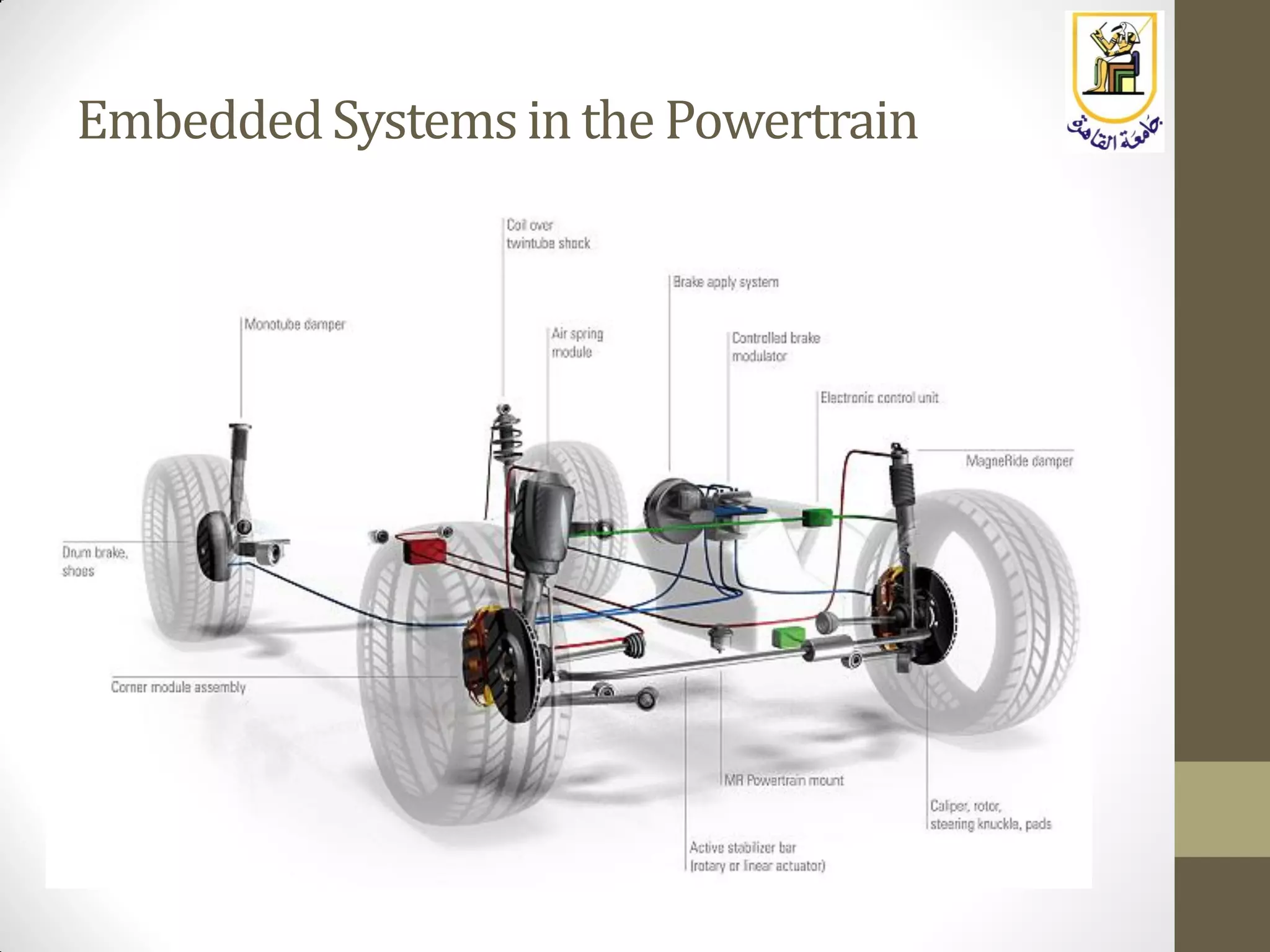
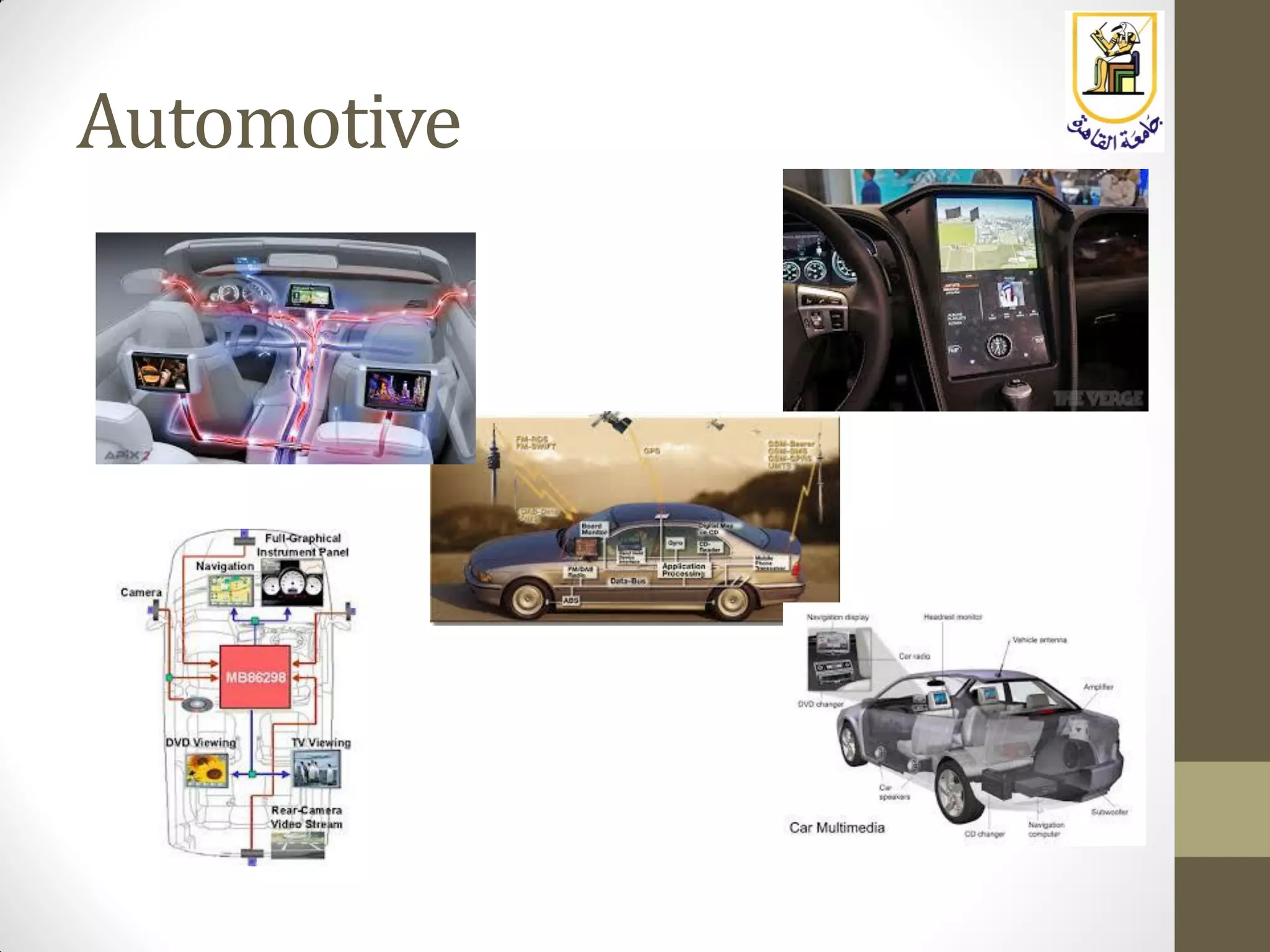
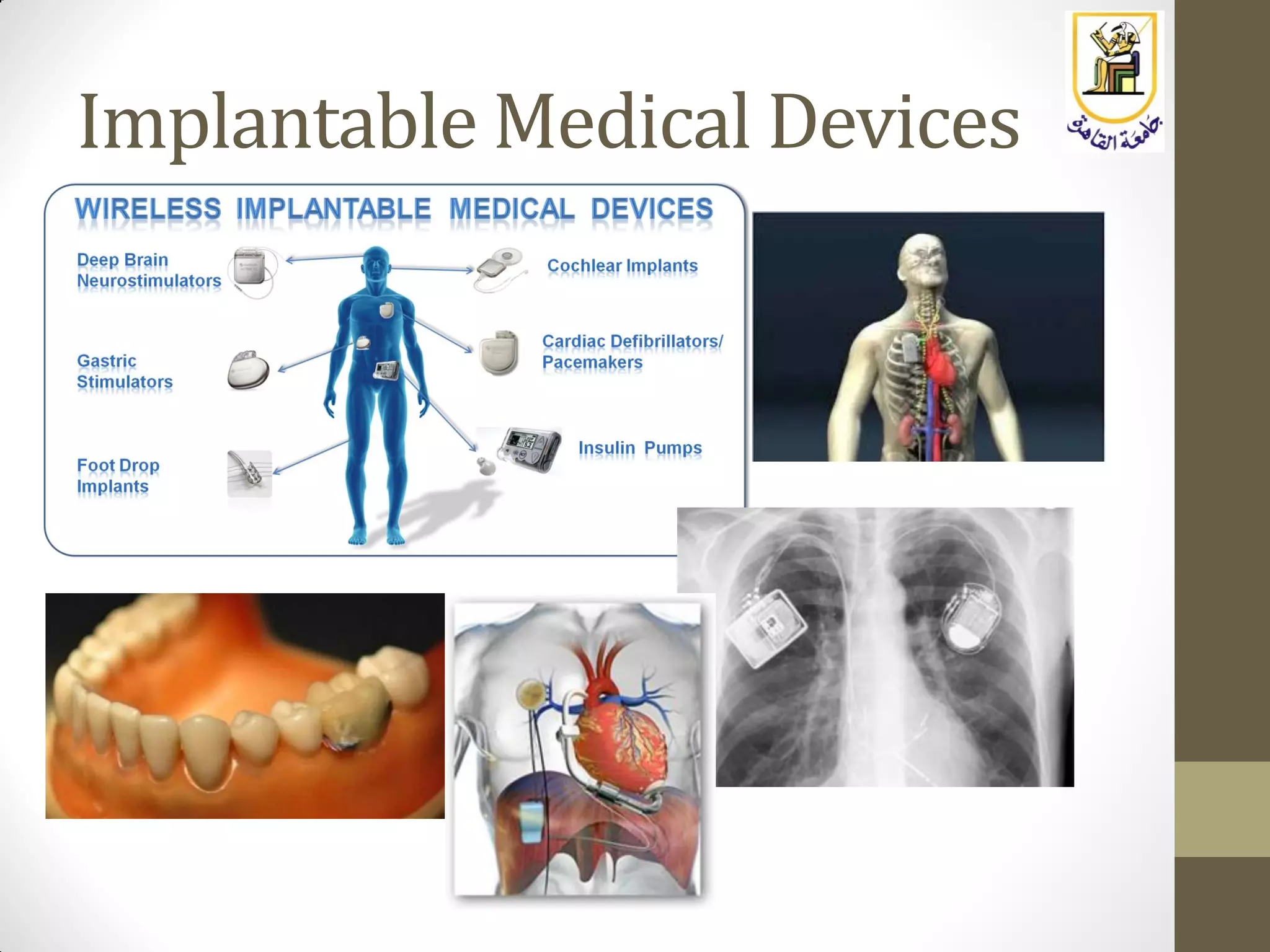
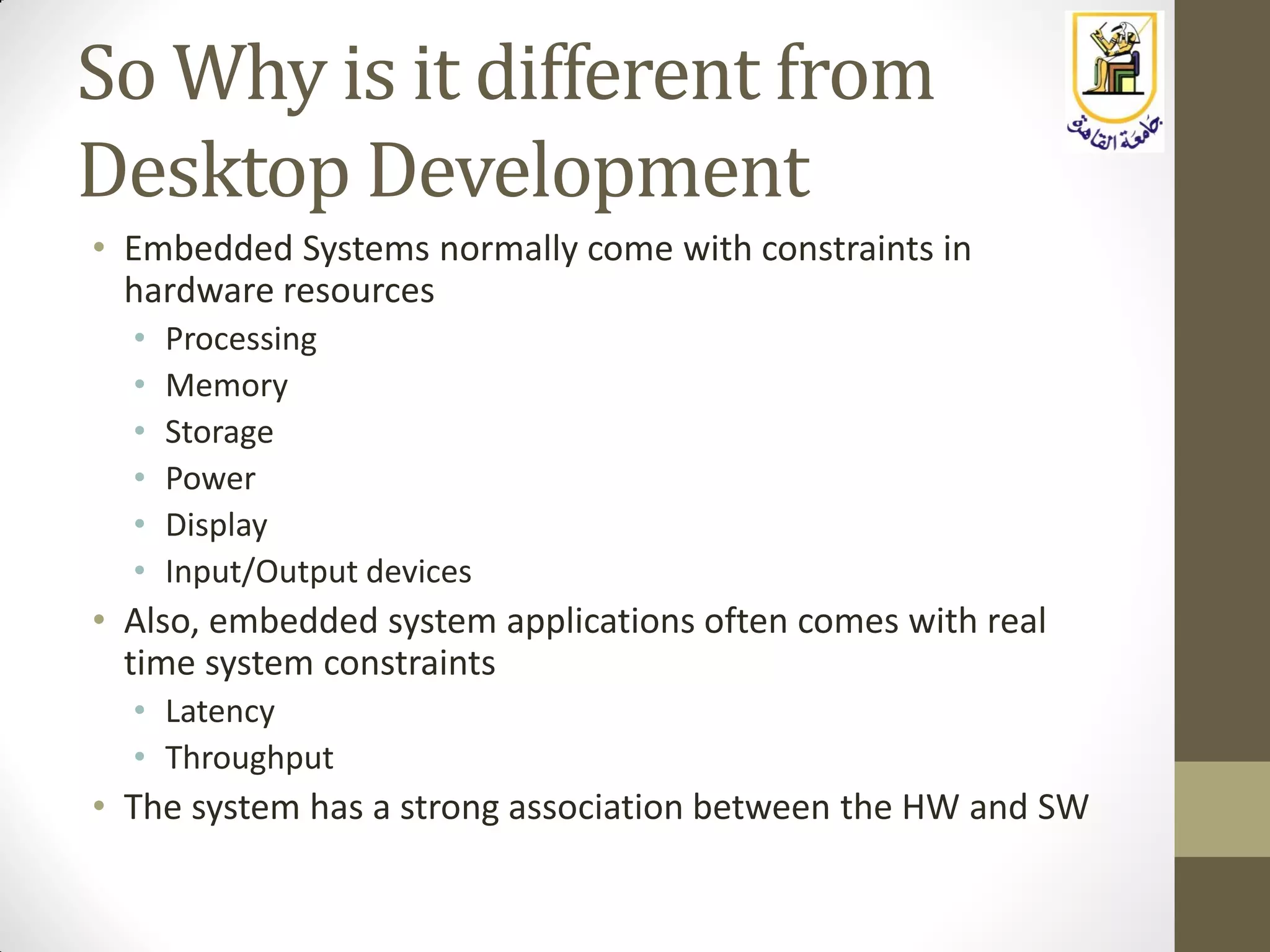
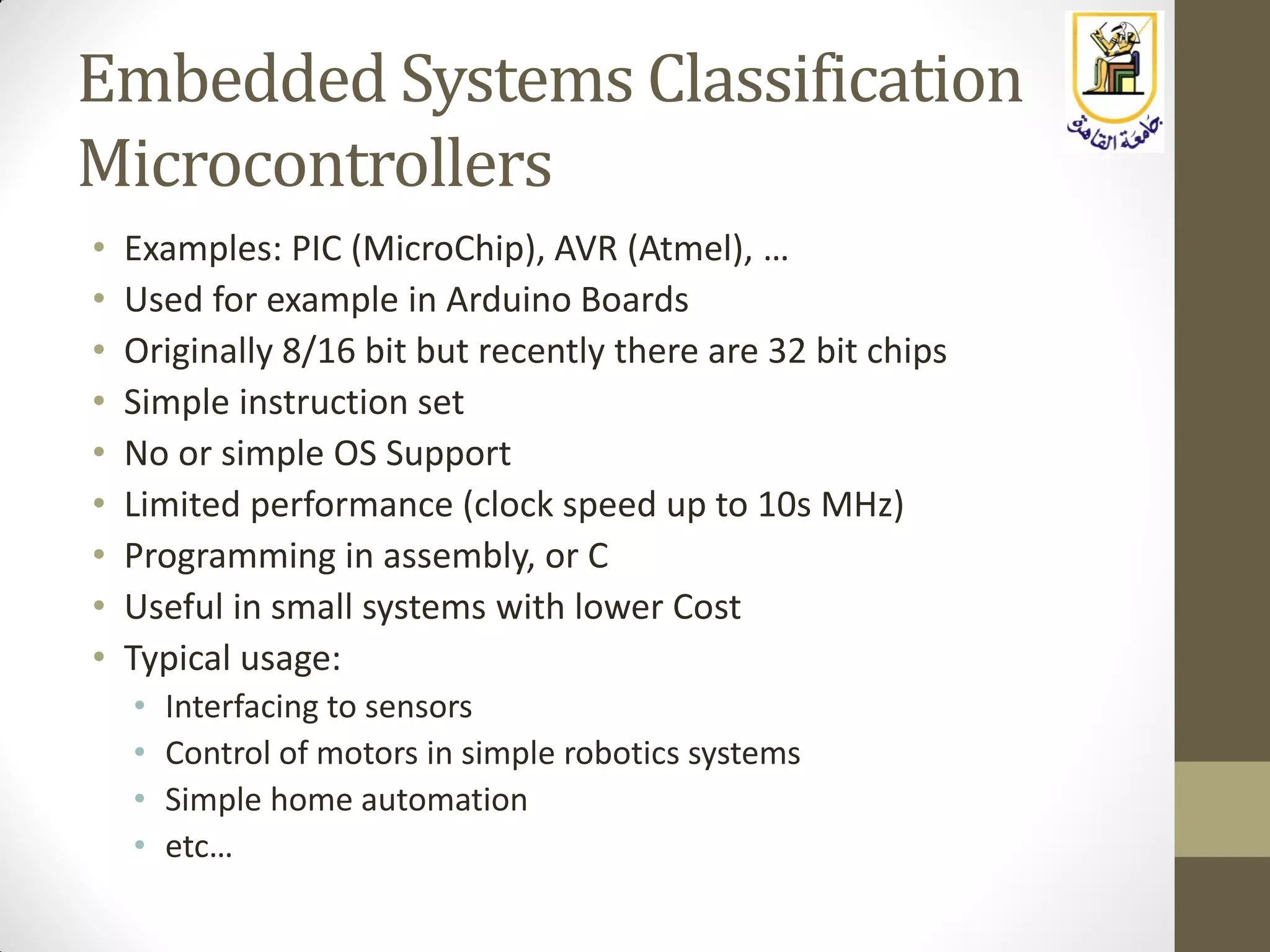
The document provides an overview of embedded systems, highlighting their distinction from traditional computer systems and detailing specific examples such as phones, cars, and medical devices. It discusses the constraints developers face, including hardware limitations and real-time system requirements, and classifies embedded systems into microcontroller and microprocessor families. The focus of the course will be on microprocessor-based systems, particularly using the Raspberry Pi, enabling more advanced projects and applications.