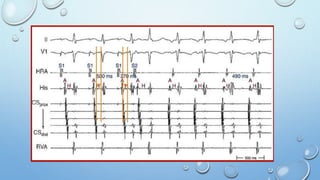
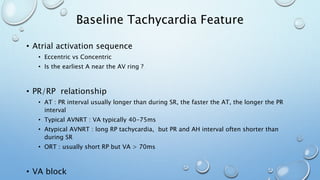
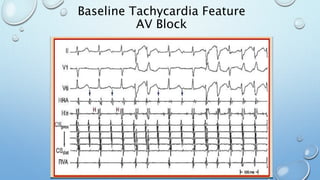
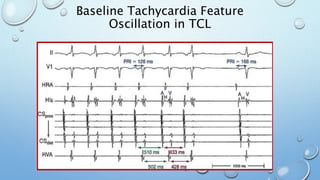
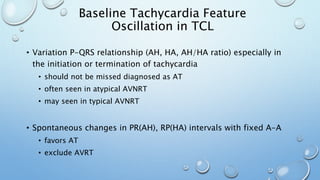
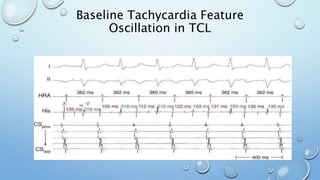
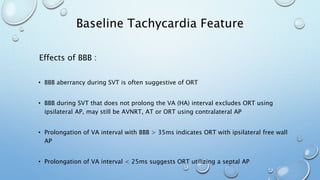
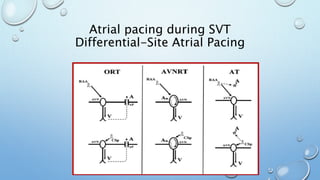
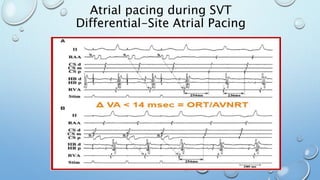
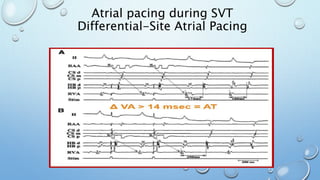
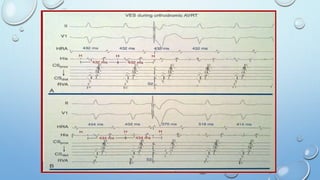
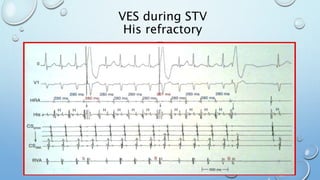
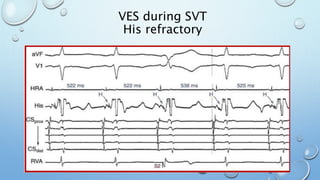
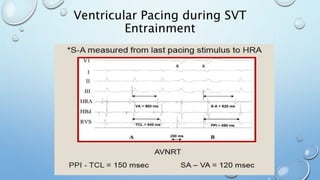
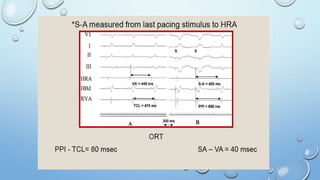
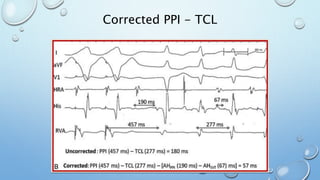
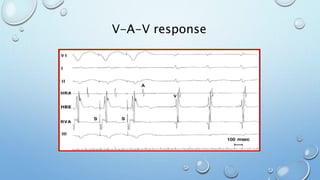
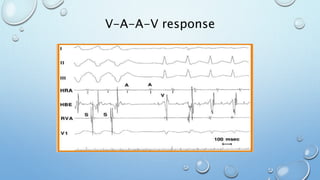
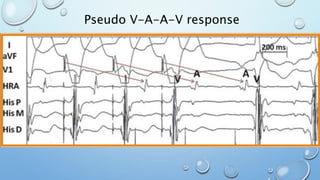
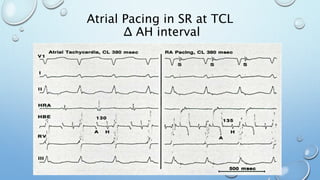
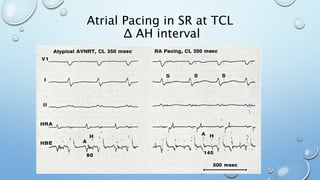
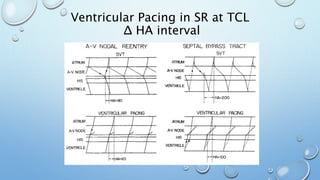
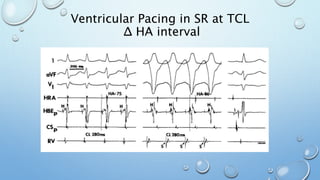
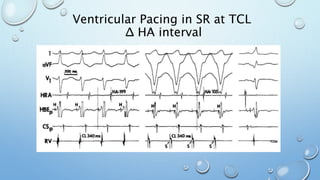
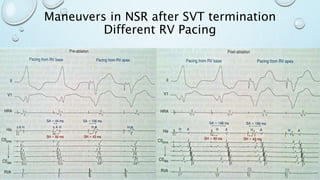
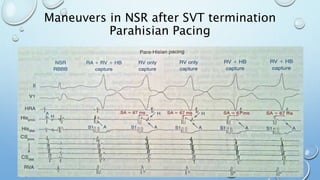
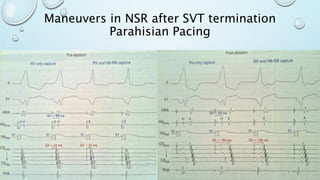
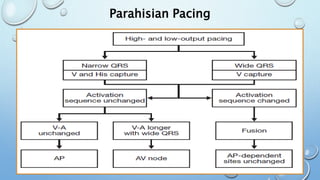
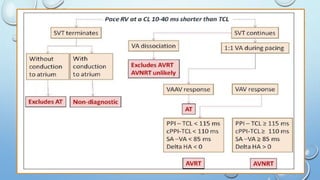
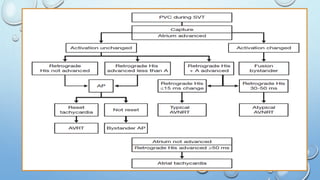
This document outlines techniques for differentiating supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). It discusses diagnostic maneuvers that can be performed during tachycardia and after termination, including induction methods, baseline tachycardia features, and effects of pacing. Key findings that help differentiate atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT), atrioventricular reentry tachycardia (AVRT), and atrial tachycardia include the response to atrial and ventricular extrastimuli, entrainment properties, delta AH/HA intervals with pacing, presence of AV or VA block, and retrograde atrial activation patterns. Parahisian pacing can also provide useful information by