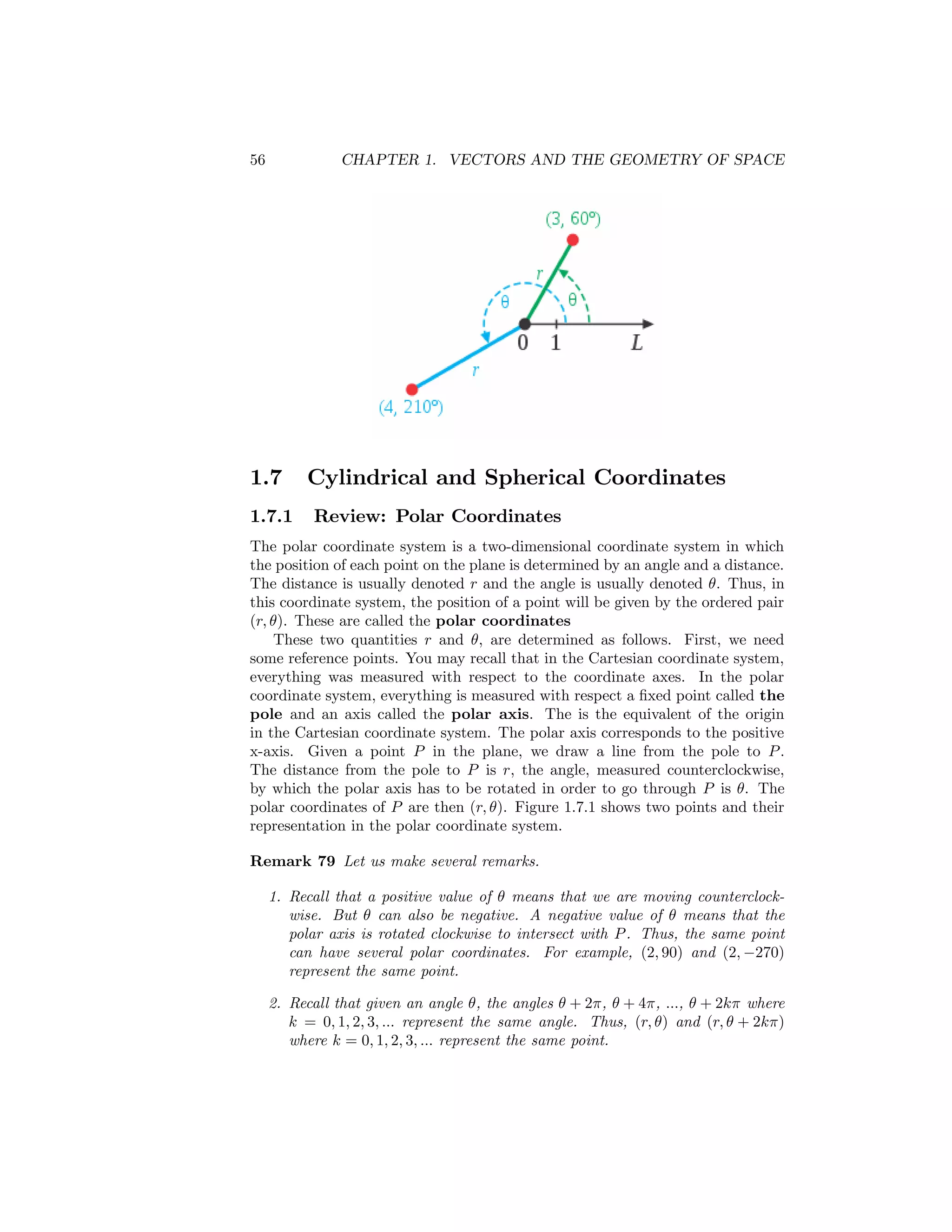
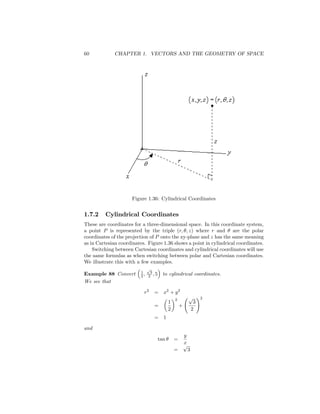
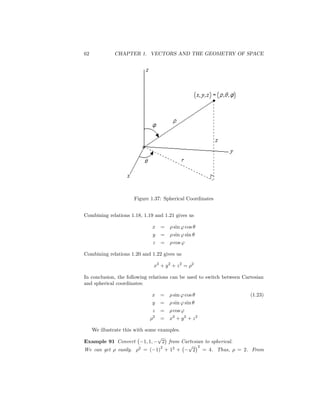
This document discusses different coordinate systems used to describe points in 2D and 3D space, including polar, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. It provides the key formulas for converting between Cartesian and these other coordinate systems. Examples are given of converting points and equations between the different coordinate systems. The key points are that polar coordinates use an angle and distance to specify a 2D point, cylindrical coordinates extend this to 3D using a z-value, and spherical coordinates specify a 3D point using a distance from the origin, an angle, and an azimuthal angle.