1. The document discusses coordinate systems which are used to reference locations on Earth through the use of latitude, longitude, and elevation data.
2. It provides background on different types of coordinate systems and their components before describing a procedure to collect elevation data at various points.
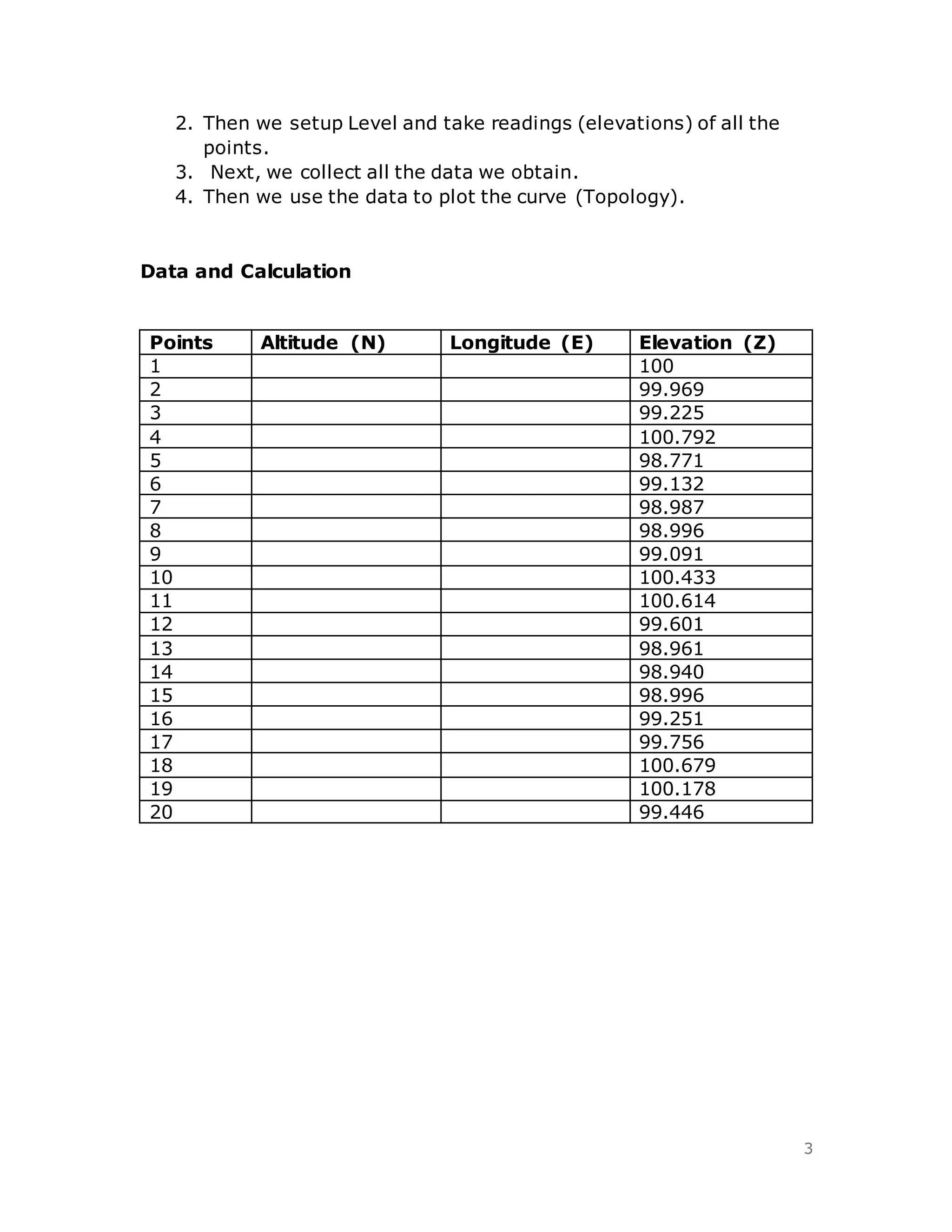
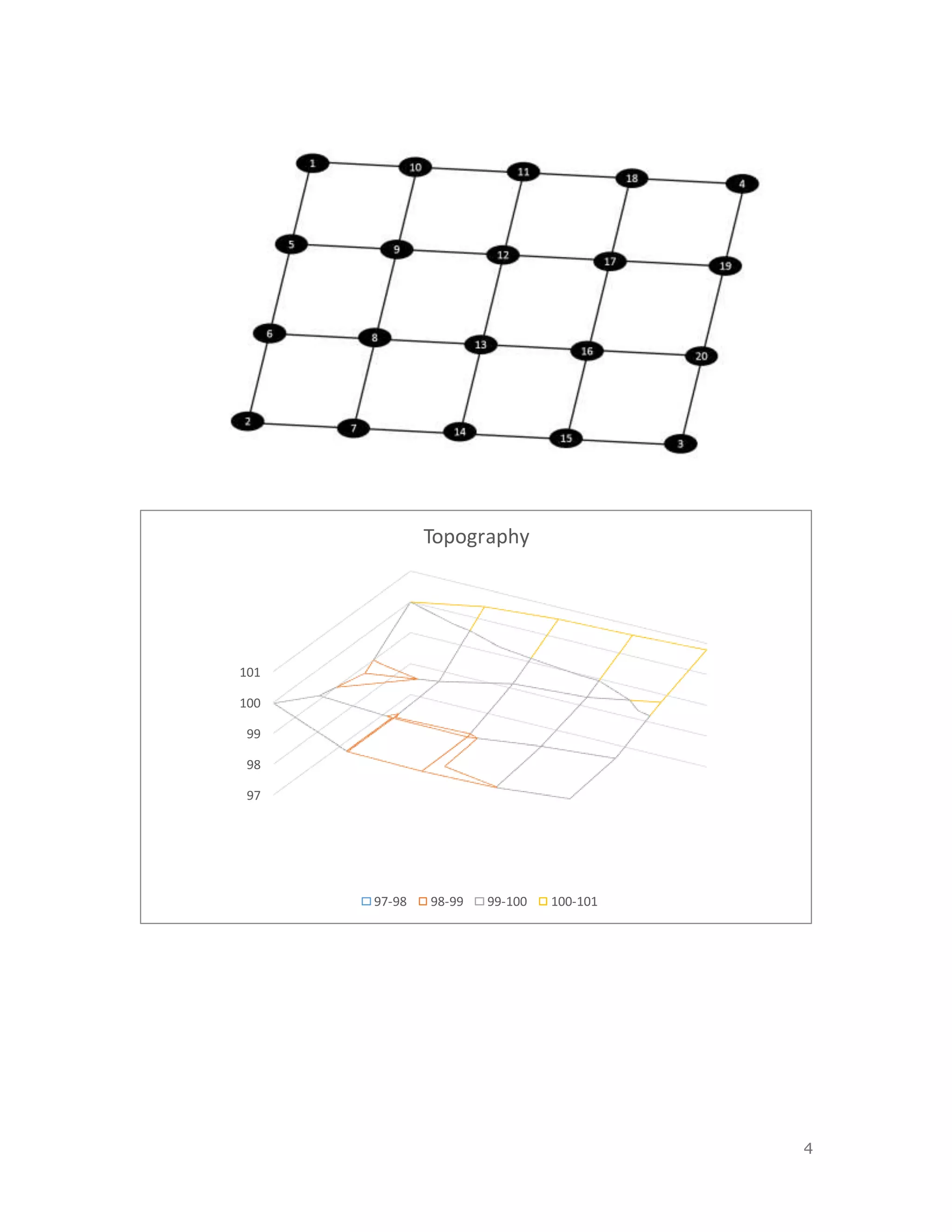
3. The results section plots the collected elevation data to sketch the topology of the area.