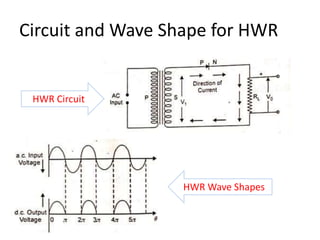
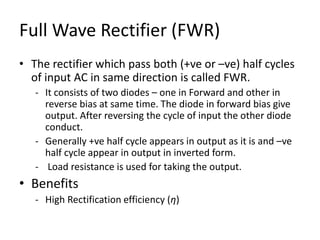
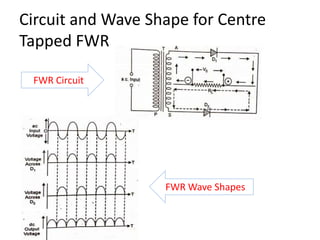
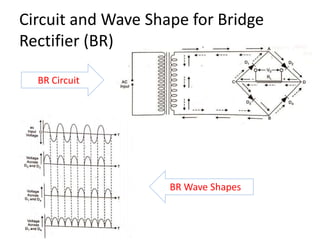
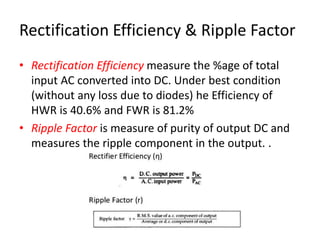
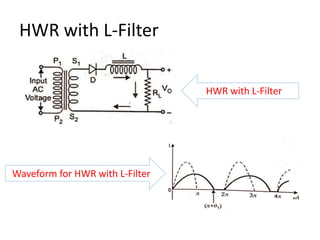
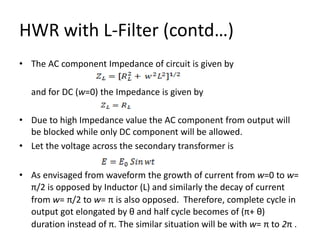
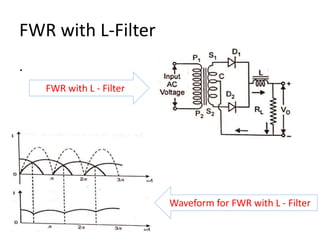
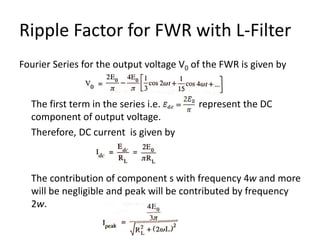
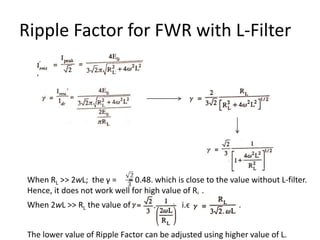
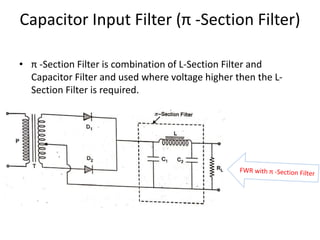
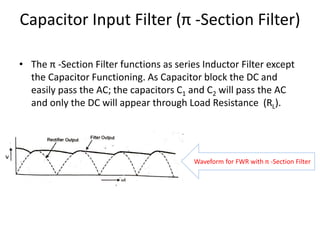
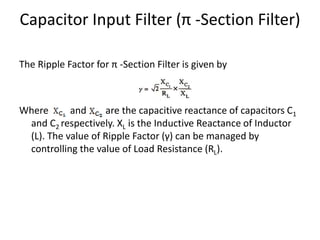
The document provides an overview of rectifiers and filter circuits, explaining the principles, types, and efficiencies of half wave rectifiers (HWR) and full wave rectifiers (FWR), including center tapped and bridge rectifiers. It also discusses the use of filter circuits to eliminate ripple in DC output from rectifiers, describing different filter types such as L-filter and π-section filter. Key metrics like rectification efficiency and ripple factor are analyzed, with assignments for further understanding.