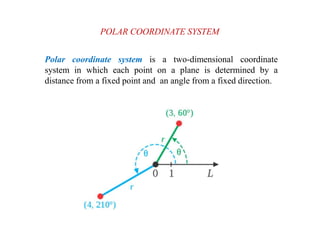
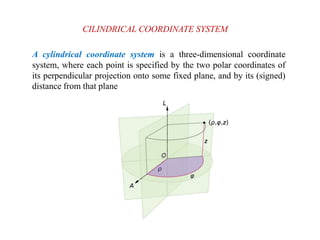
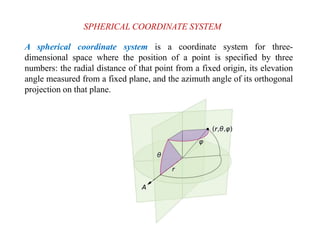
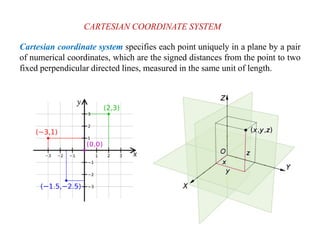
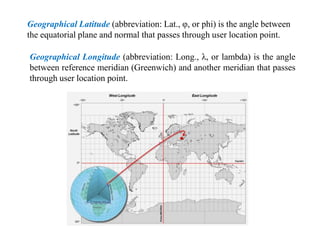
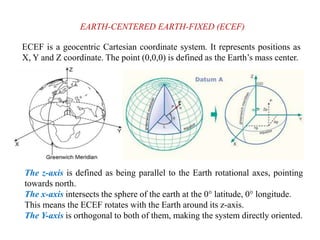
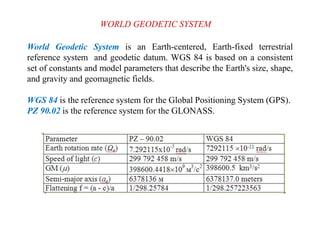
This document discusses various coordinate systems used to define positions in satellite navigation. It describes geocentric systems like ECEF and ECI that use the Earth's center as the origin, as well as topocentric systems that use the observer's location. It also discusses spherical coordinate systems that define positions using radial distance, elevation and azimuth angles. Key systems covered include WGS-84 used in GPS and PZ-90.02 used in GLONASS. While definitions are close, realized coordinates between the two systems can differ by up to 0.5 meters.