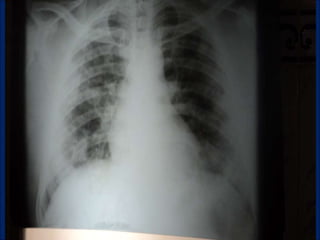
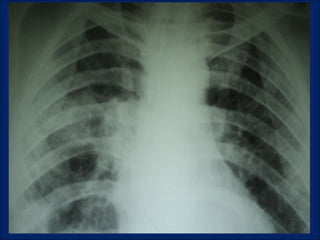
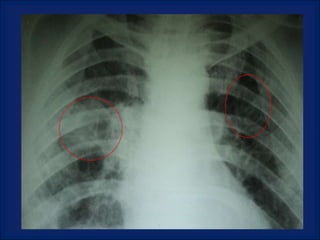
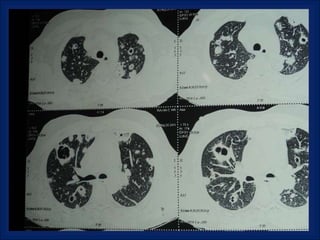
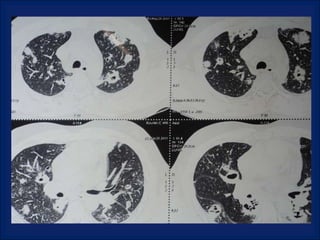
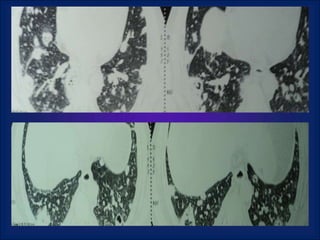
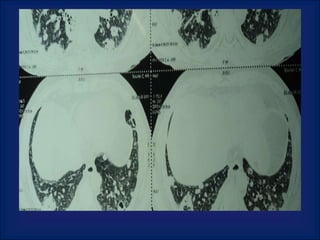
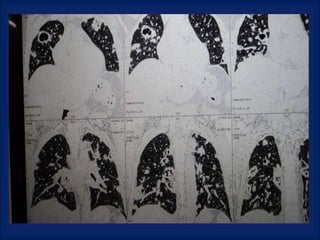
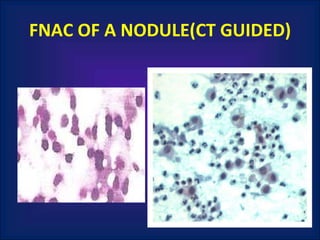
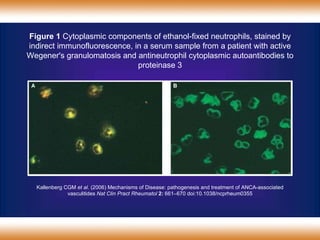
A 38-year-old male smoker presented with swelling all over the body for the past 4 months. Examination revealed pitting pedal edema. Investigations showed elevated ESR, CRP and P-ANCA positivity. CT scan showed multiple cavitary lung lesions. A diagnosis of Wegener's granulomatosis was made based on clinical features, lab investigations and radiological findings.