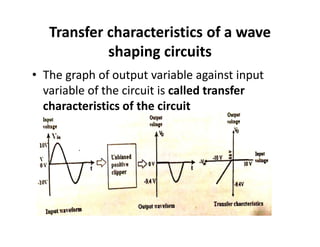
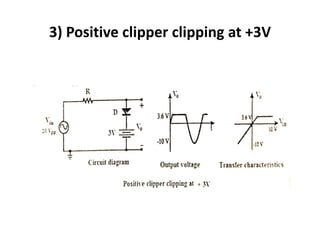
Wave shaping circuits modify the shape of a waveform by passing it through either linear or non-linear elements. There are two main types: linear circuits which change amplitude and phase but not shape, and non-linear circuits which use elements like diodes to modify shape. Common non-linear wave shaping circuits are clippers and clampers. Clippers cut off portions of the waveform above or below certain thresholds, while clampers shift the entire waveform up or down without changing its shape. Both have applications in signal processing and protection of electronic components.