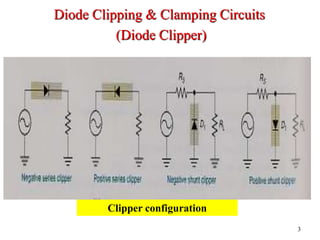
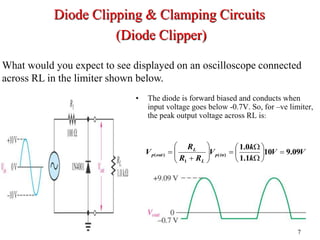
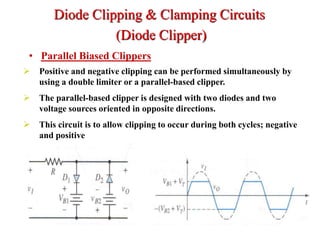
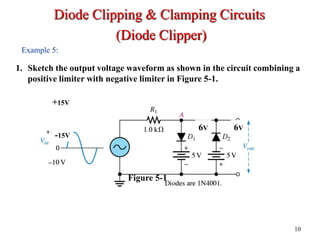
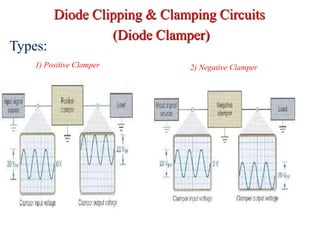
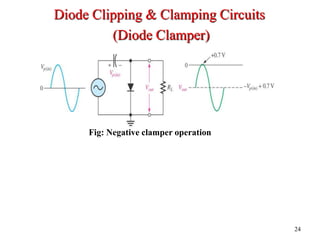
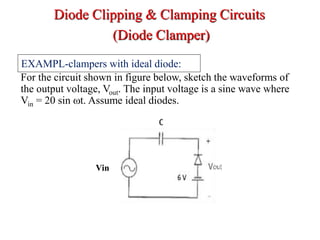
Clippers and clampers use diodes to limit or shift signal voltages. There are four basic clipper configurations that use diodes in either series or parallel to clip either the positive or negative portions of a signal. Clampers use a diode along with a capacitor and resistor to shift a signal voltage to a different DC level without distorting its shape. Common applications of clippers and clampers include transient protection, amplitude modulation detection, and DC restoration in television receivers.