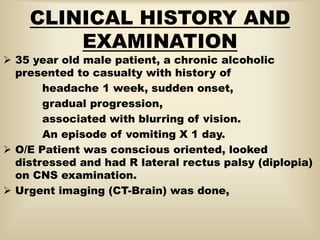
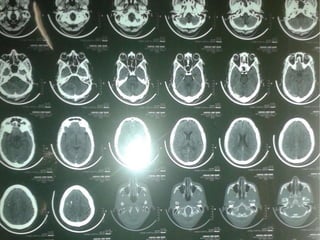
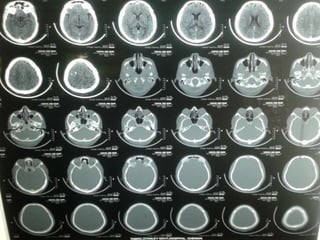
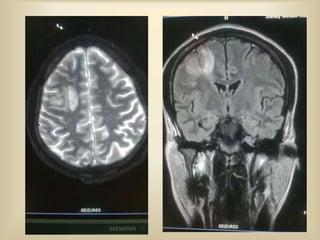
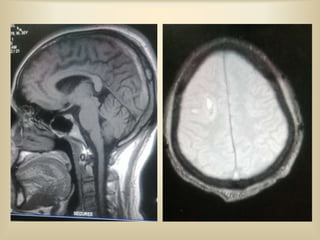
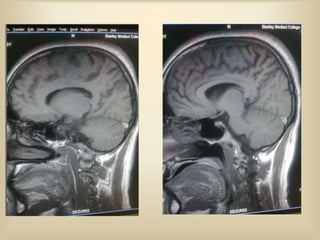
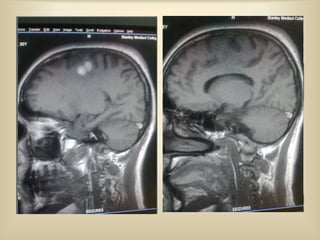
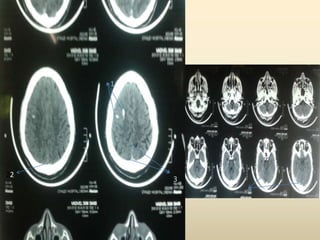
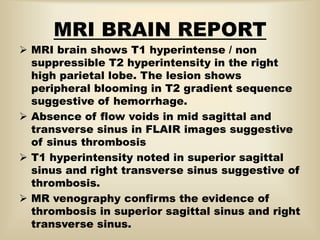
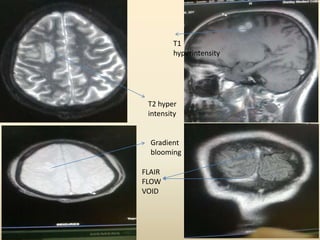
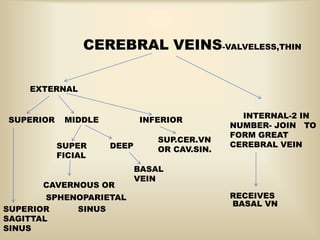
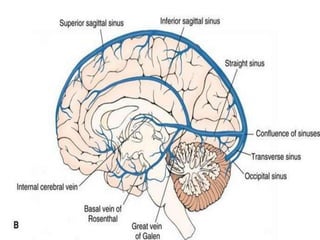
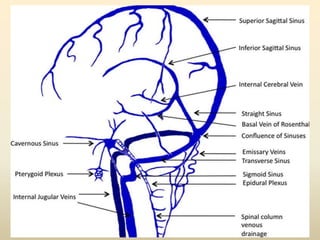
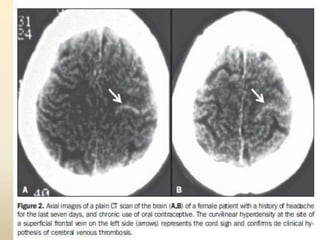
A 35-year-old male chronic alcoholic presented with a week-long headache and blurry vision. On examination, he had right lateral rectus palsy. CT brain showed hyperdensity in the right frontal region, right transverse sinus, and hypodensity in the superior sagittal sinus, suggestive of parenchymal hemorrhage with cortical vein thrombosis or calcified granuloma. MRI brain found a hemorrhagic lesion in the right high parietal lobe, absence of flow voids in sinuses, and T1 hyperintensity in sinuses confirming sinus thrombosis, which was shown on MR venography. The patient was diagnosed with cerebral vein thrombosis based on imaging findings.