This document provides an overview of computer hardware and software topics, covering:
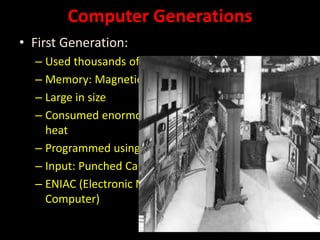
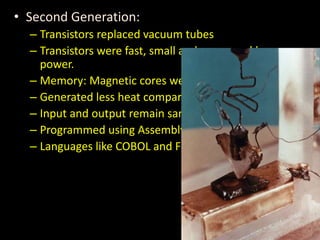
1. The background and generations of computers from the abacus to modern devices.
2. The types of computers based on size from supercomputers to smartphones.
3. Key components inside a computer like the CPU, memory, ports, and input/output devices.
4. How computers are connected in networks and different network topologies.
5. The different types of software including system software that manages hardware and application software for specific tasks.