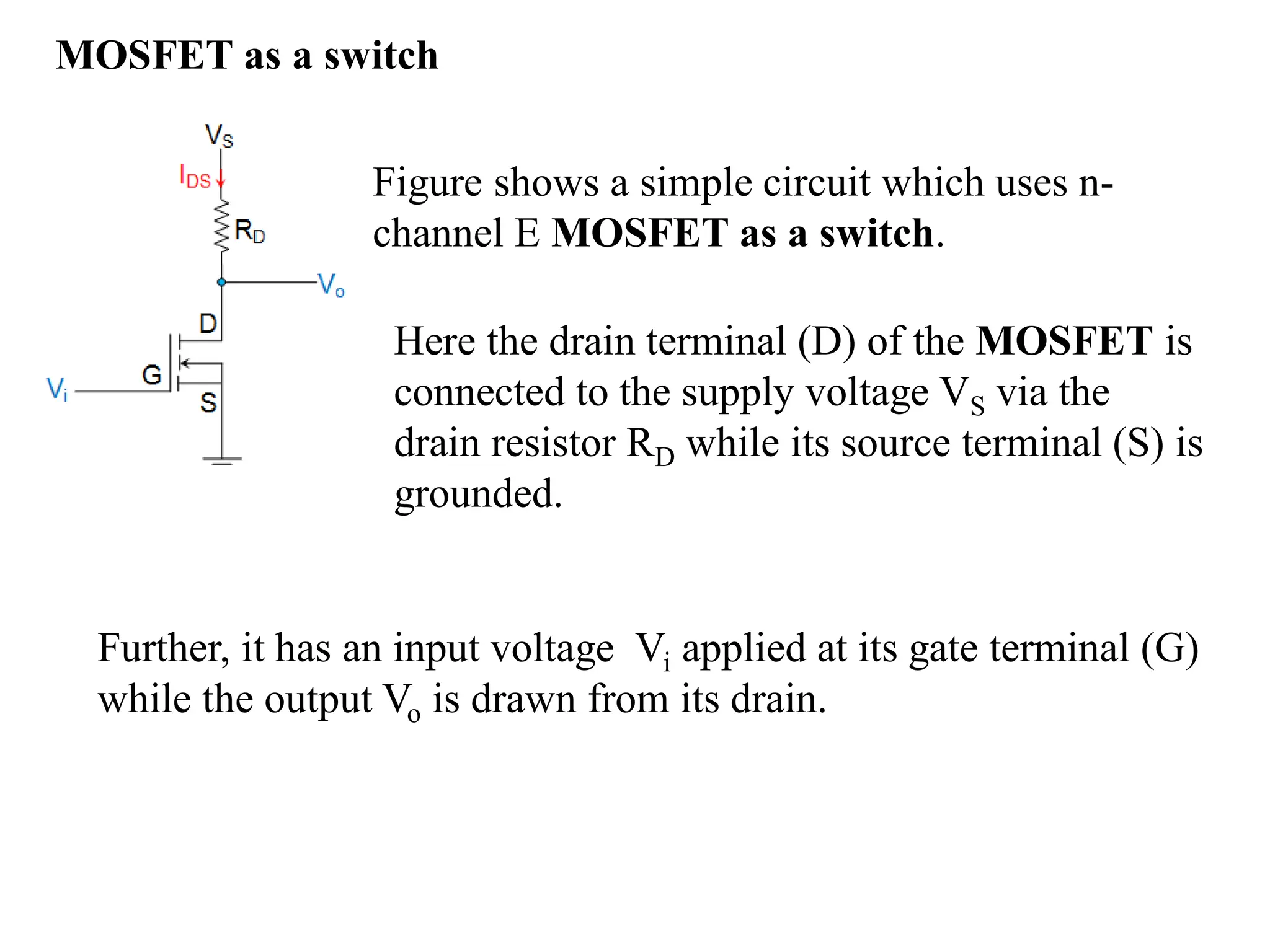
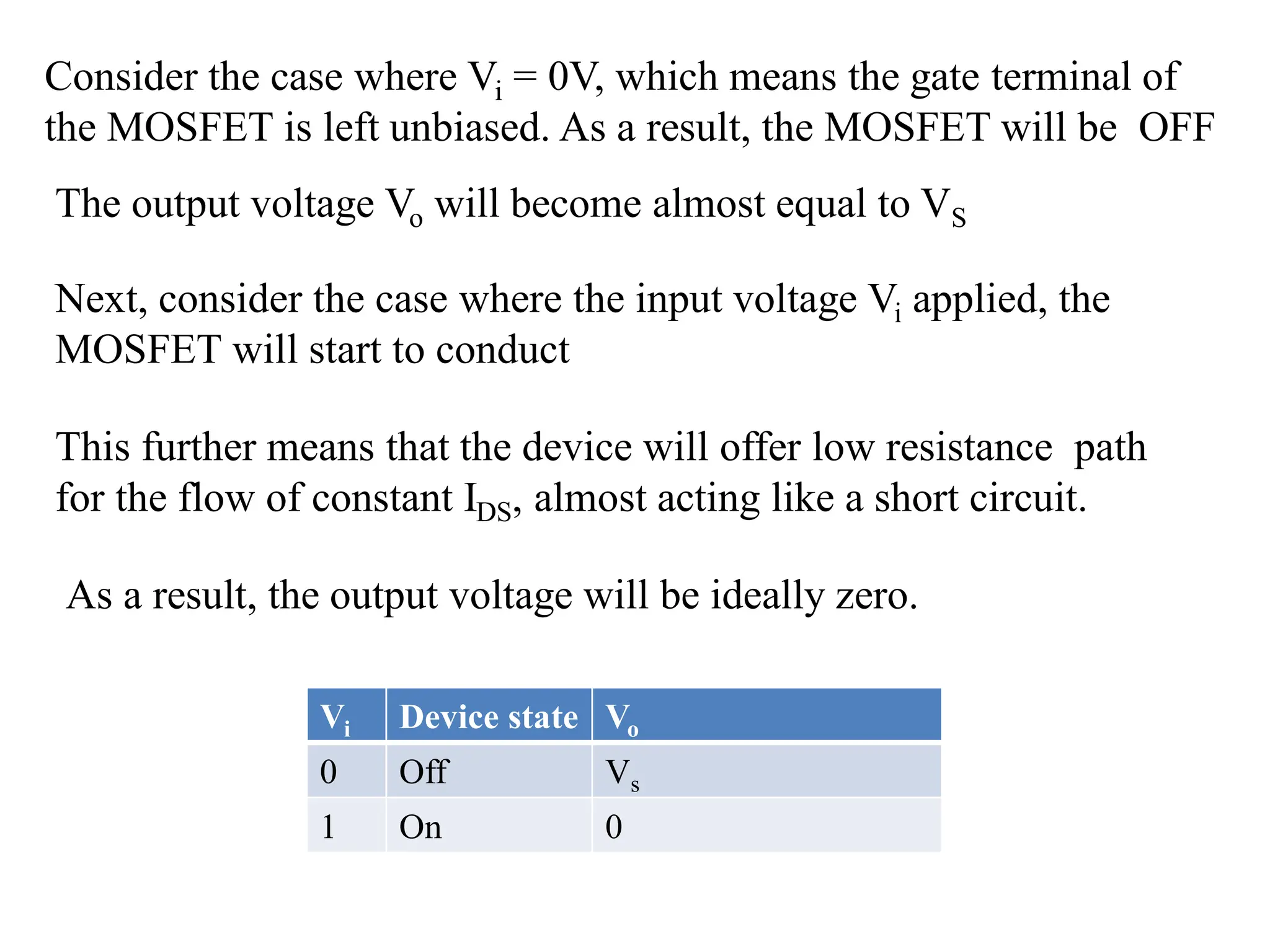
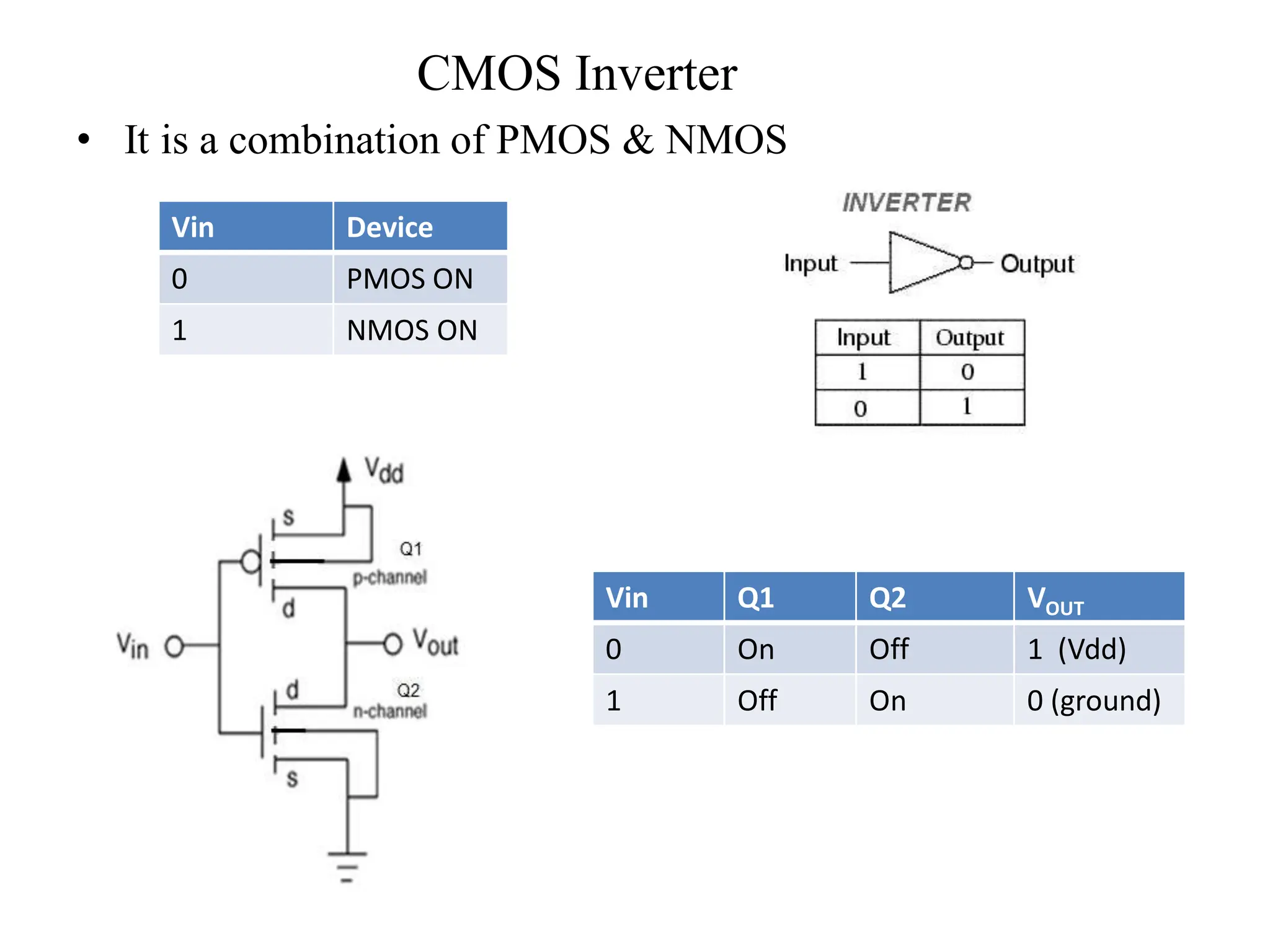
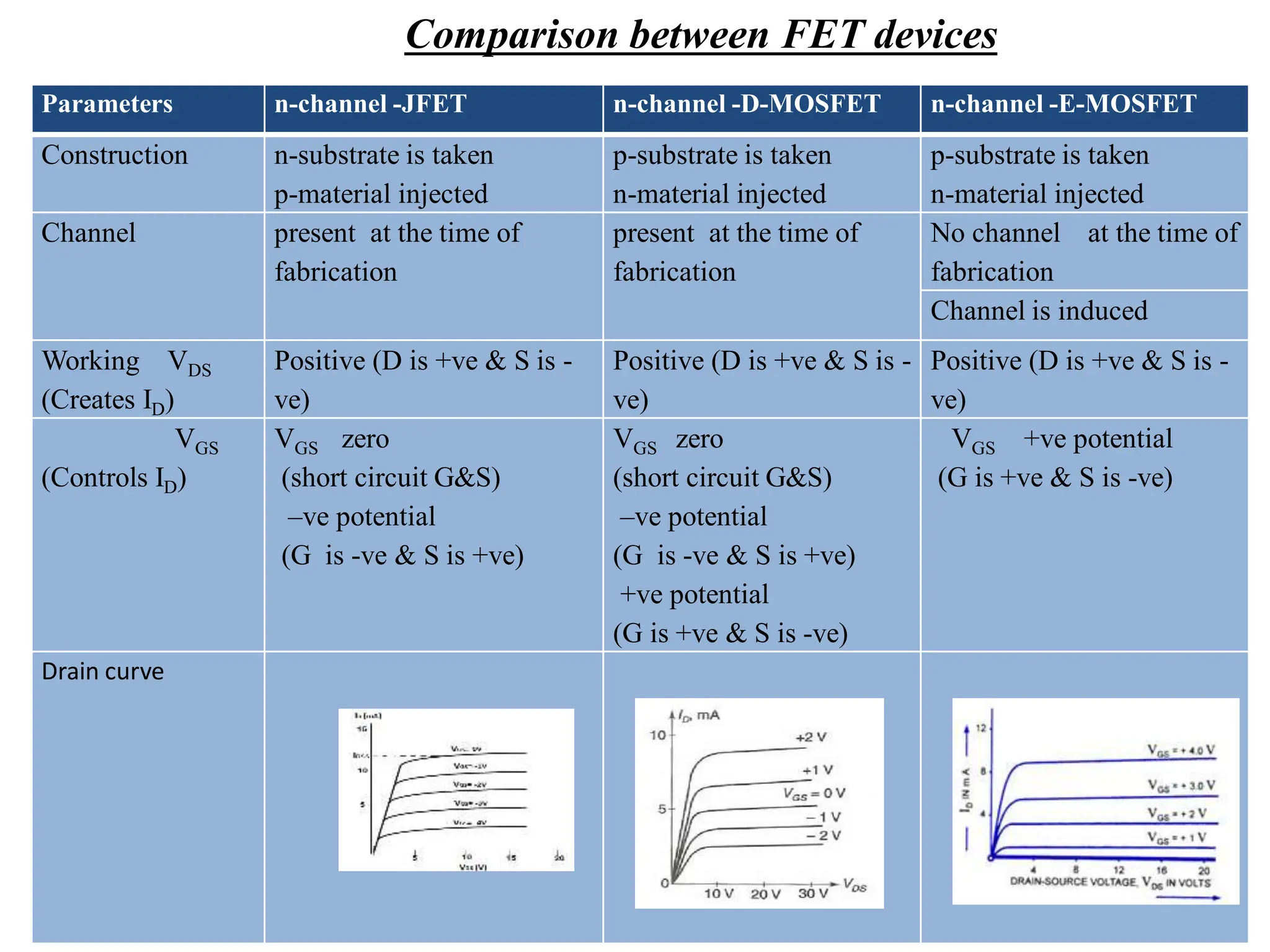
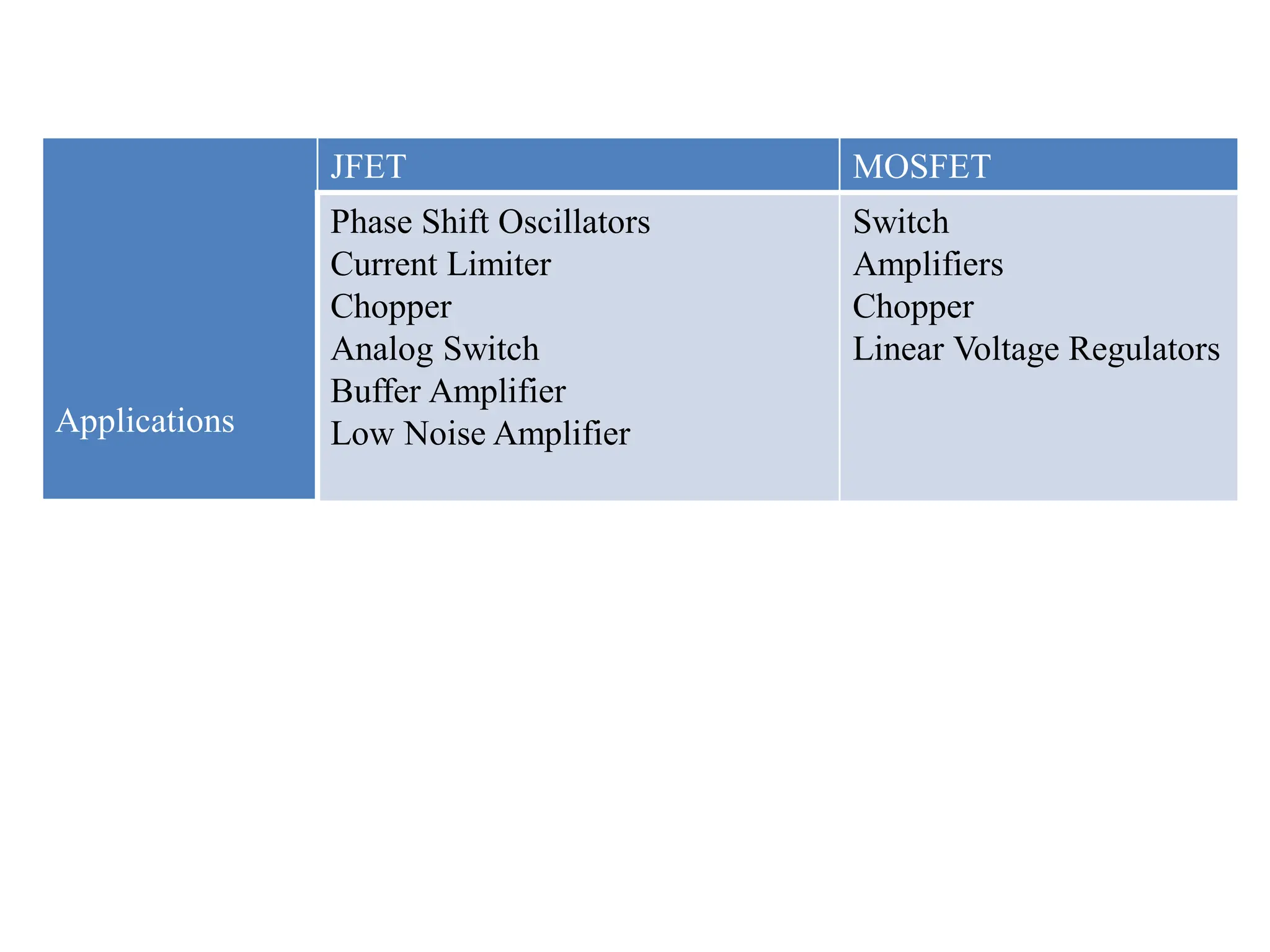
This document compares BJT, FET, and MOSFET transistors and describes how MOSFETs can be used as switches. It also explains the construction and operation of a CMOS inverter. A MOSFET can act as a switch by turning fully on or off depending on the input voltage. A CMOS inverter consists of a PMOS and NMOS device with common gates and drains. It outputs a high voltage when the input is low and vice versa. MOSFETs have advantages over BJTs and FETs like higher input impedance, lower output resistance, and faster switching speed.