Embed presentation
Downloaded 33 times

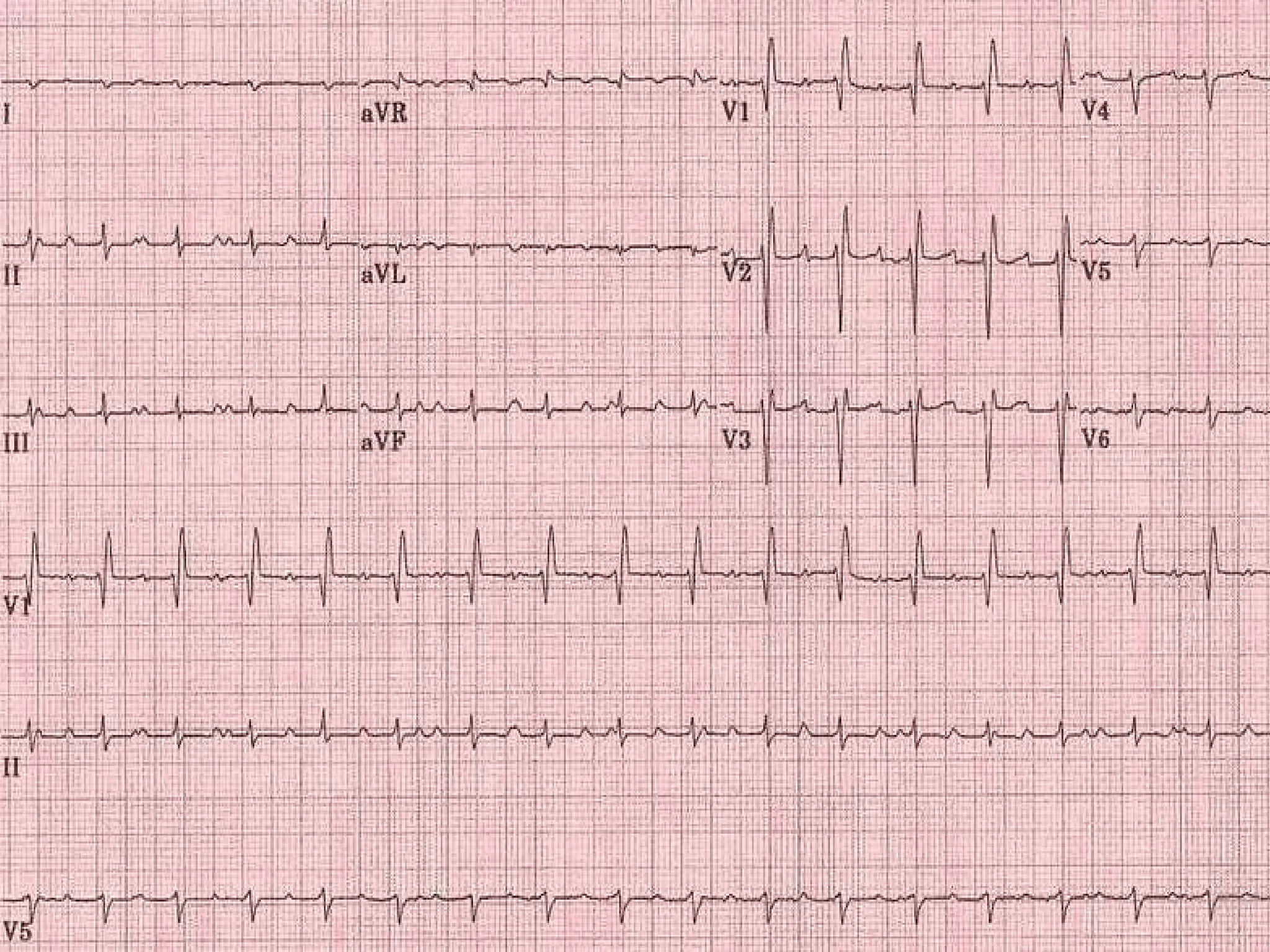





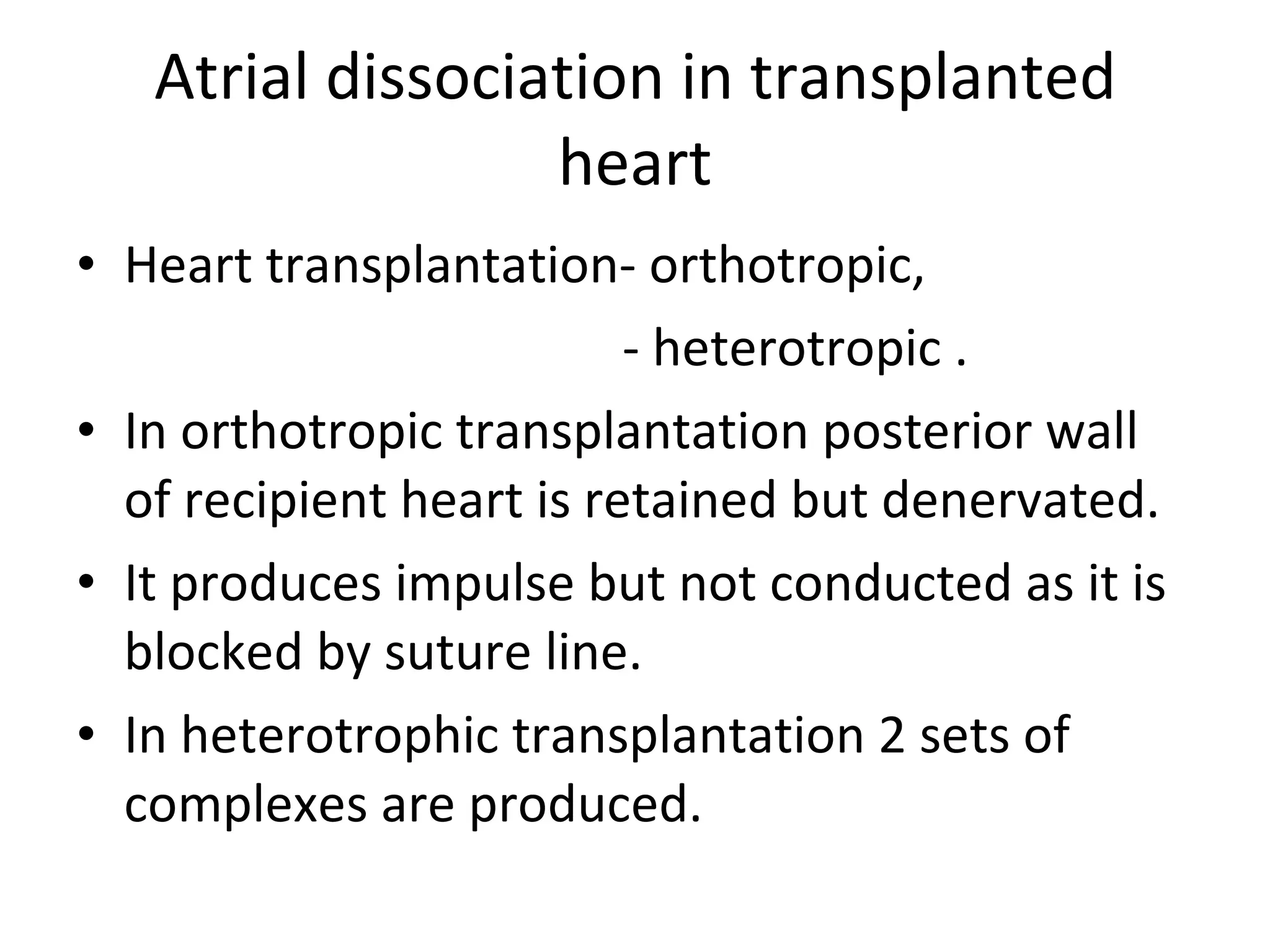
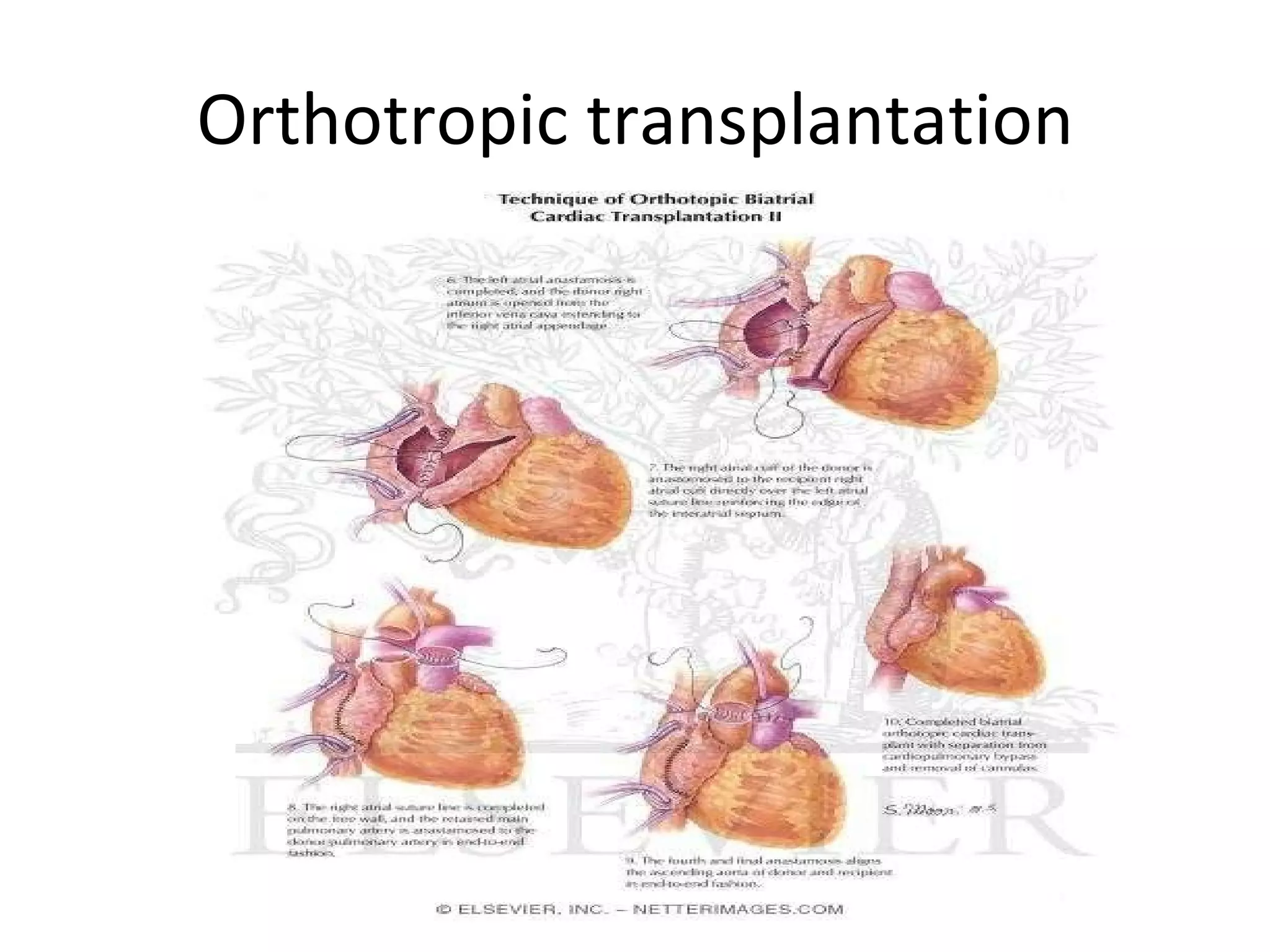
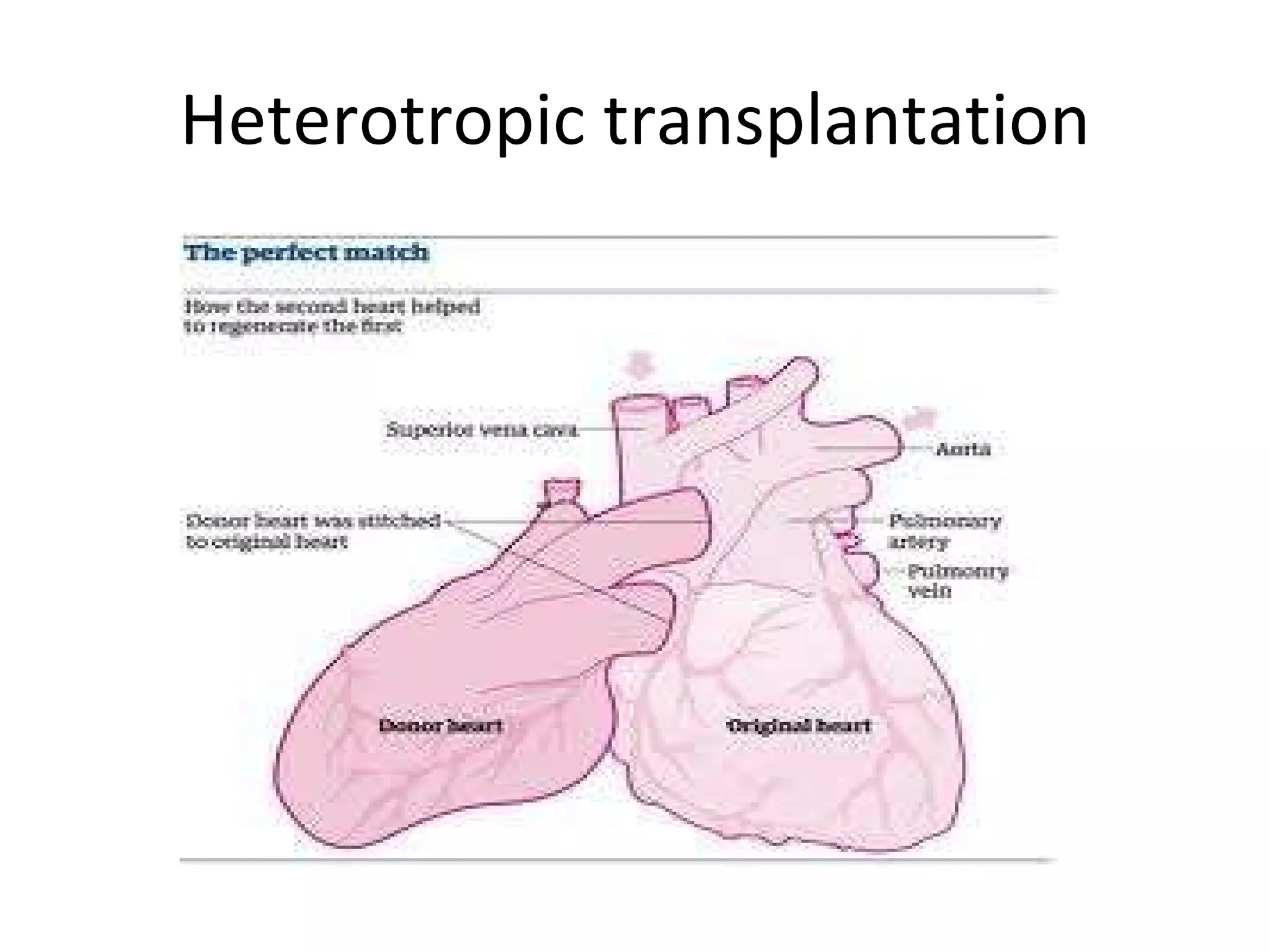
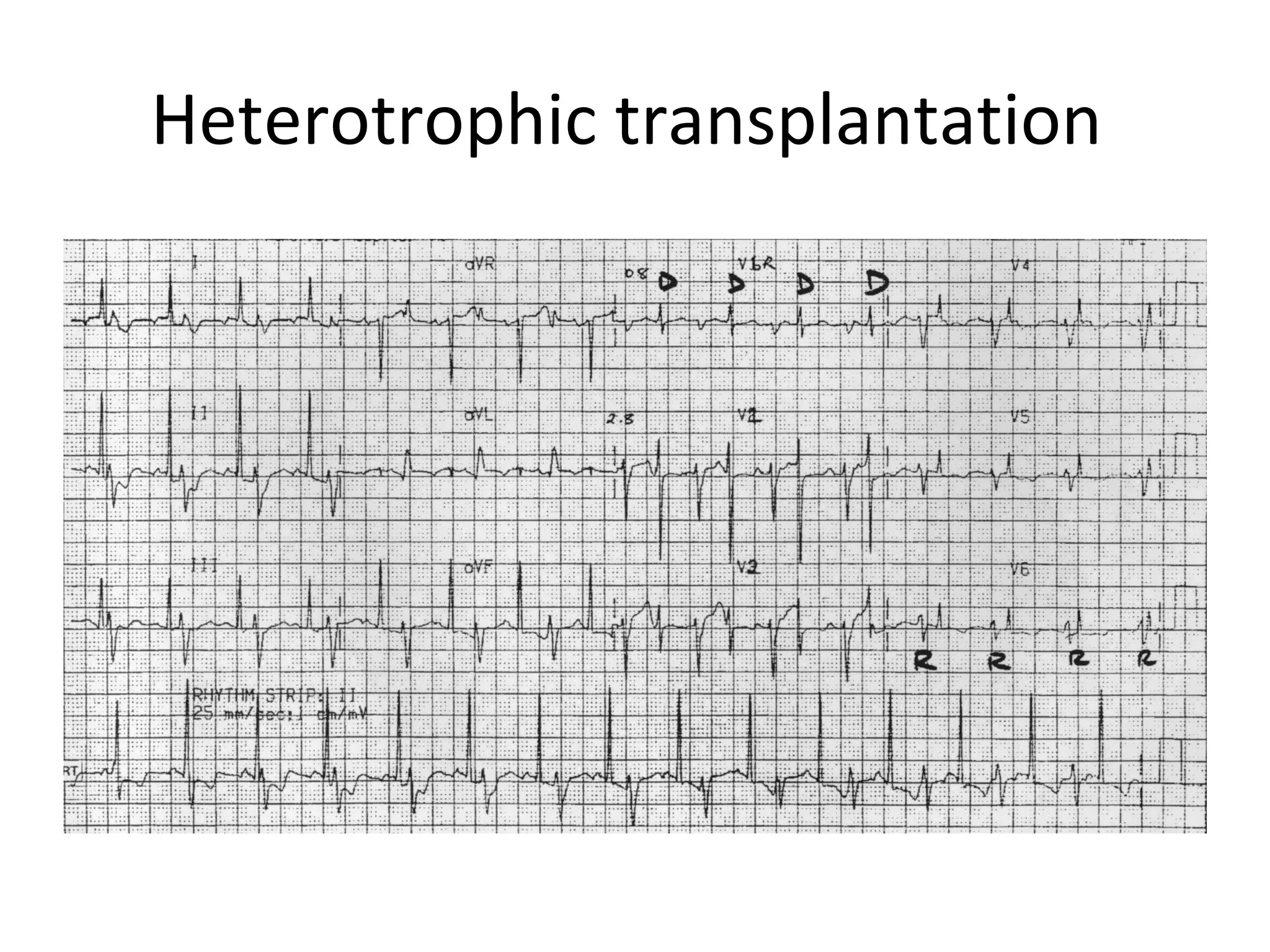
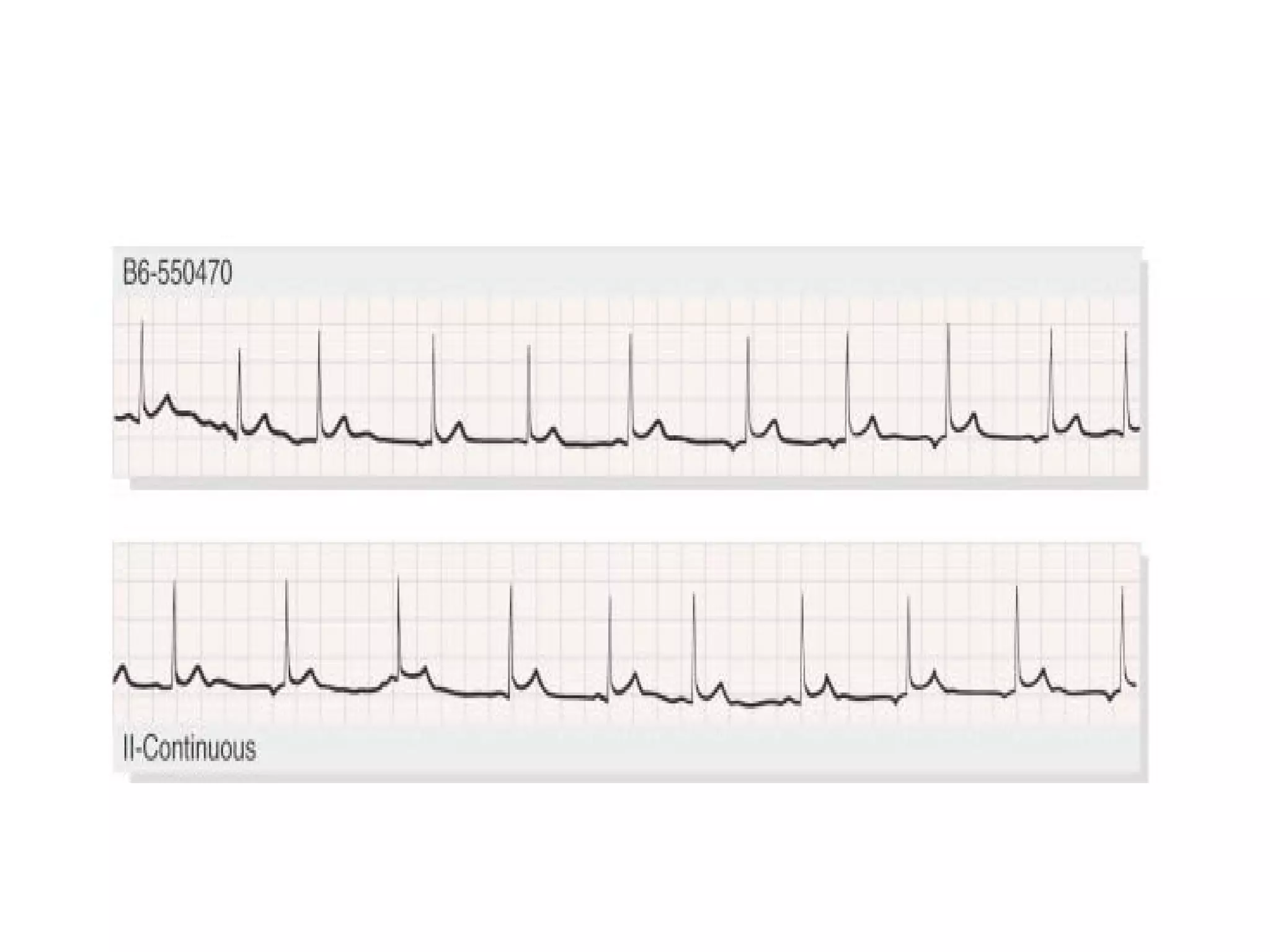
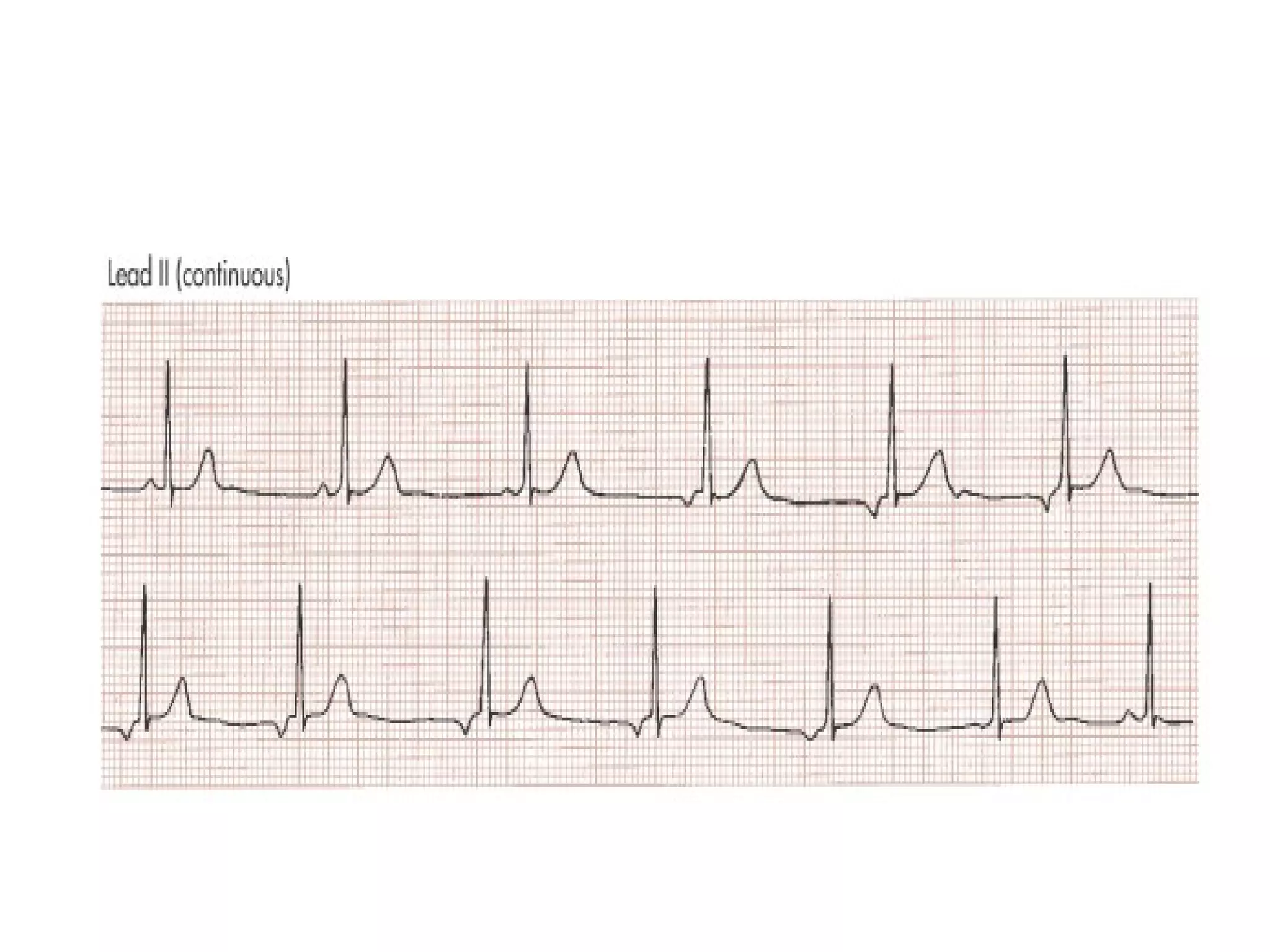




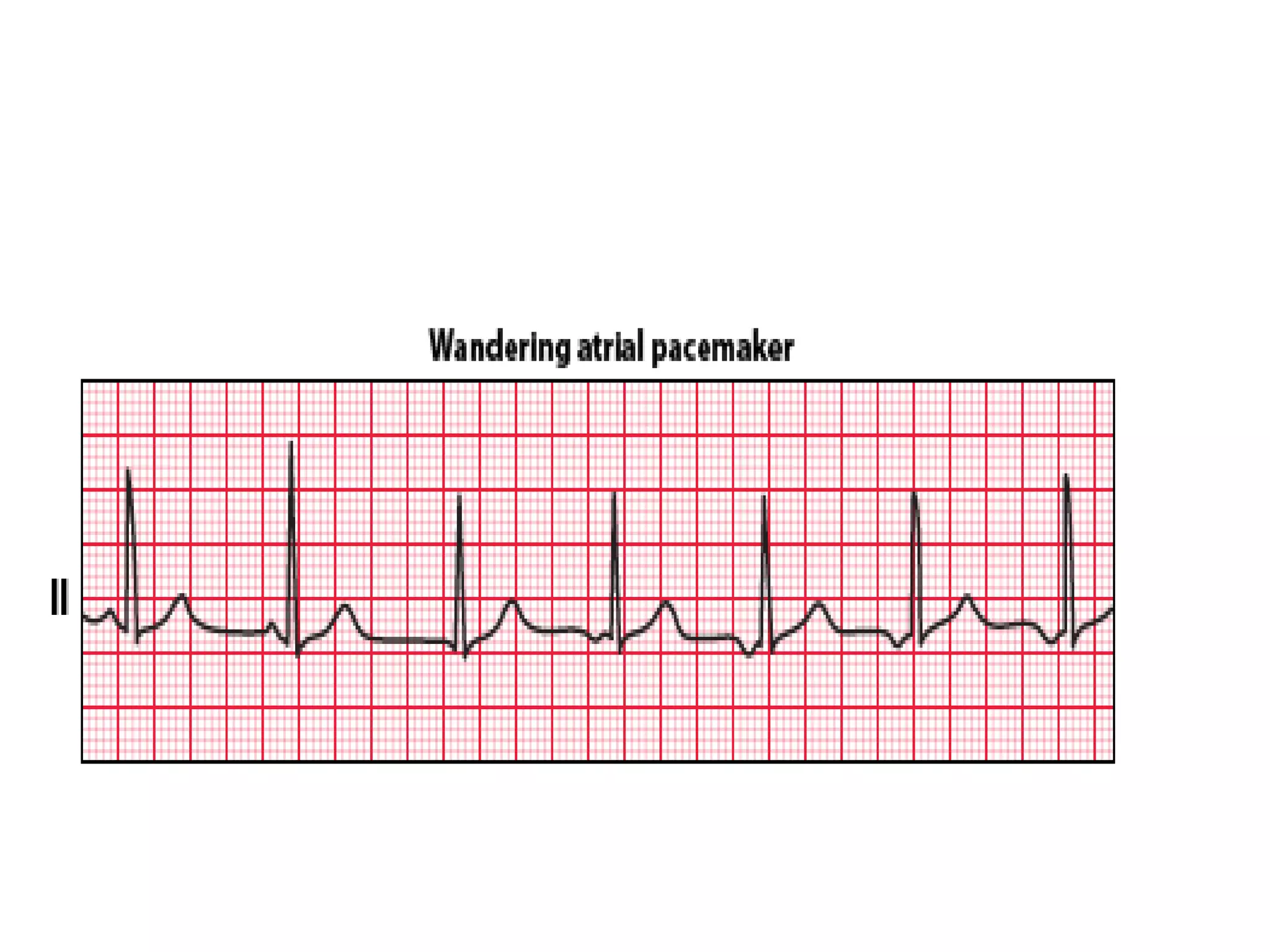

This ECG shows atrial dissociation in a 70-year-old male with a history of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and cardiac transplantation 6 months prior. Atrial dissociation is seen as two independent sets of P waves with varying PP and PR intervals. Atrial dissociation occurs when each atrium beats separately due to blockage of the Bachmann's bundle interatrial pathway. It can occur in orthotopic and heterotopic heart transplant patients as the posterior atrial wall is retained but denervated after orthotopic transplant.



















