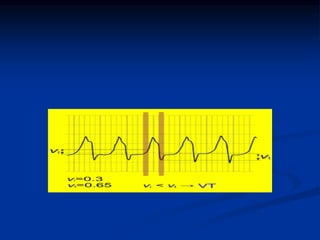
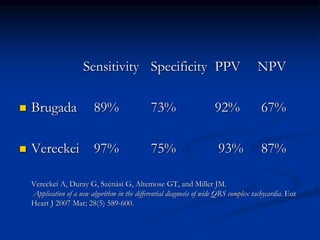
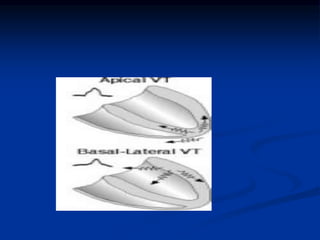
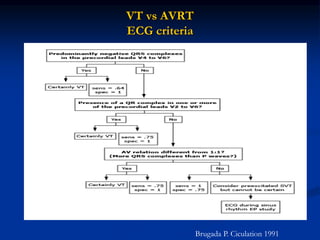
- ECG criteria that suggest VT vs SVT such as axis, QRS duration, concordance, AV dissociation
- Maneuvers such as carotid sinus pressure that can help differentiate
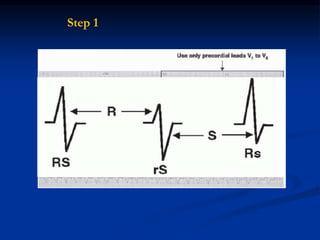
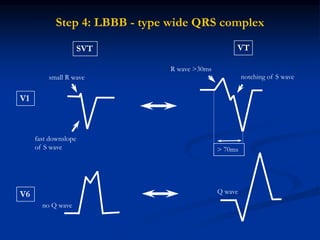
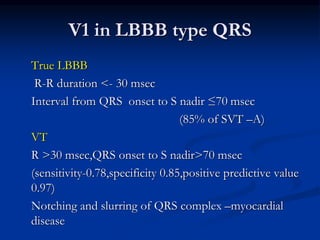
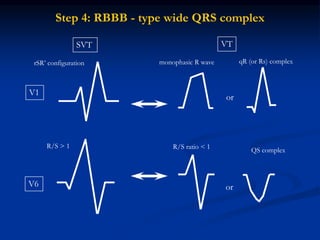
- Evaluation of ECG leads such as V1, V6, aVR lead for LBBB and RBBB patterns




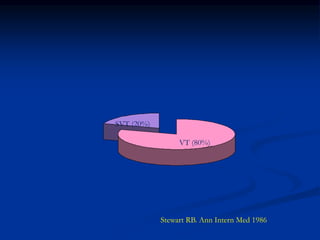



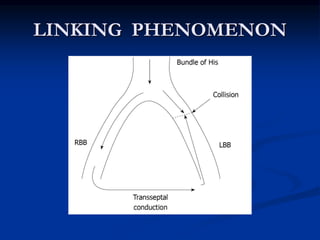
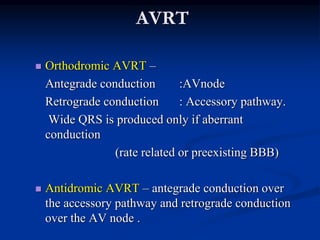
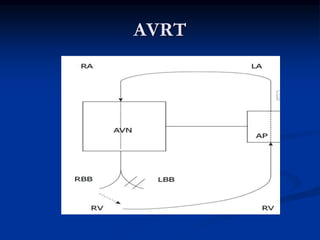

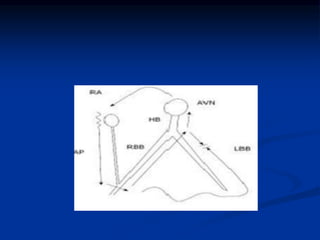
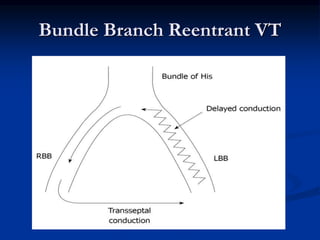


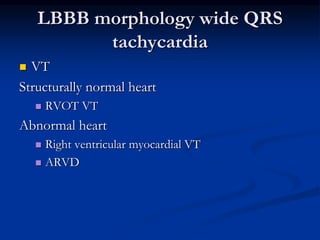


![SVT vs VT
Clinical history
Medication Drug-induced tachycardia → Torsade de pointes
Diuretics
Digoxin-induced arrhythmia → [digoxin] ≥2ng/l or
normal if hypokalemia
Age - ≥ 35 ys → VT (positive predictive value of 85%)
Underlying heart disease Previous MI → 90% VT
Pacemakers or ICD Increased risk of ventricular tachyarrhythmia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/widecomplextachycardiadrpradeep-240331173033-8f046065/85/WIDE-COMPLEX-TACHYCARDIA-DR-PRADEEP-ppsx-21-320.jpg)