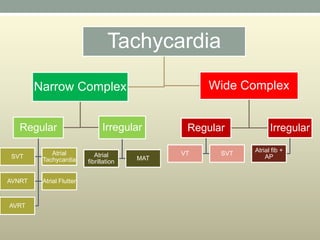
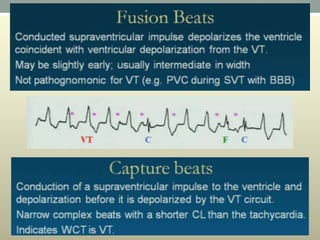
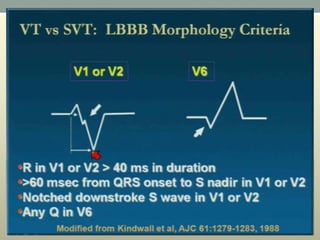
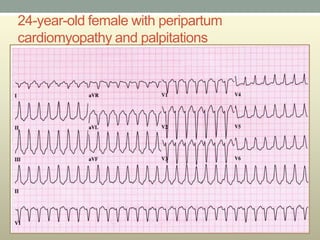
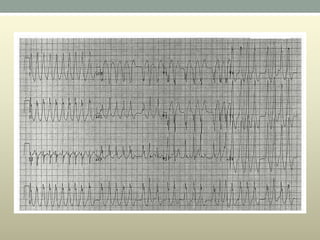
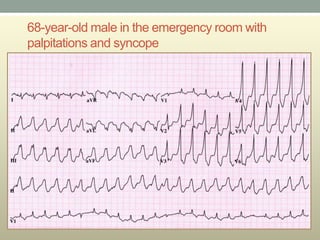
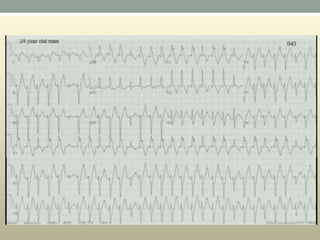
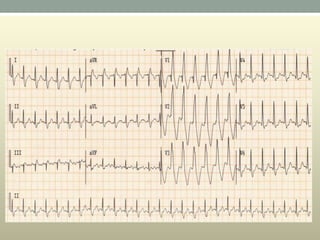
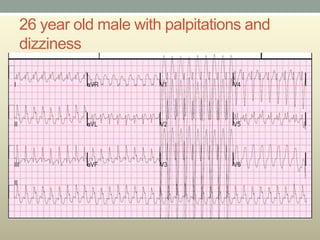
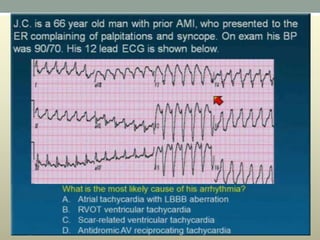
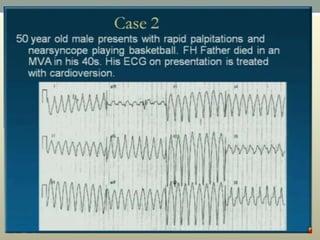
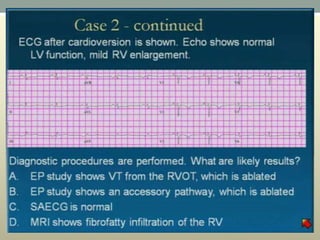
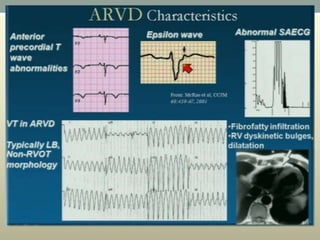
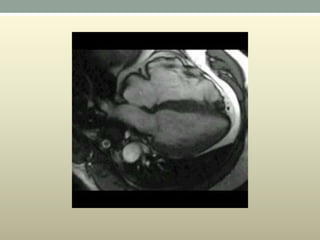
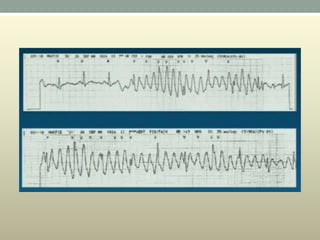
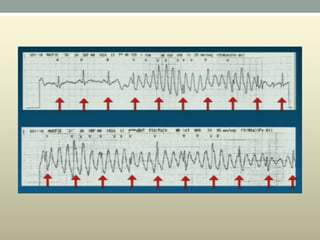
This document discusses wide complex tachycardia (WCT), which is ventricular in origin 80% of the time. In patients with structural heart disease, 95% of WCT is ventricular tachycardia (VT). VT can be life-threatening and cause sudden death or tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy. The document describes types of VT based on morphology and duration, symptoms of VT, features that appear on ECGs during VT like abnormal wide QRS complexes and AV dissociation, and examples of patients presenting with potential VT.