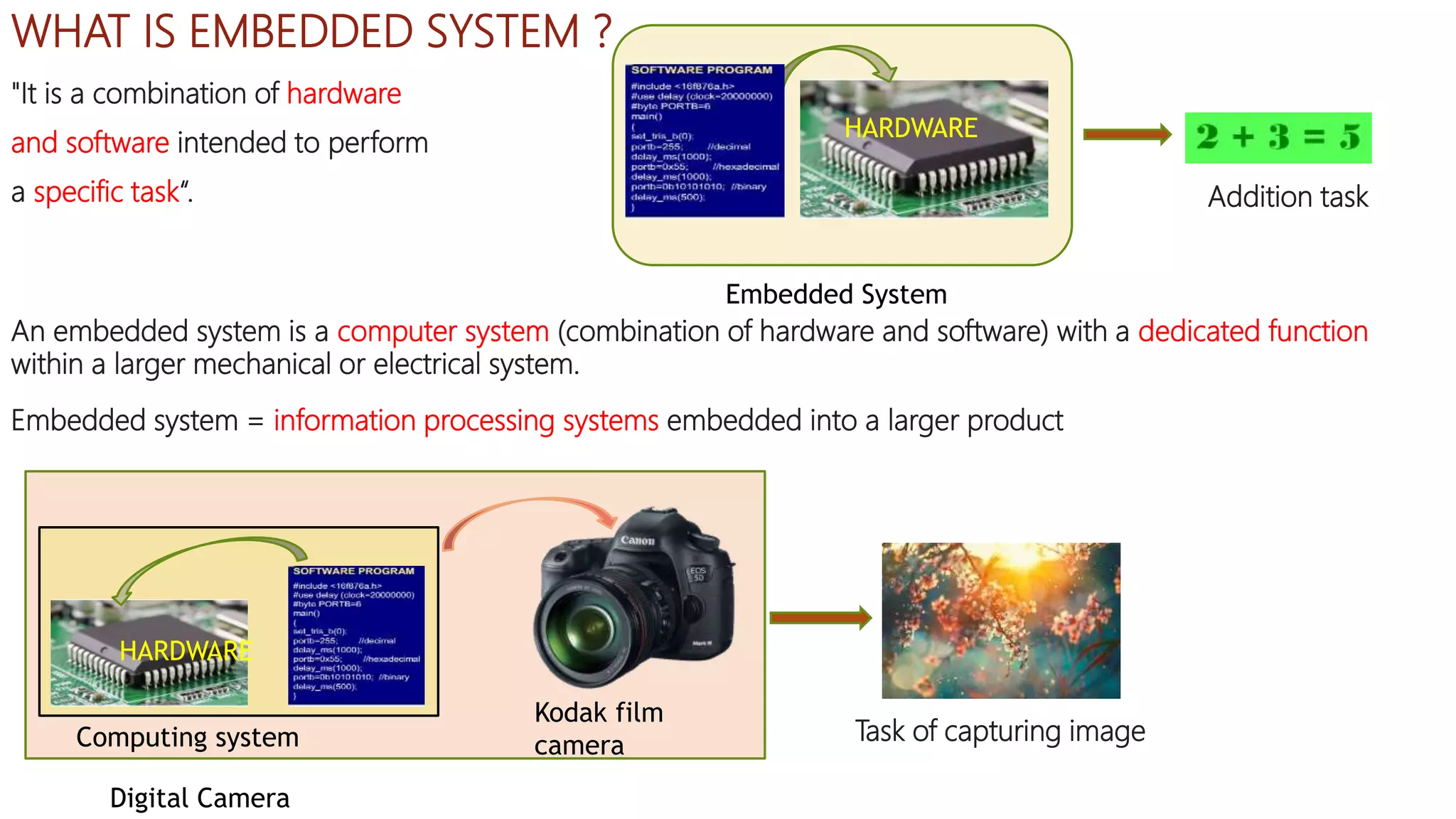
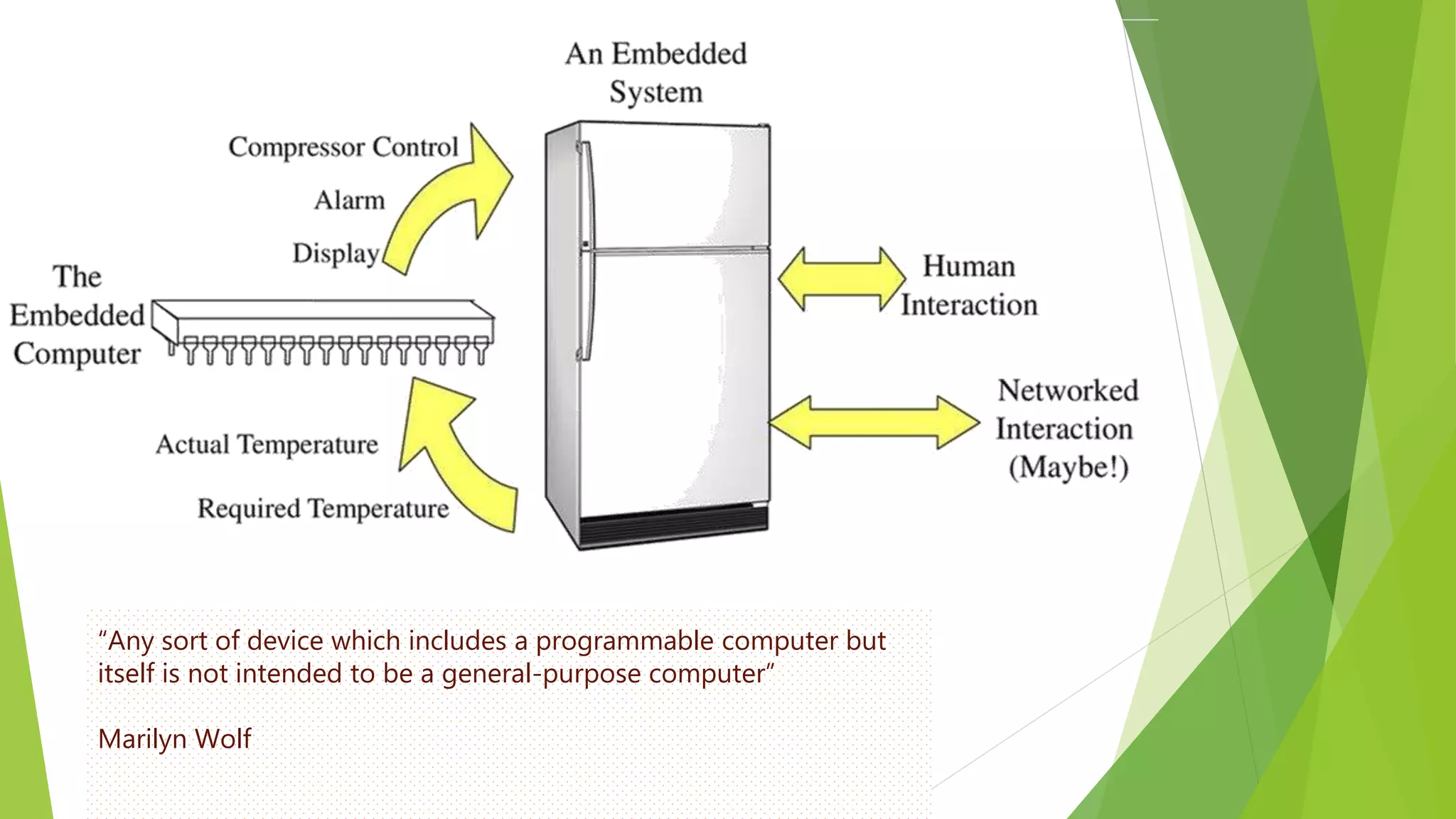
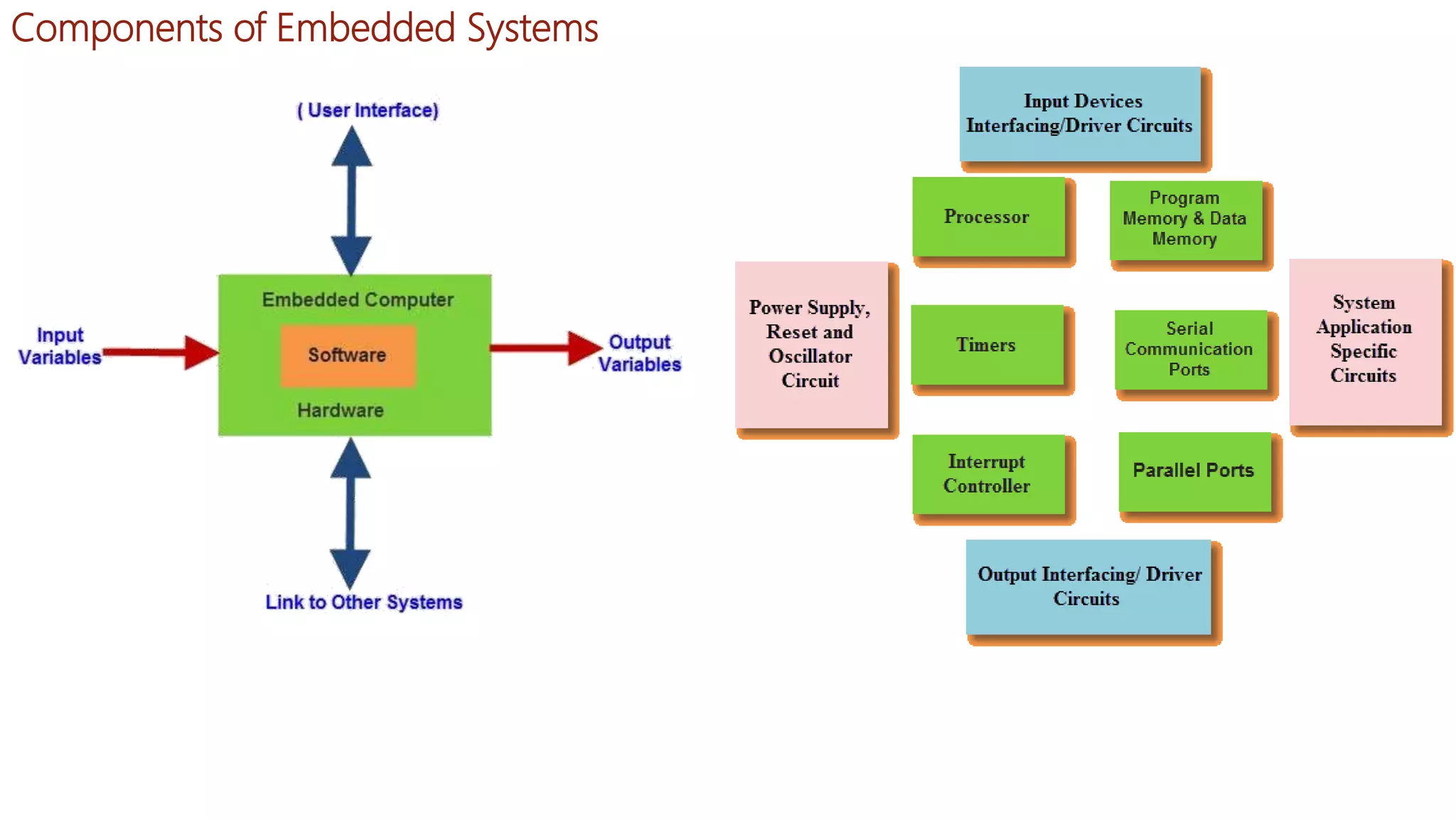
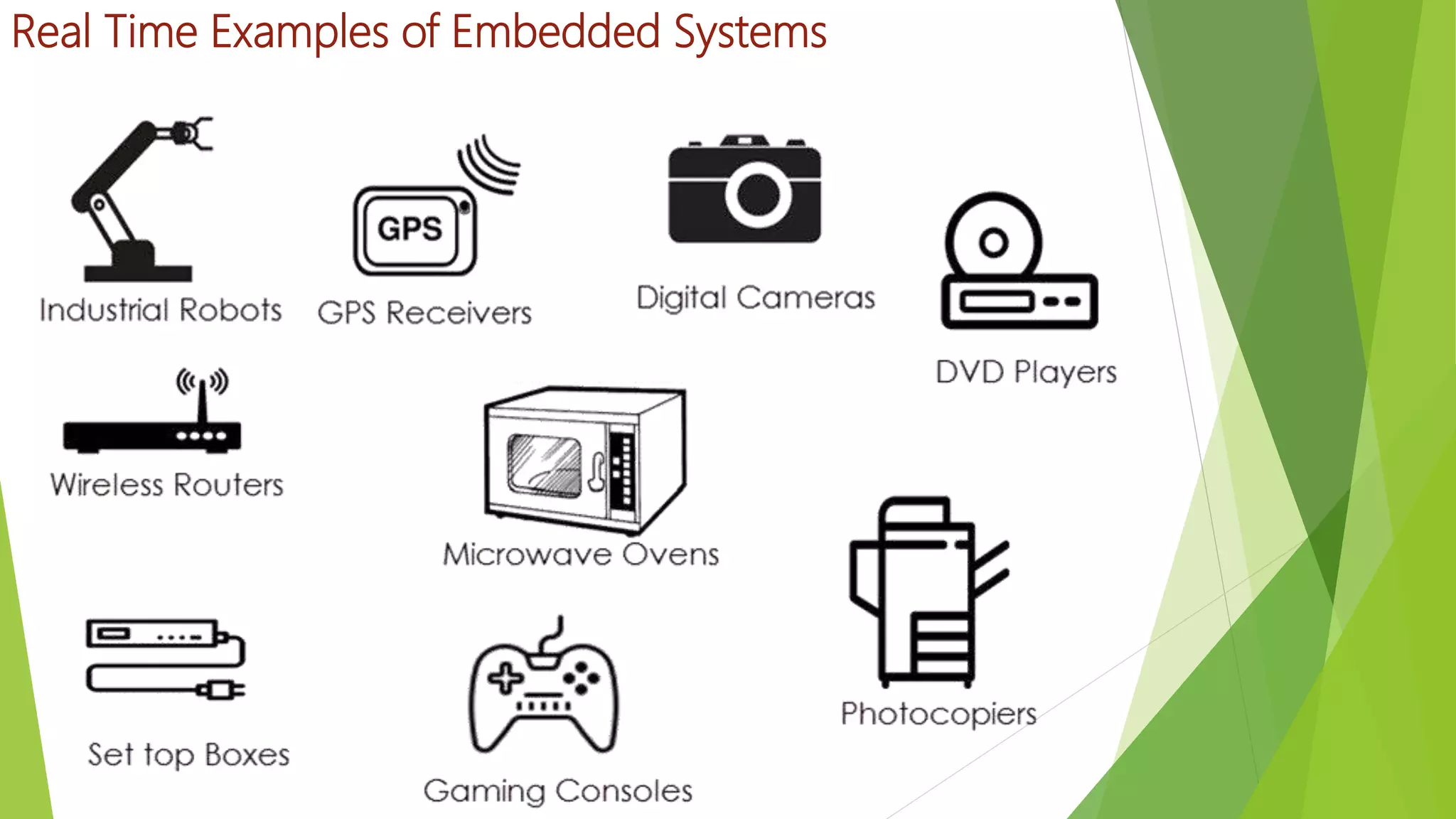
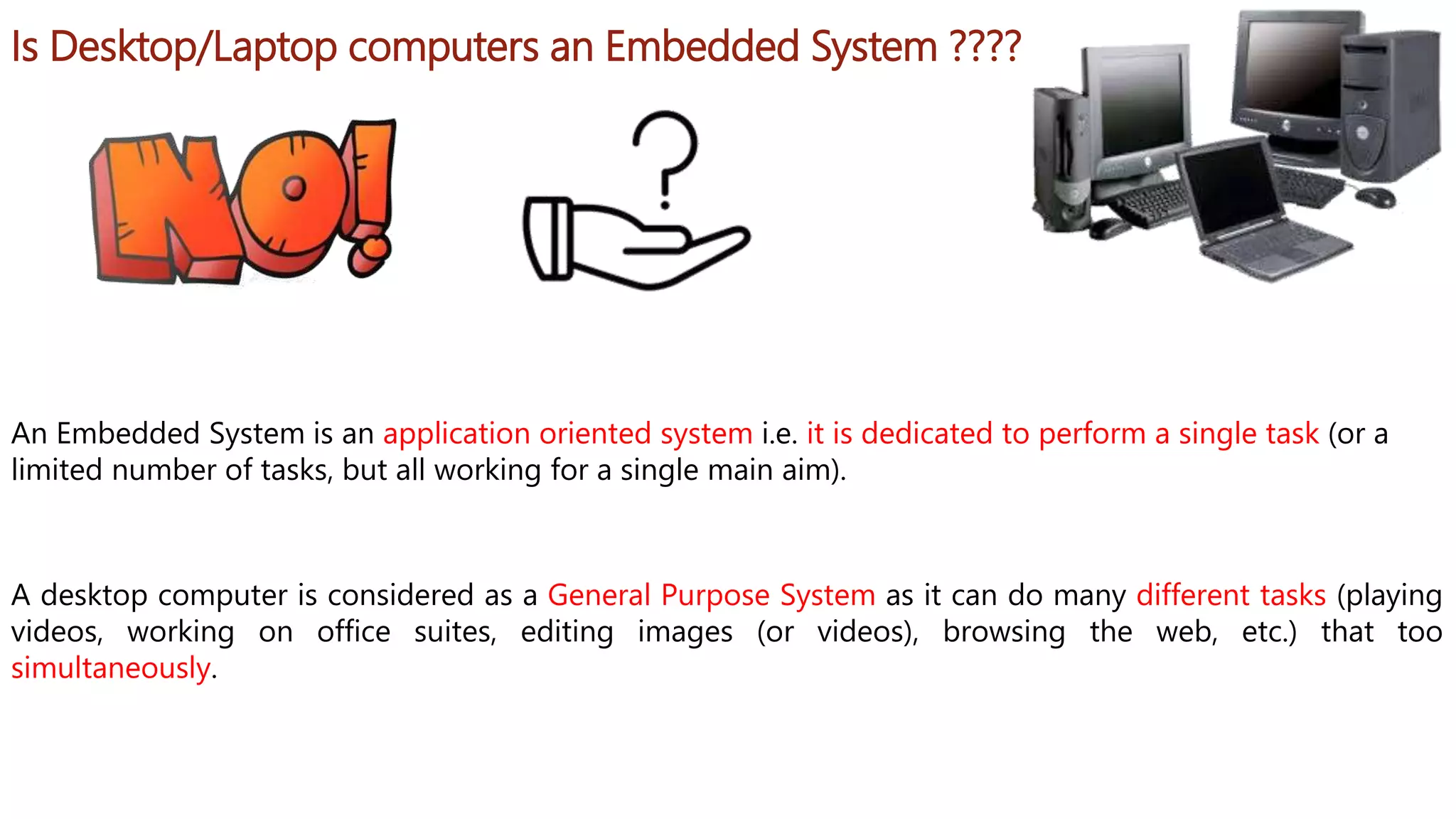
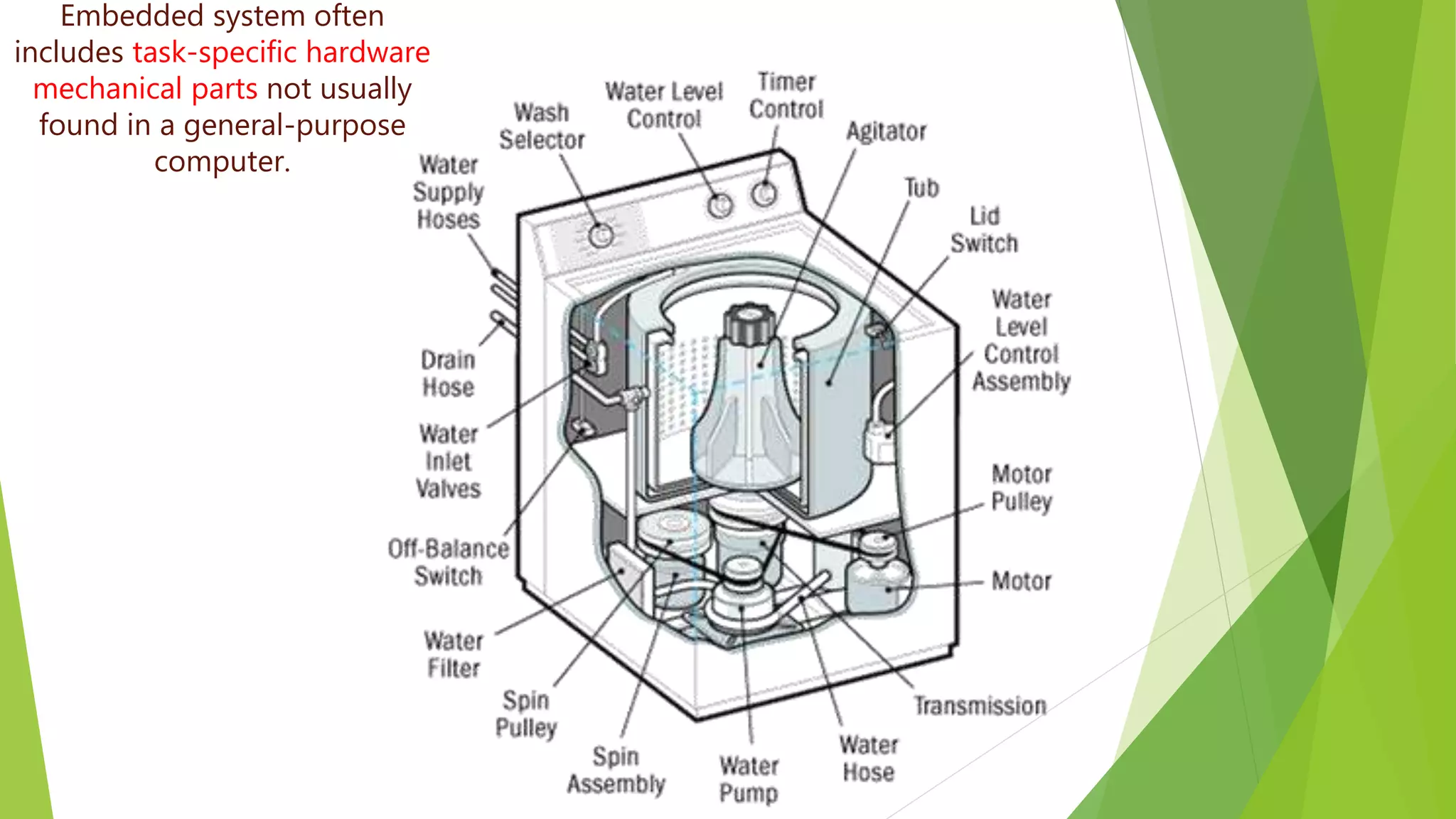
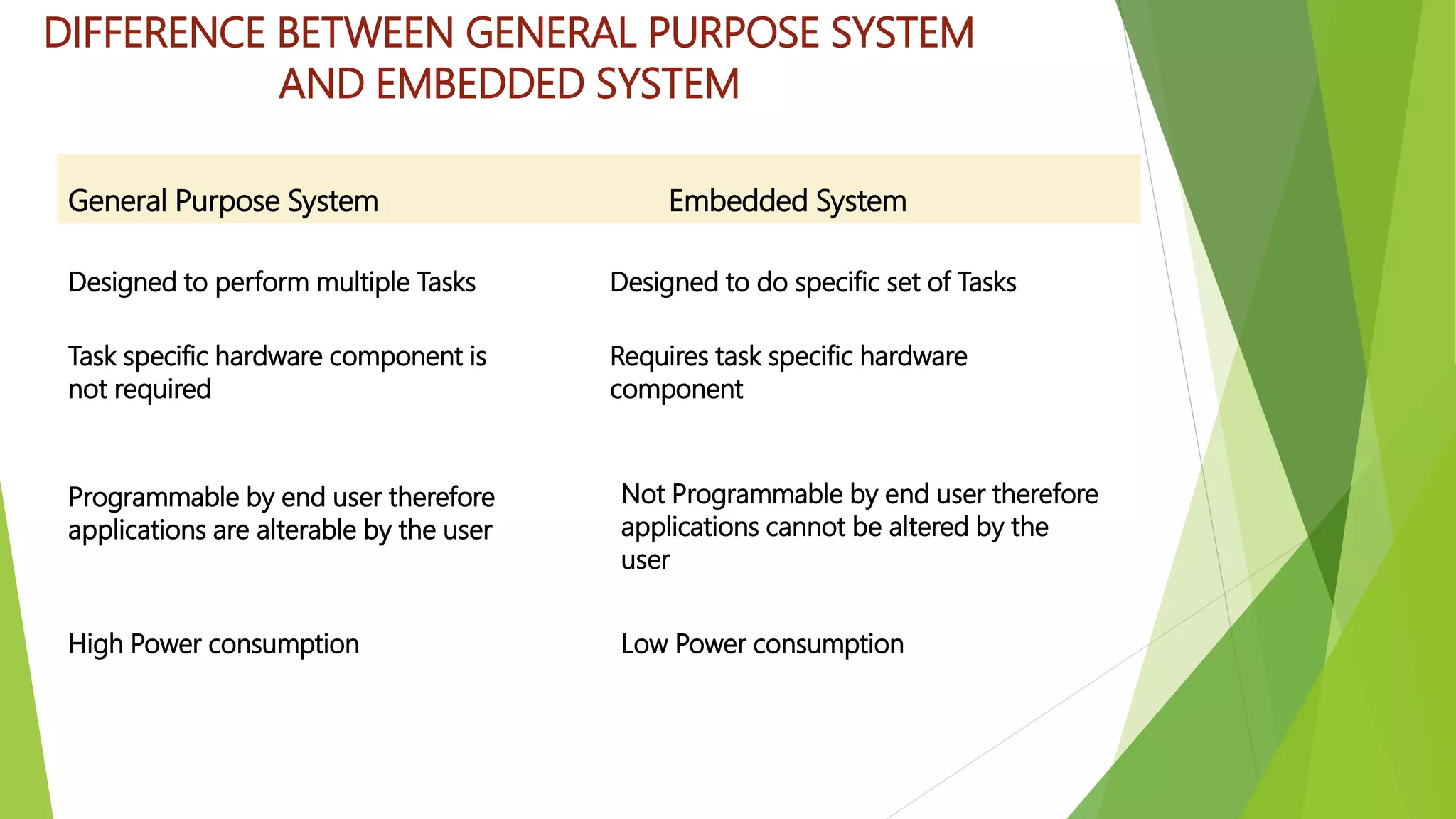
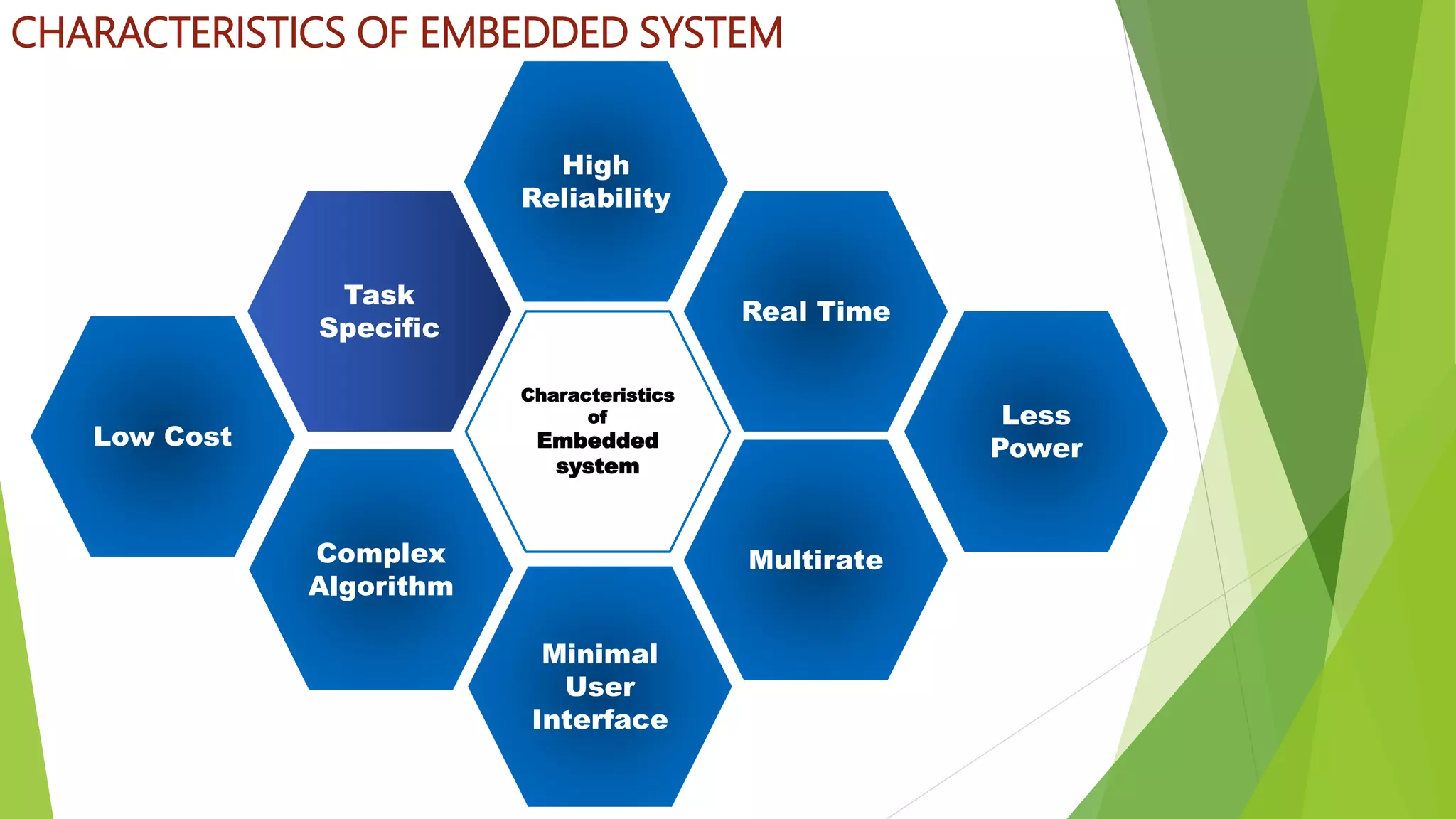
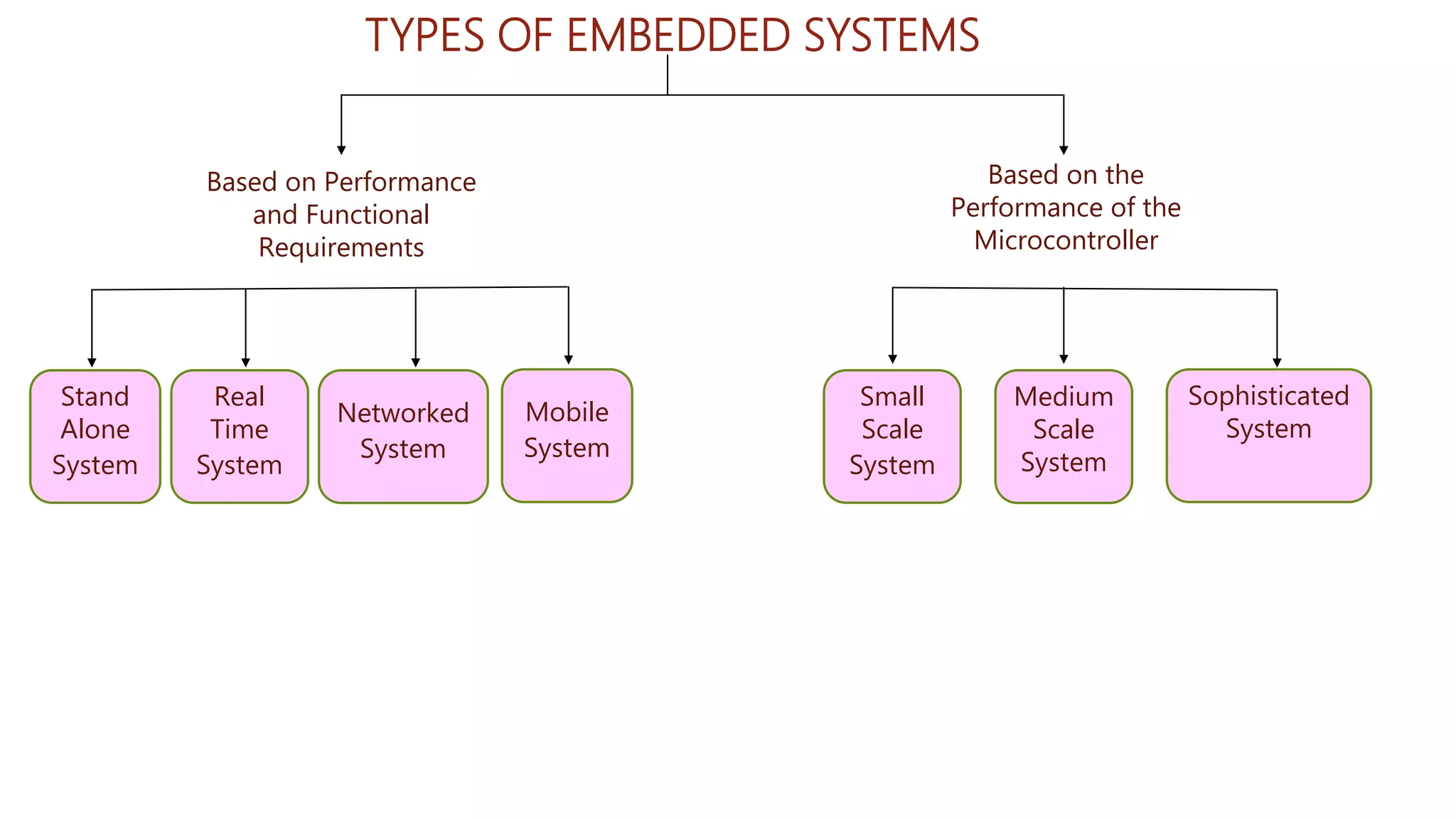
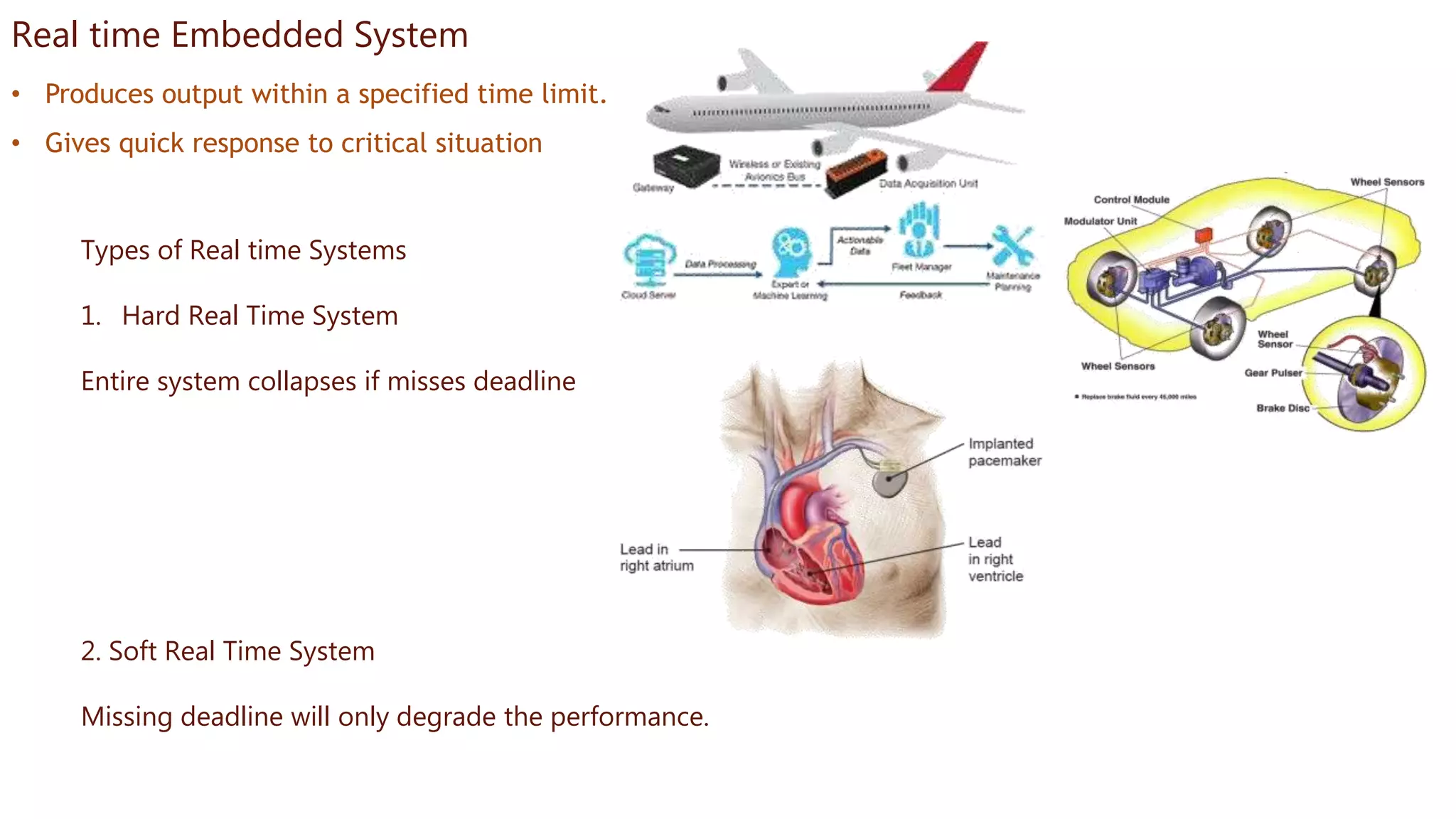
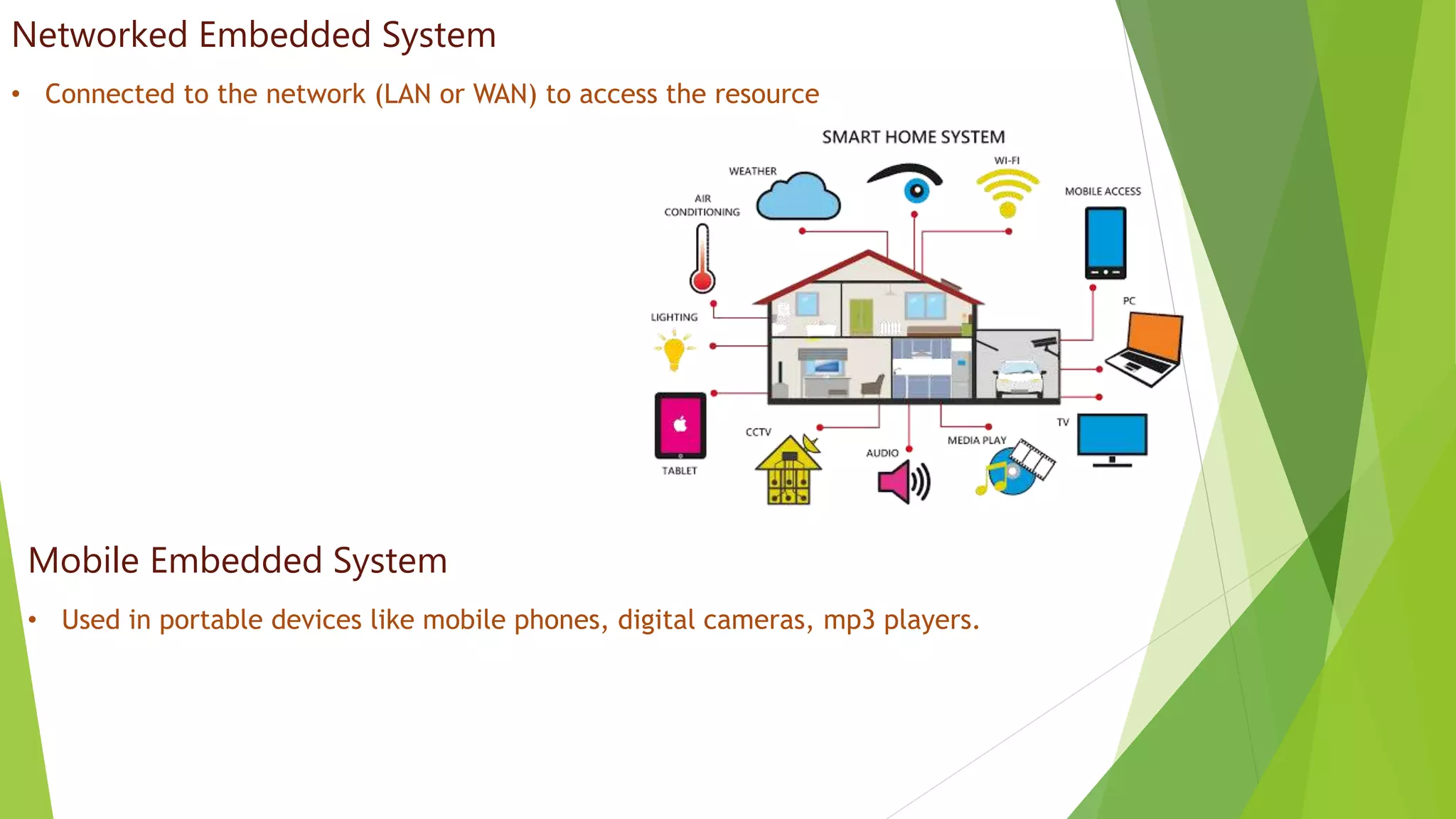
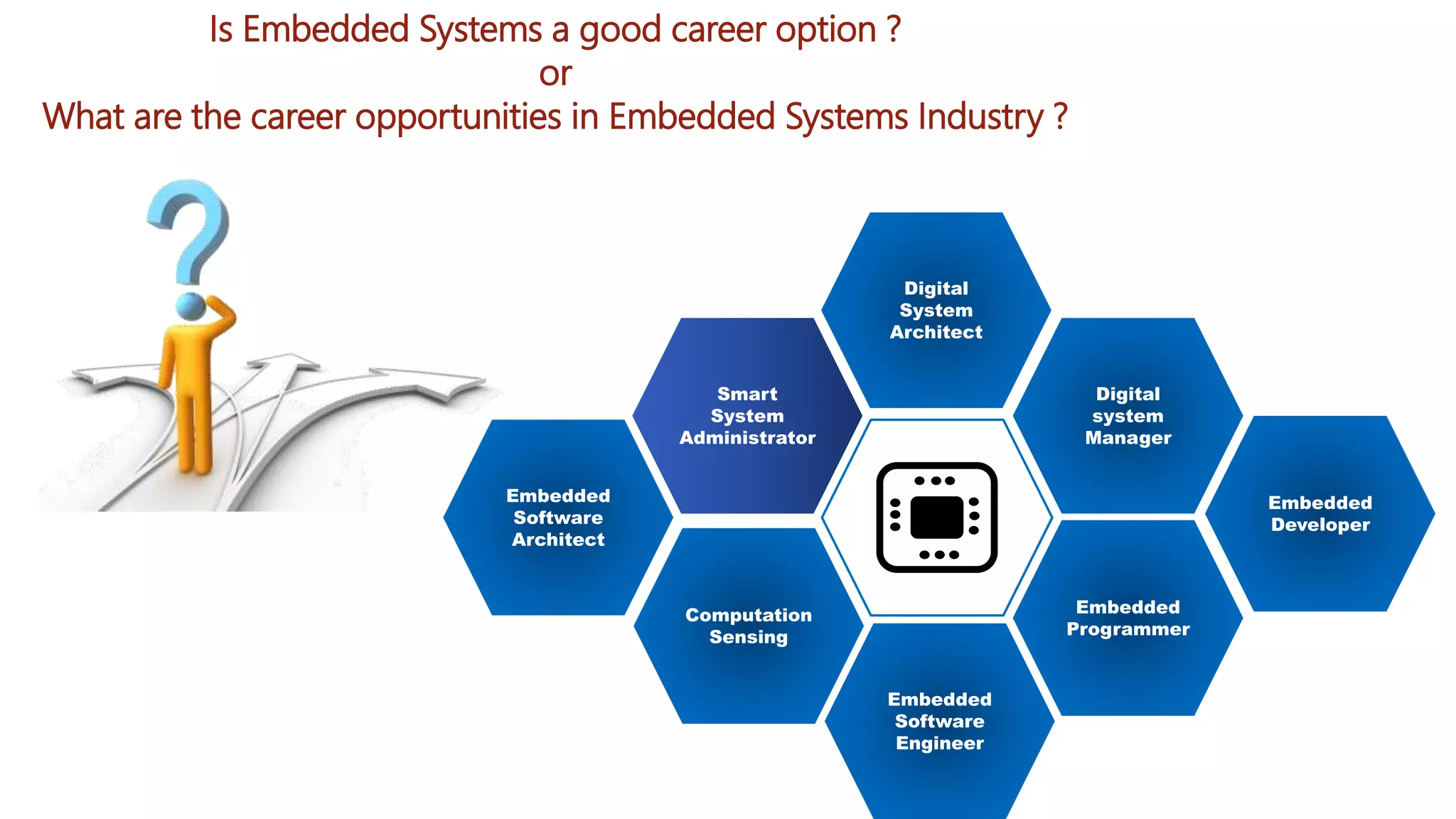
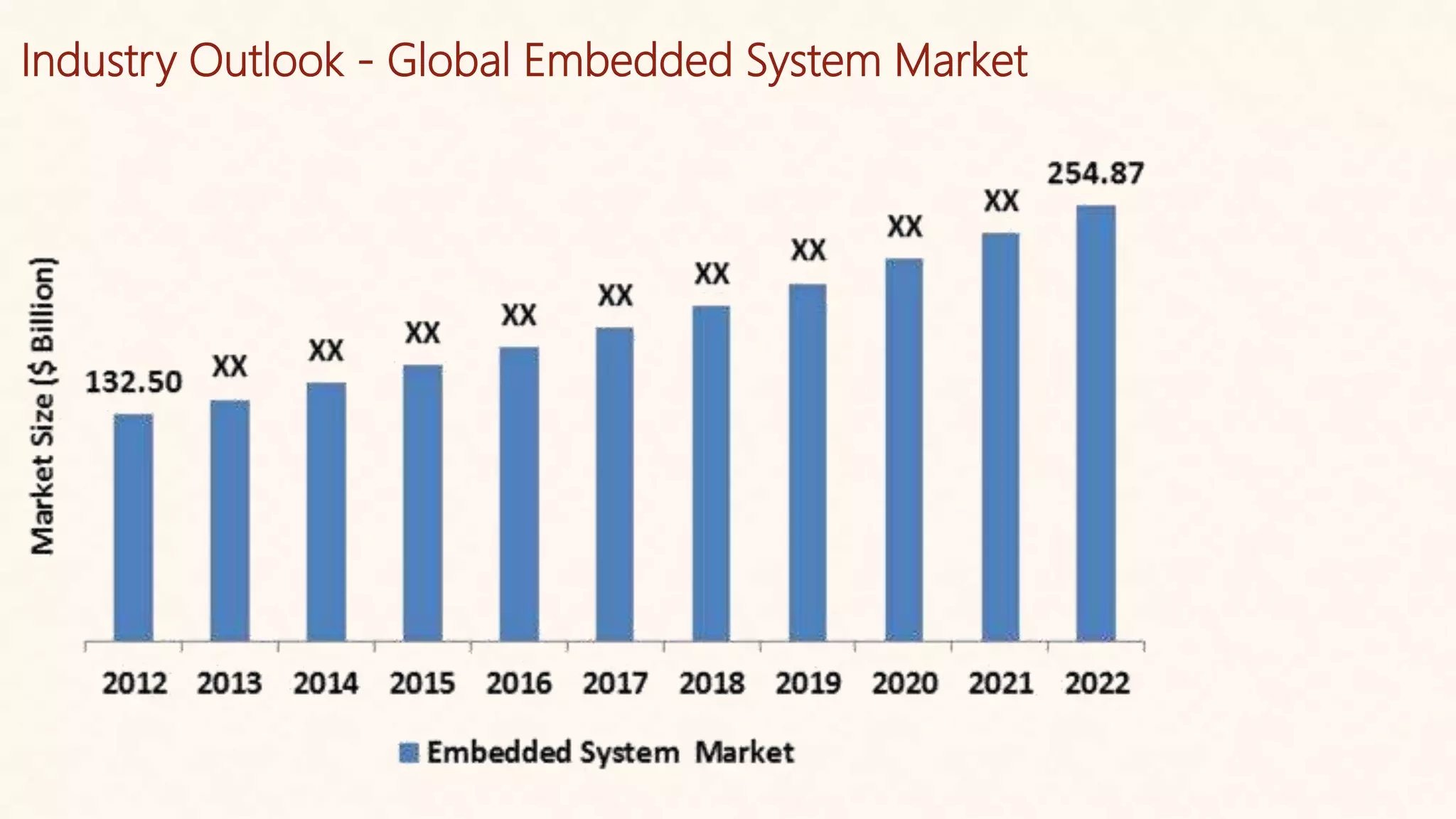
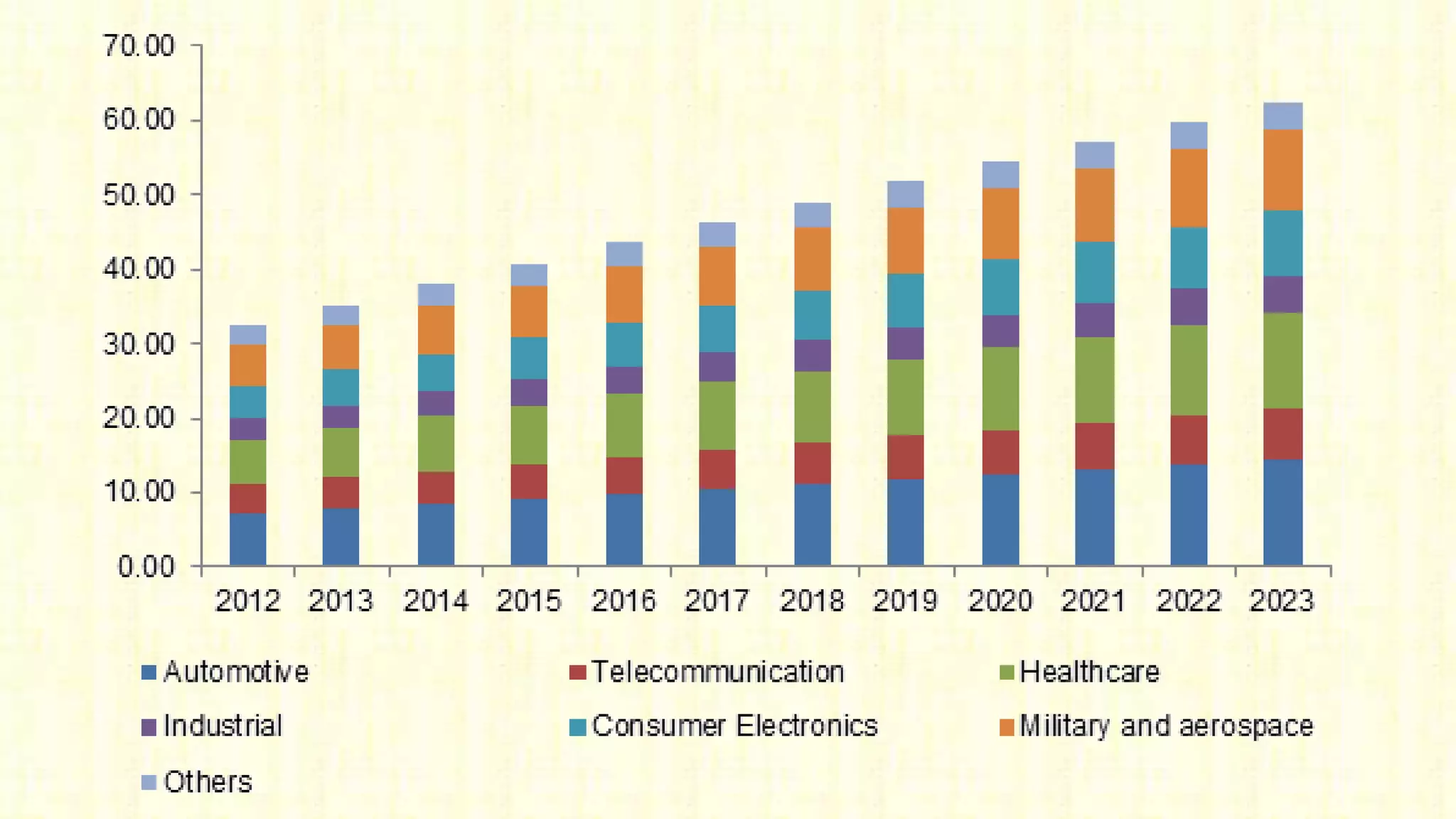
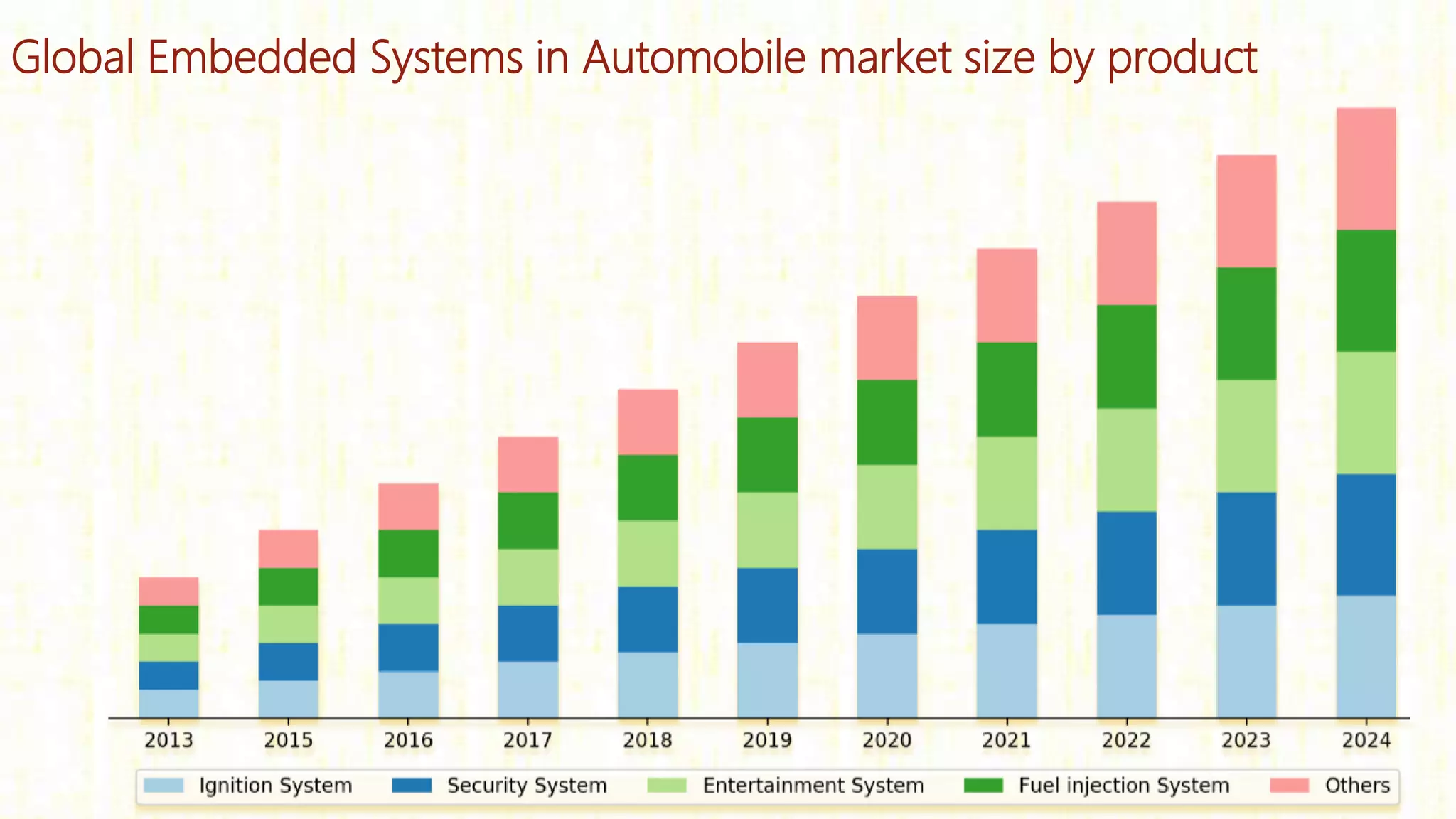
Embedded systems are dedicated hardware and software combinations designed to perform specific tasks within larger mechanical or electrical systems, distinct from general purpose systems which handle multiple tasks. They feature characteristics such as high reliability, low power consumption, and minimal user interfaces, with various types including real-time, standalone, and networked systems. Career opportunities in this field include roles like embedded software engineers and hardware designers, requiring skills in electronic circuit design, embedded programming, and teamwork.