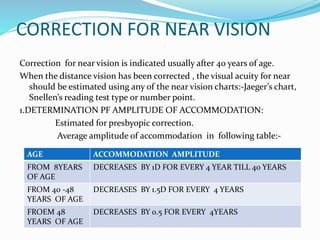
Subjective refraction is used to find the best corrective lenses for a patient and requires their cooperation. It involves monocular refraction of each eye separately to determine the cylindrical lens power and axis as well as best spherical lens. This is followed by binocular balancing to ensure clear vision with both eyes open. Techniques like fogging, cross-cylinders, and Maddox rods are used in monocular refraction while techniques like fogging with occlusion, duochrome testing, and prism dissociation are used for binocular balancing. Determining the near vision correction involves estimating accommodation amplitude and adding readers if needed for presbyopia.