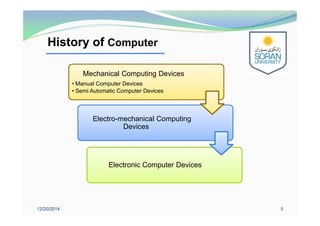
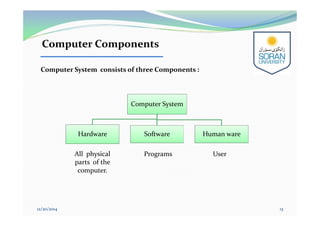
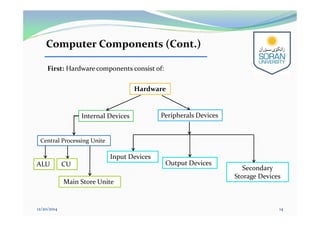
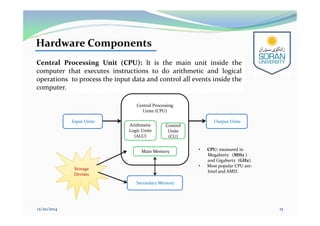
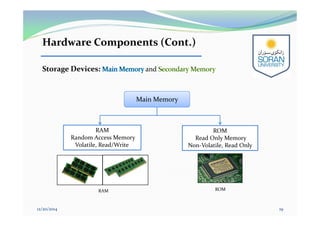
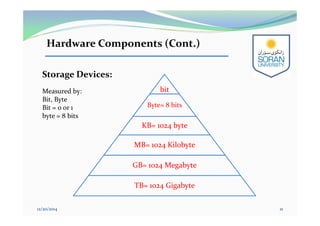
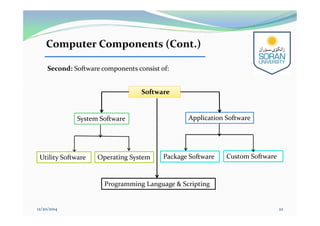
This document provides an overview of computing for engineering. It discusses the history of computers from early mechanical devices to modern electronic computers. It also covers the characteristics, components, and classification of computers. The four main generations of computers are described based on the technology used. The components of a computer system include hardware, software, and humanware. Hardware consists of the central processing unit and various input/output and storage devices. Software includes operating systems, applications, and programming languages.