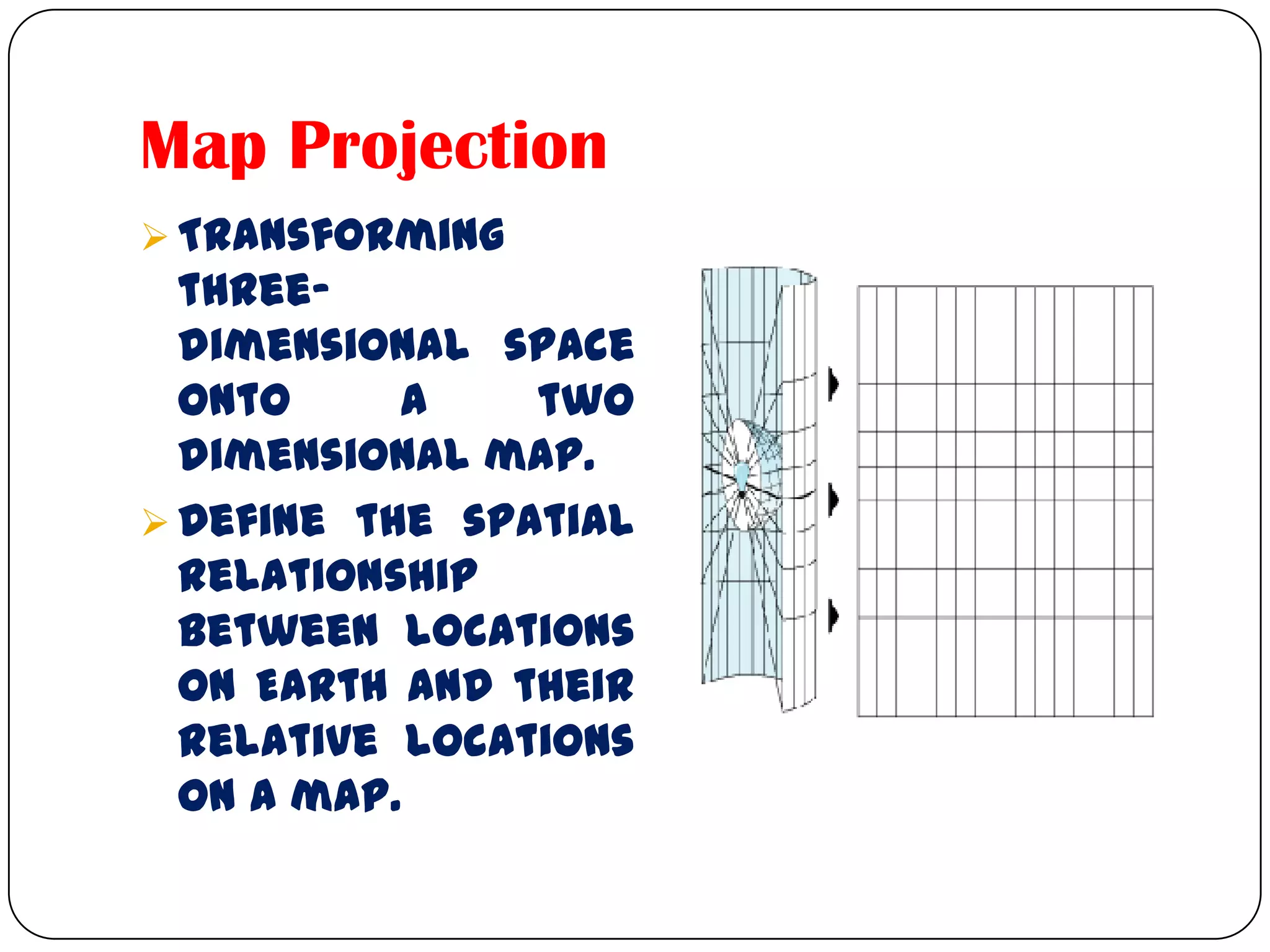
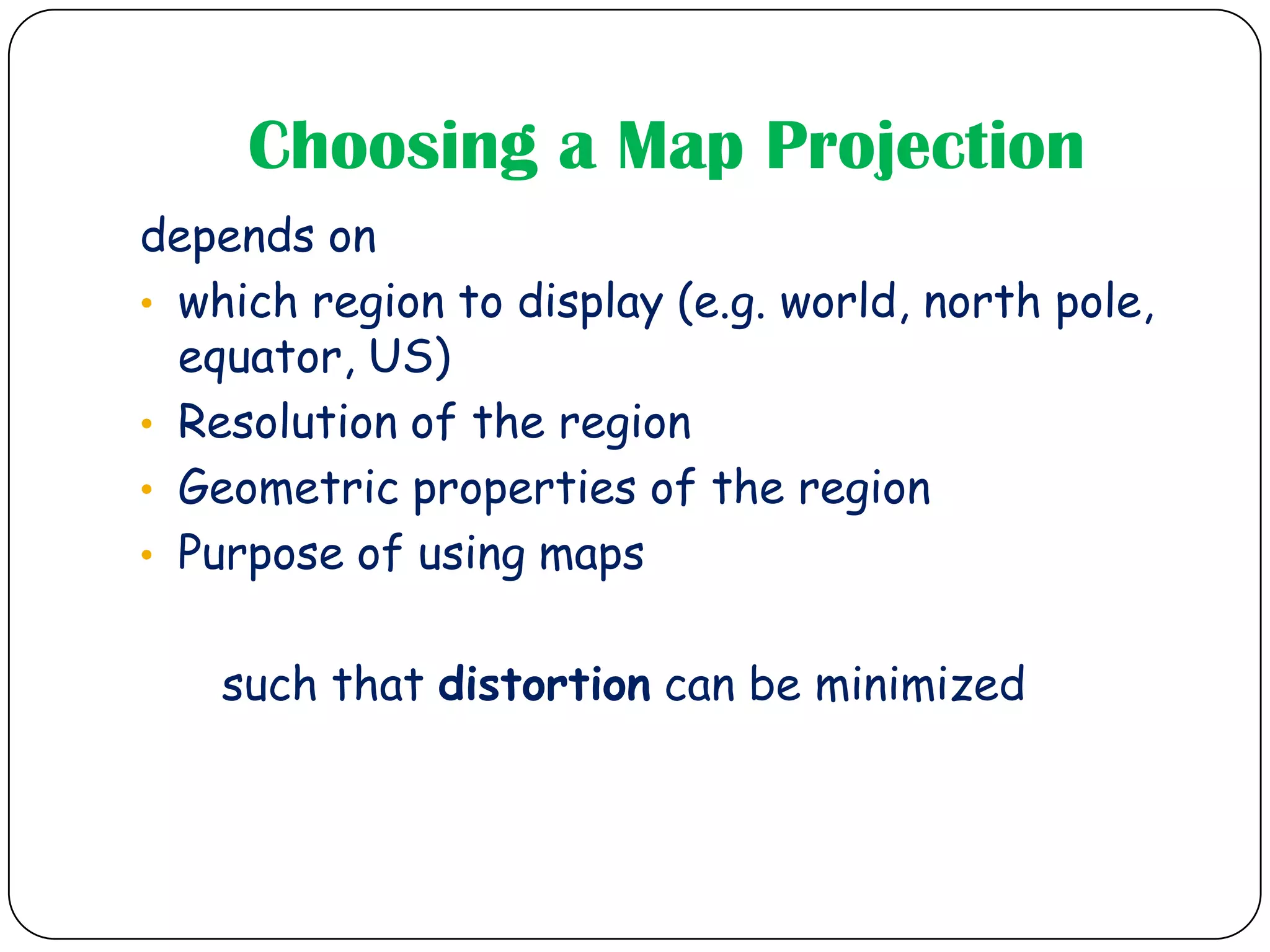
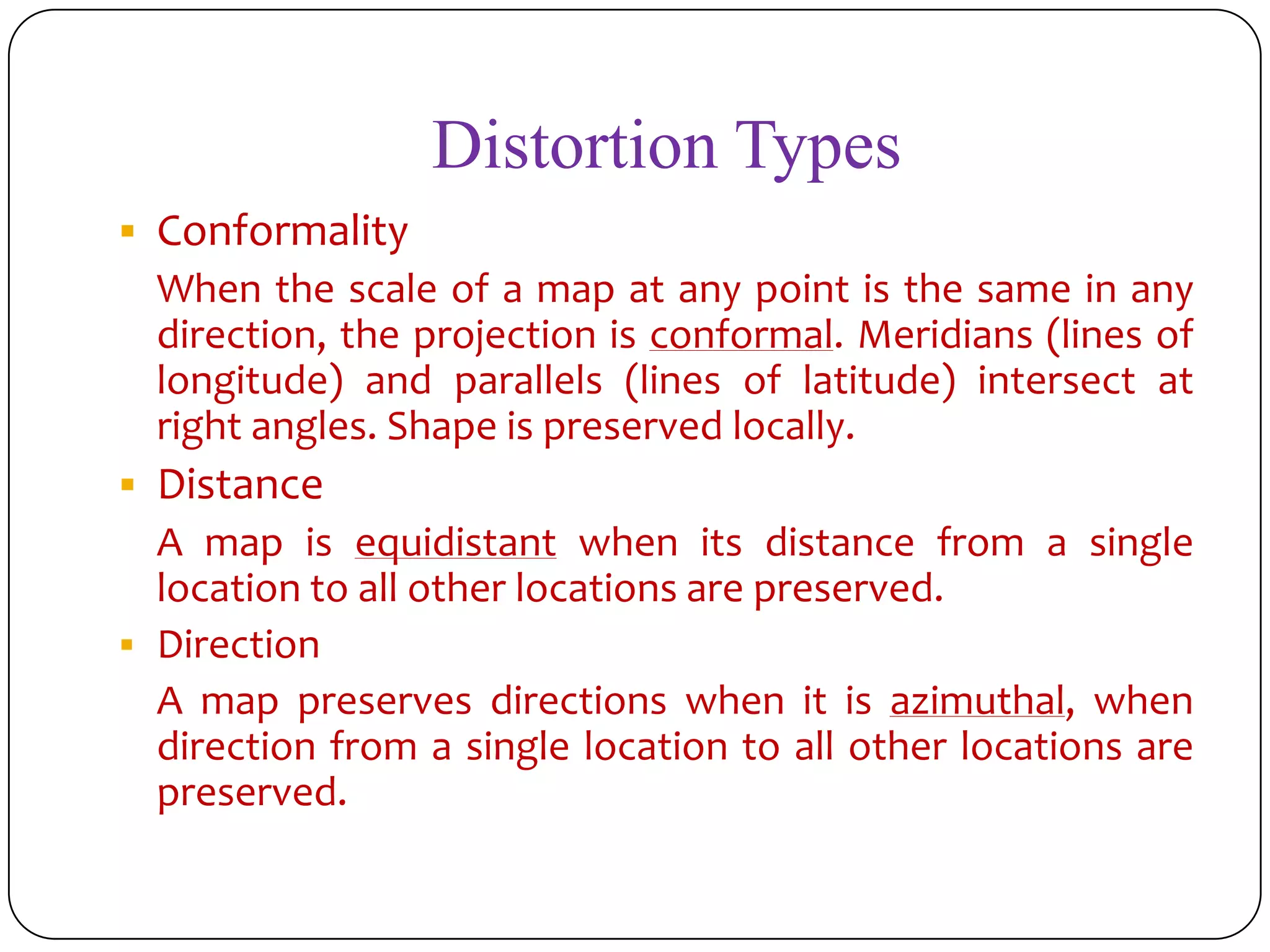
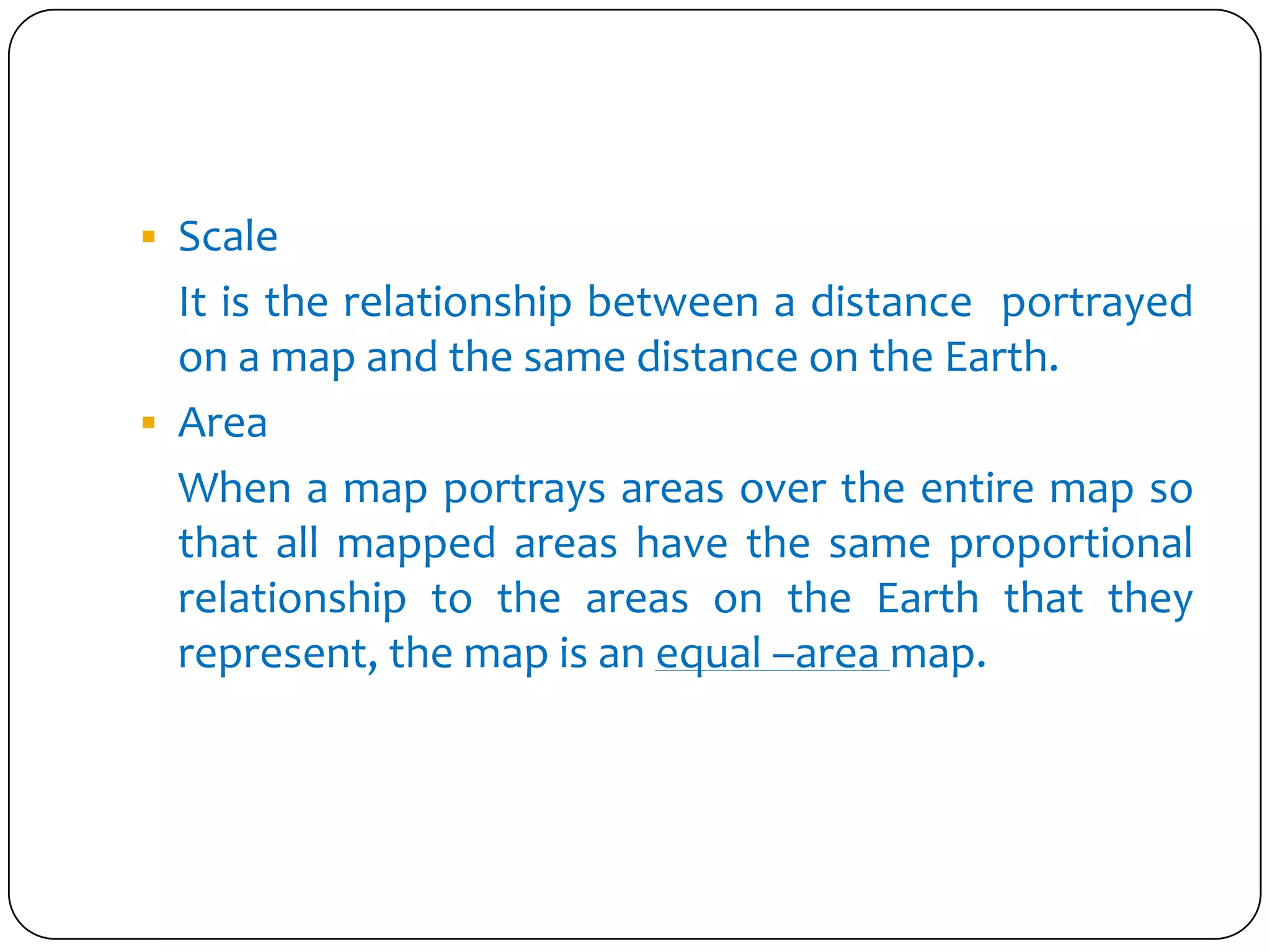
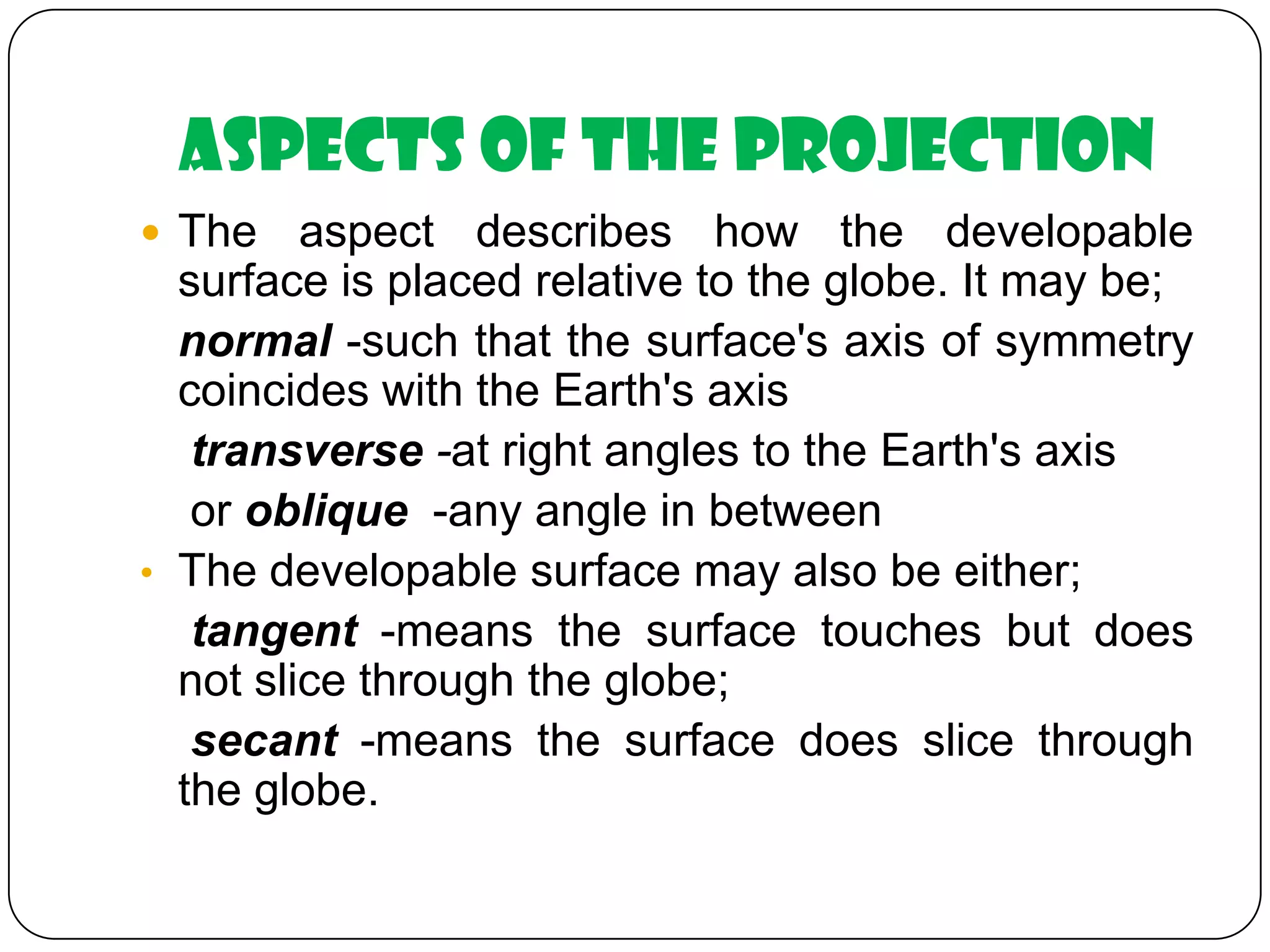
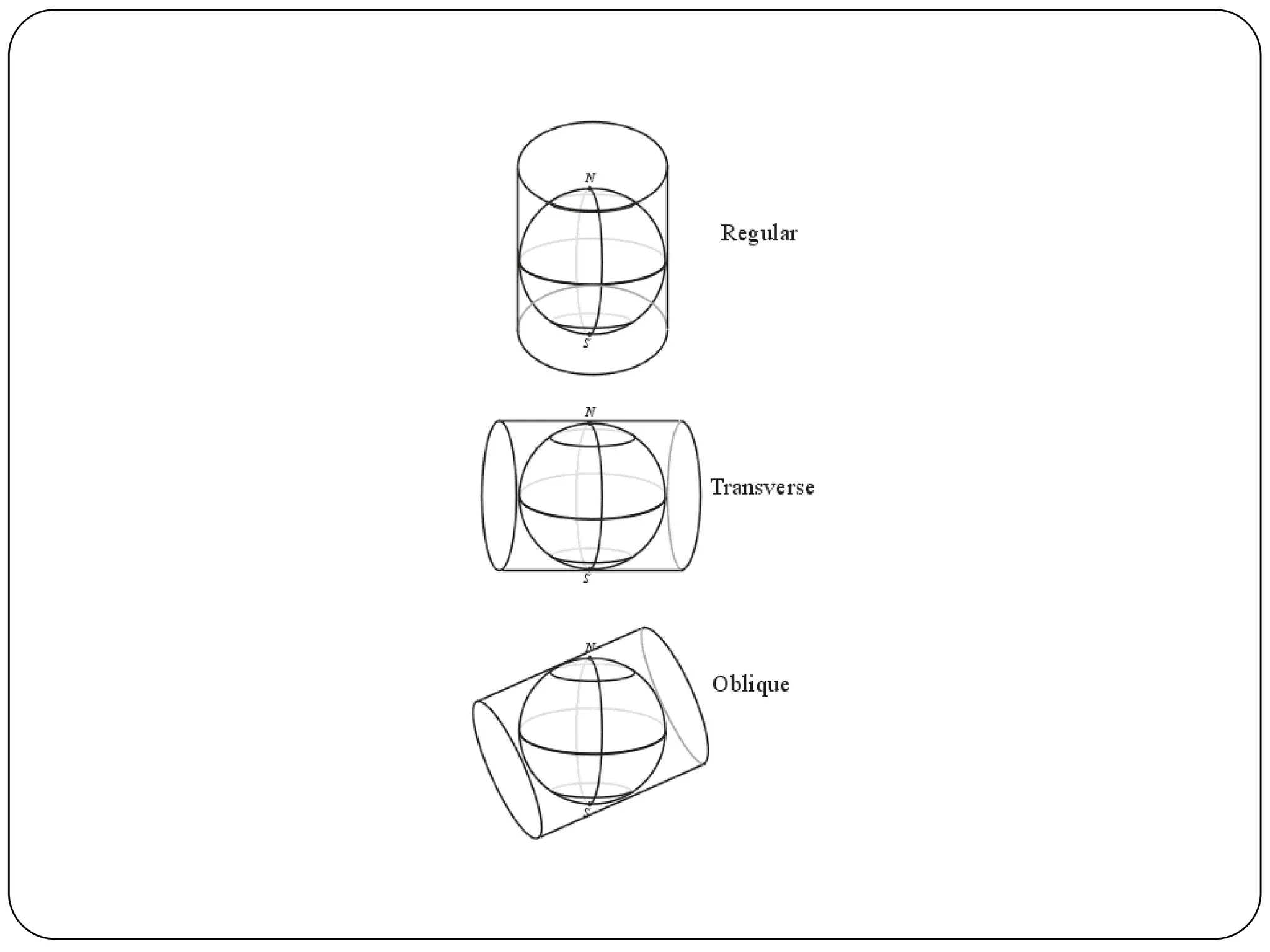
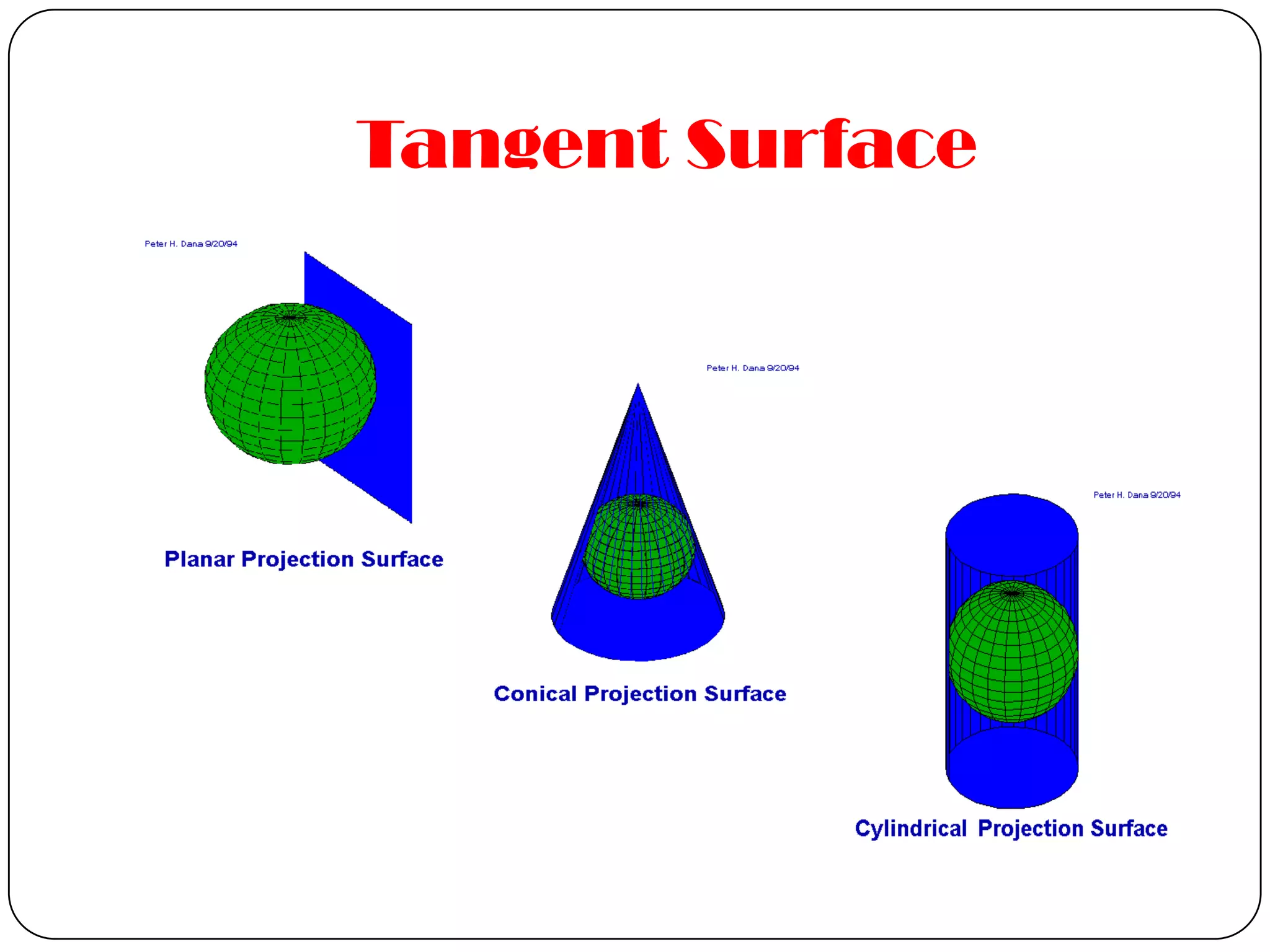
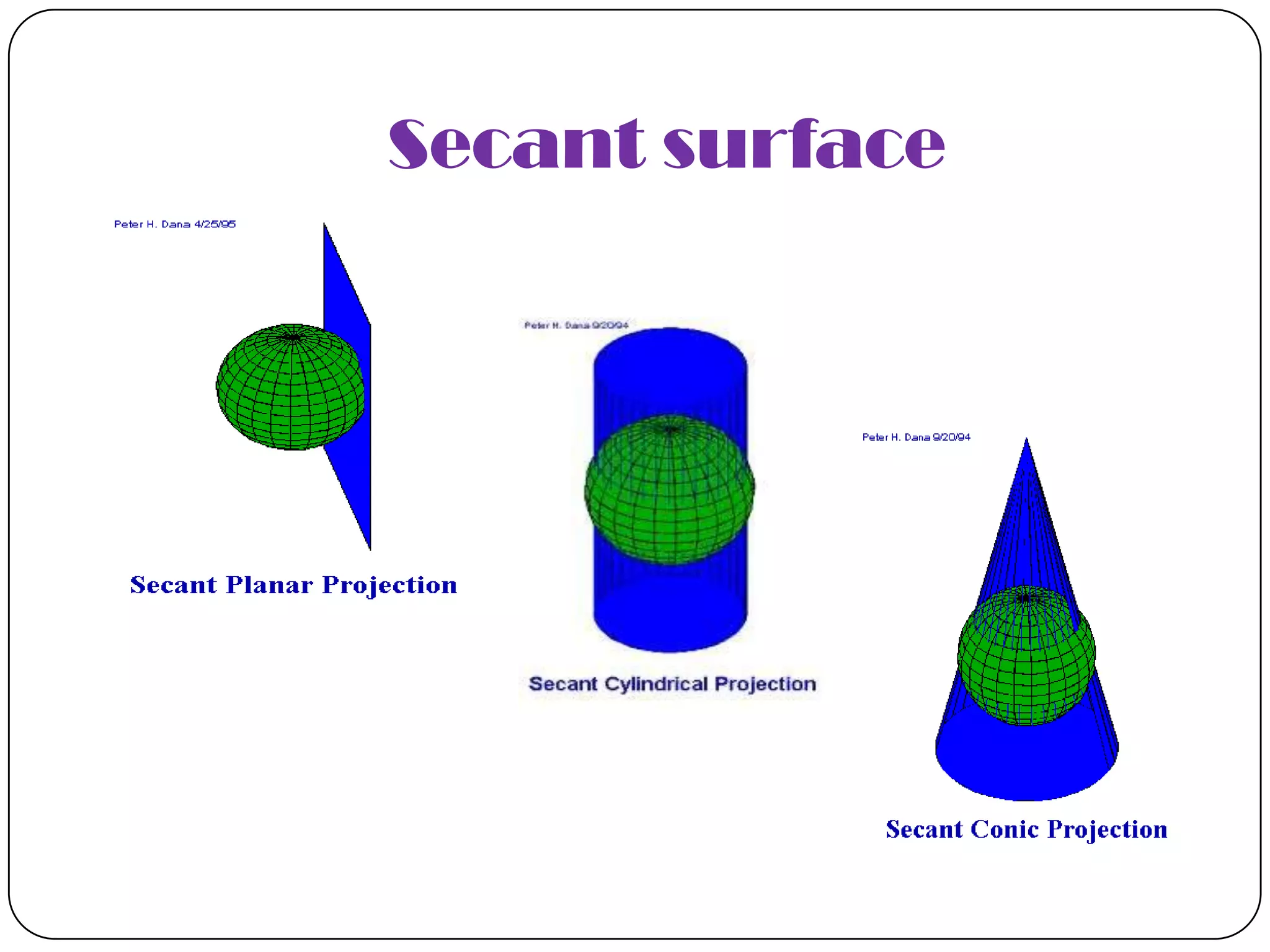
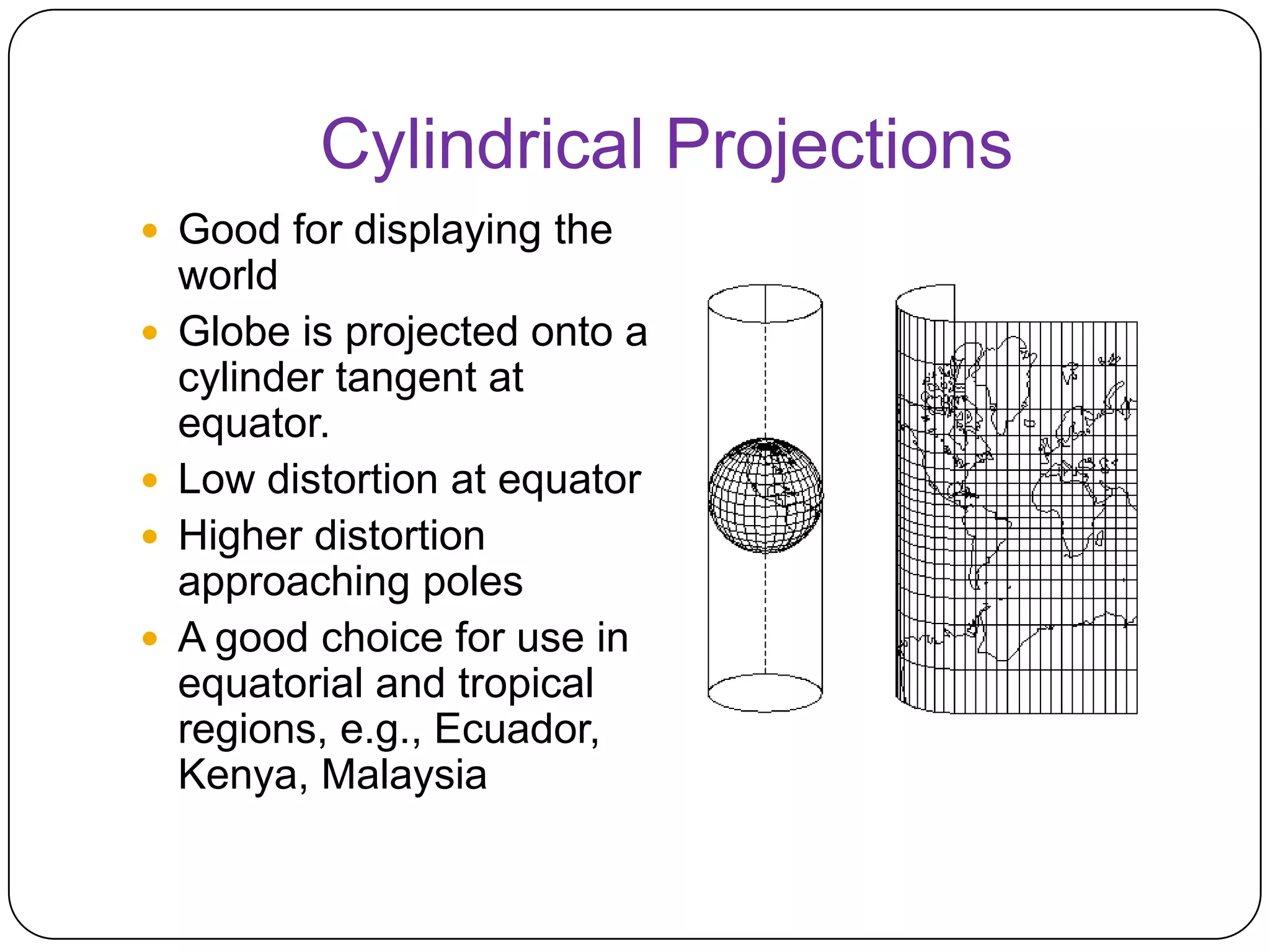
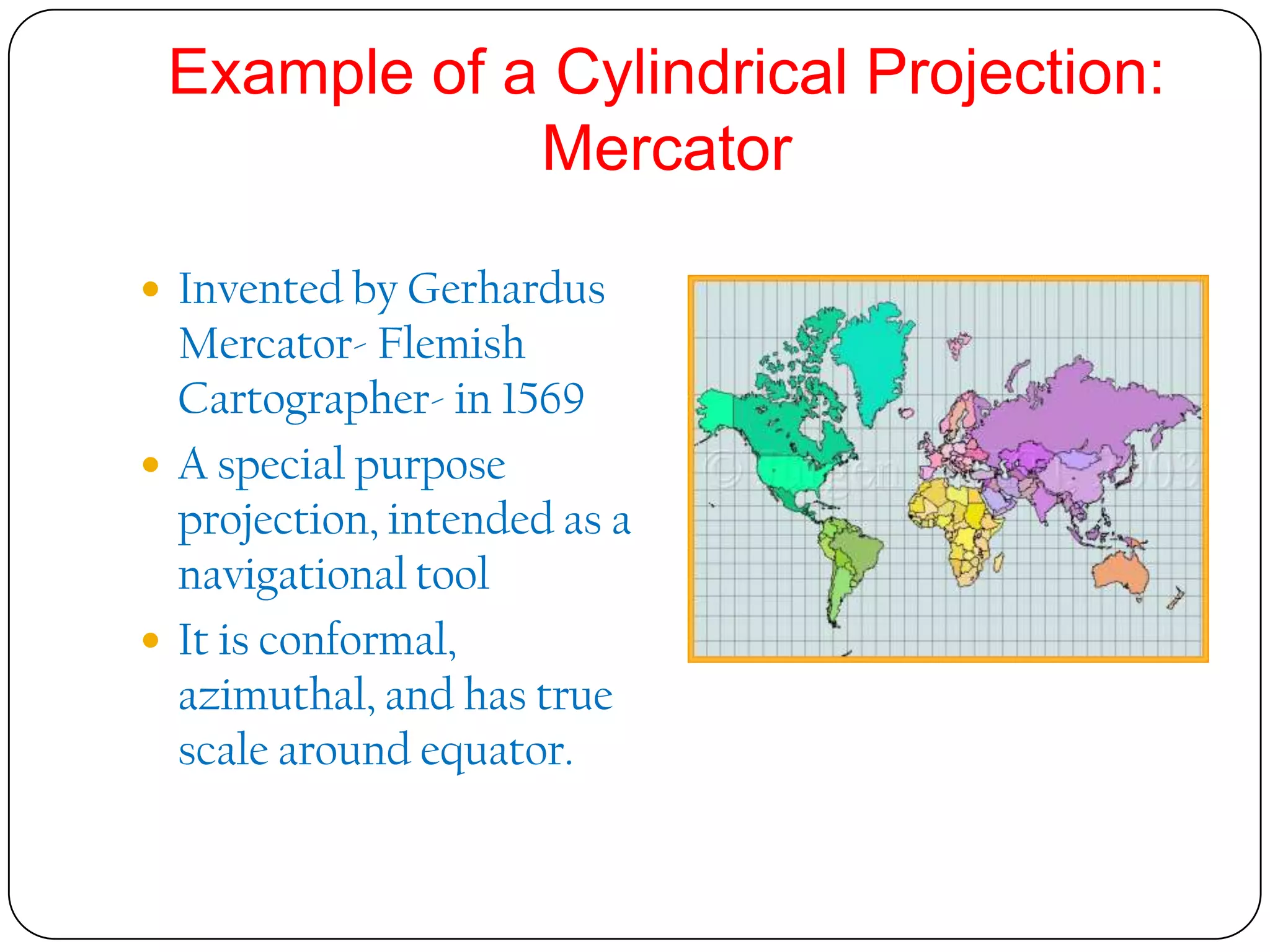
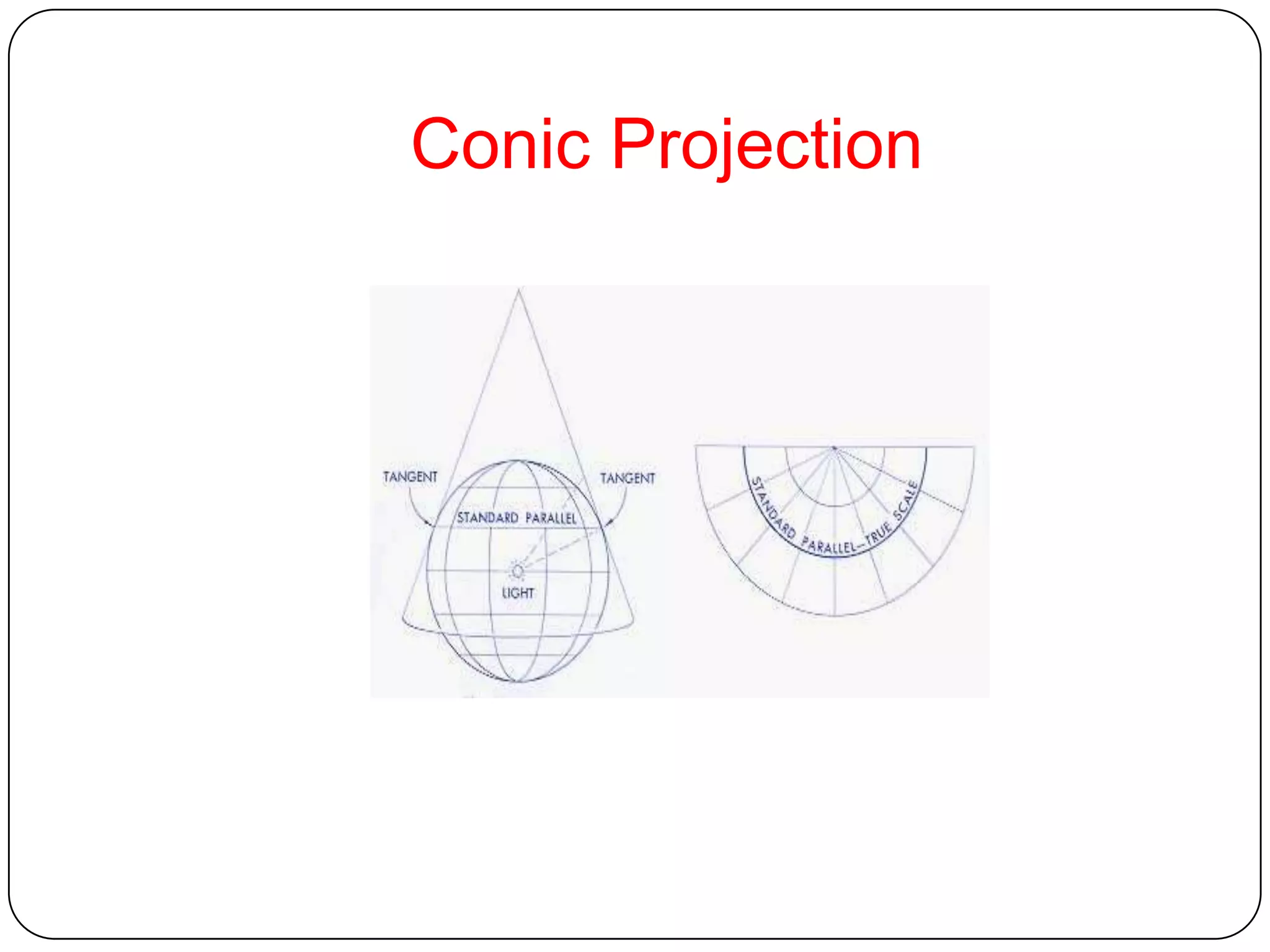
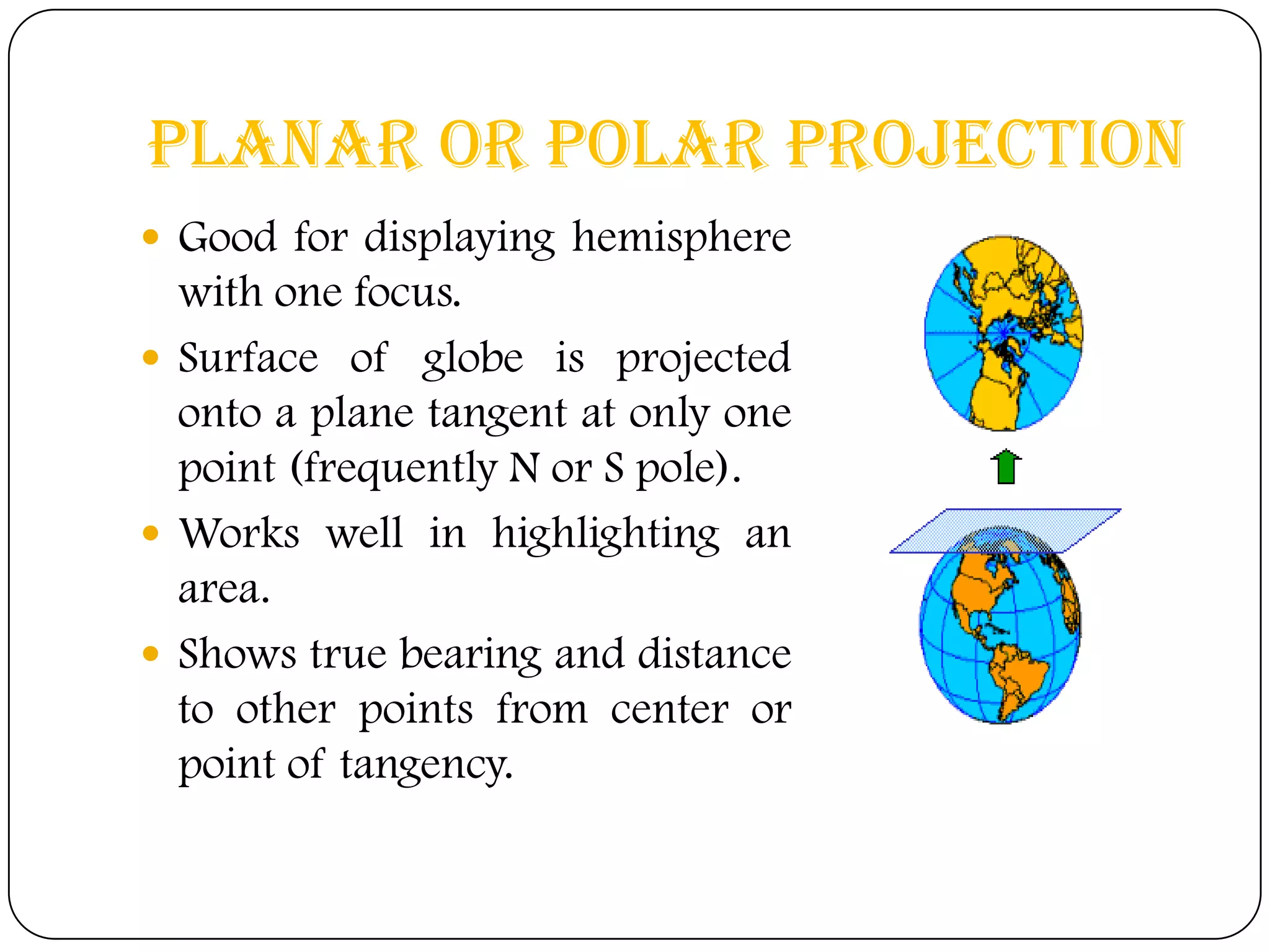
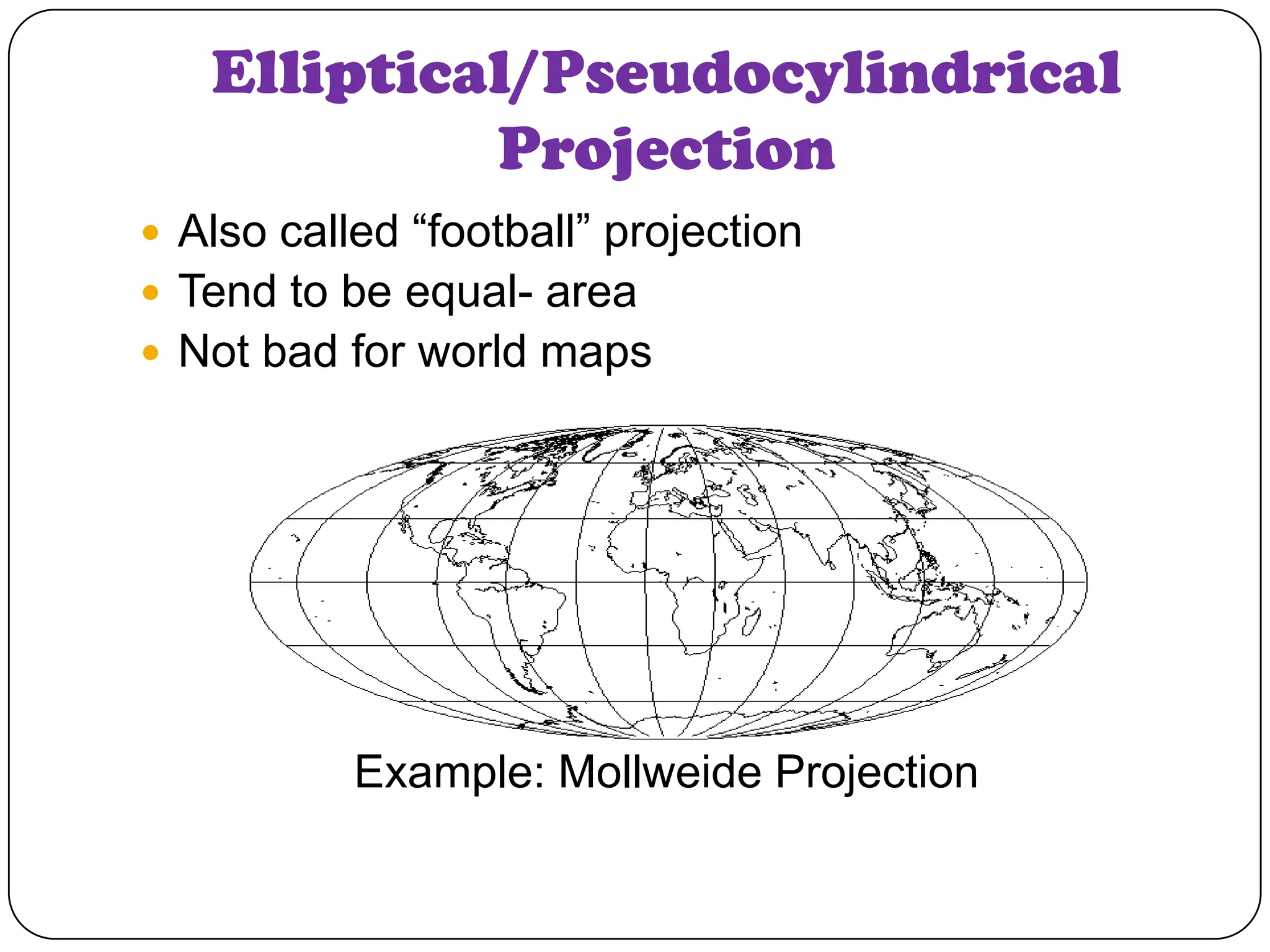
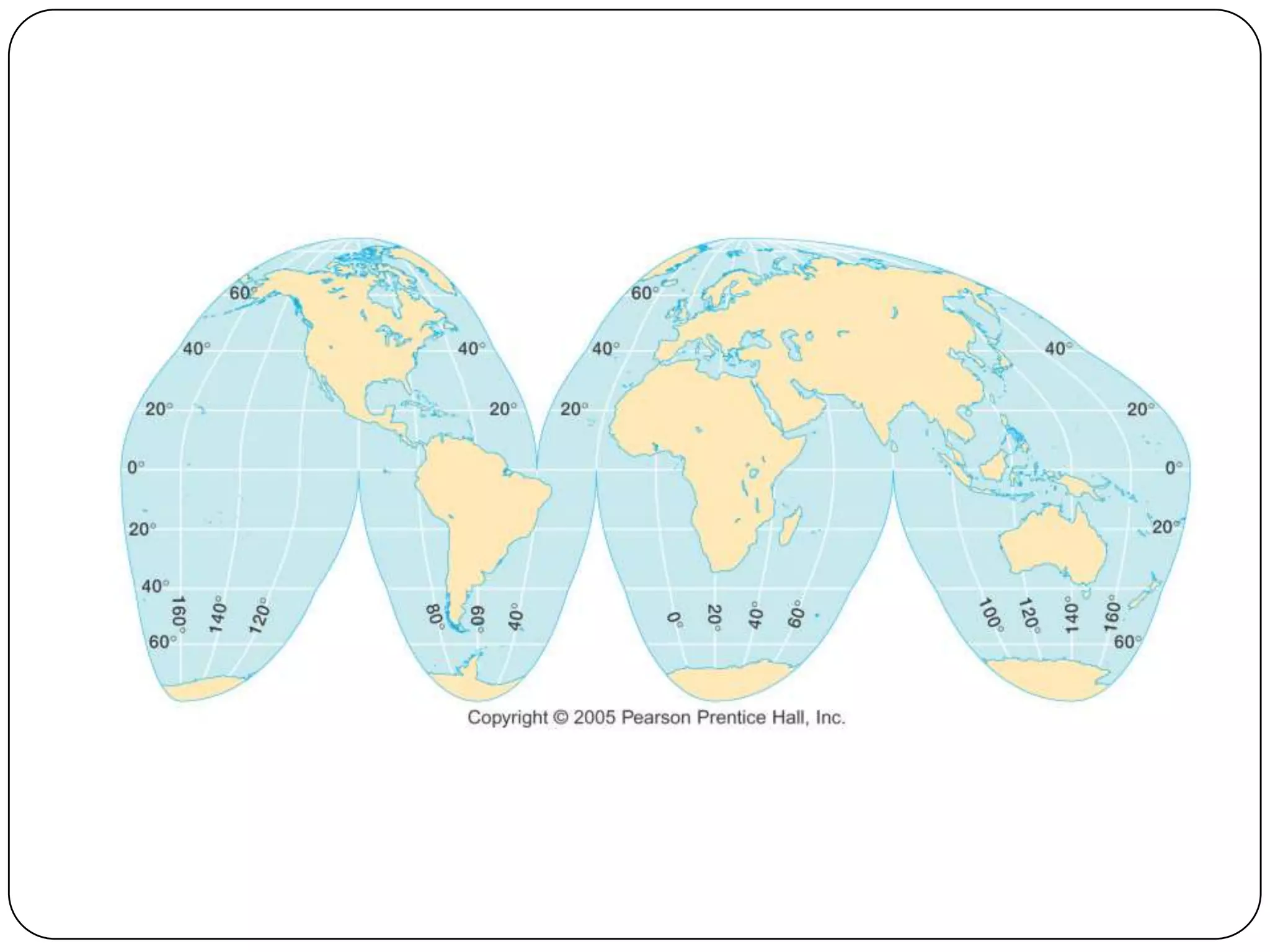
This document discusses map projections and their properties. Map projections transform the three-dimensional globe onto a two-dimensional surface, necessarily introducing some distortions. The best projection depends on the map's purpose and region. Common projections include cylindrical (like Mercator), conic, and planar/polar types. Key properties that projections aim to preserve, like shape, area, distance and direction, often involve tradeoffs. Choosing a projection minimizes distortions for a map's intended use and geographic extent.