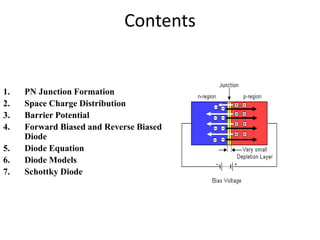
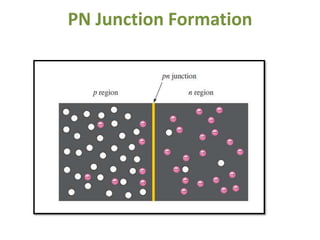
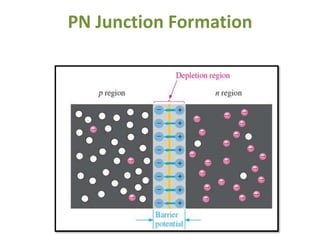
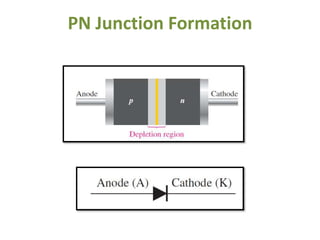
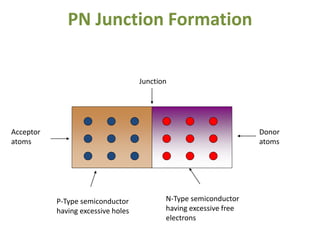
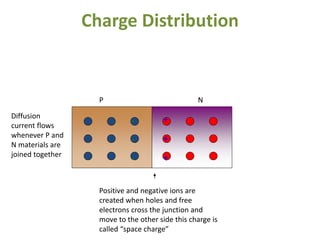
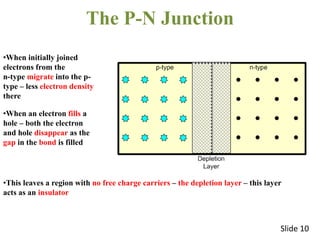
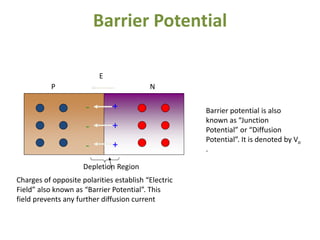
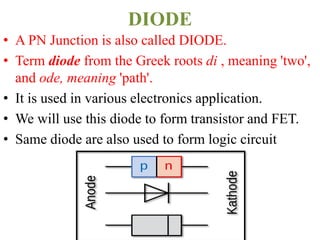
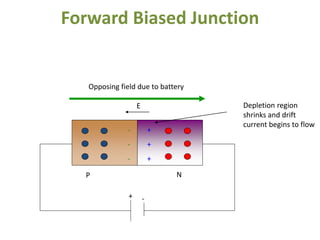
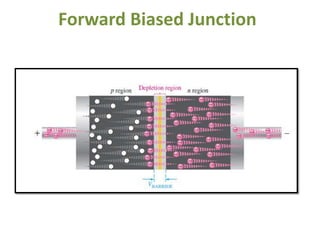
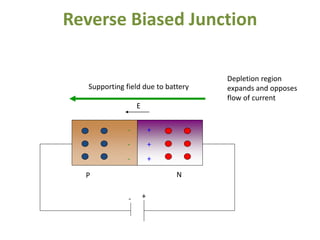
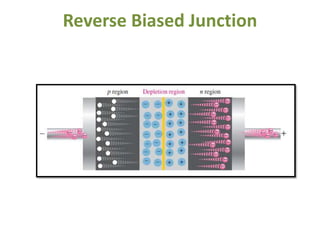
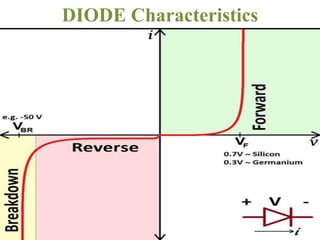
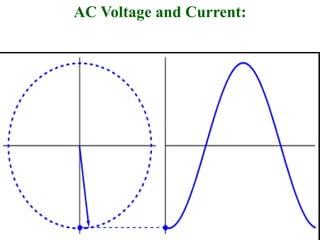
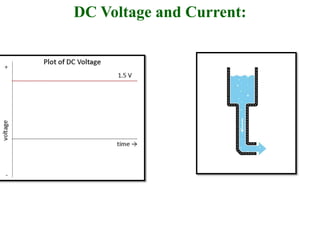
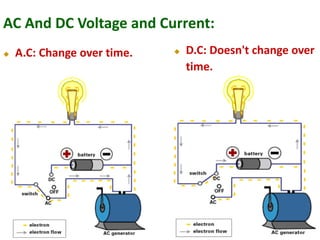
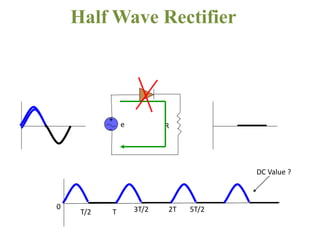
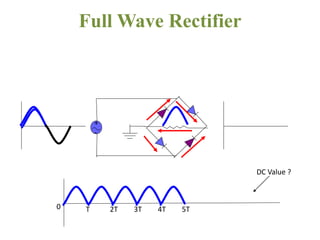
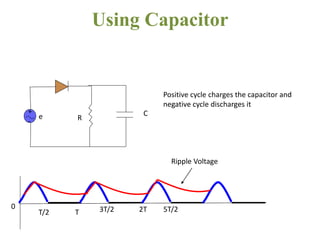
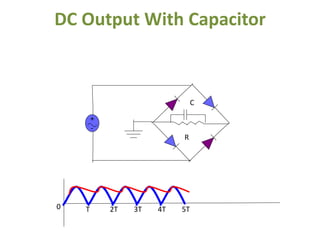
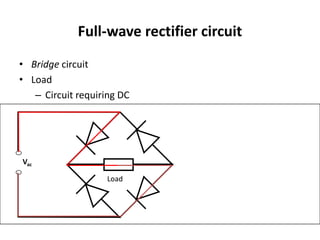
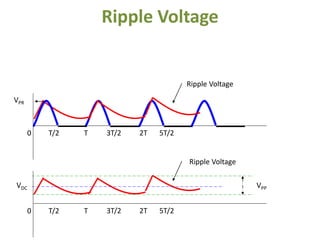
The document covers the formation and characteristics of p-n junctions and diodes, detailing concepts such as barrier potential, forward and reverse bias conditions, and the diode equation. It explains the usage of diodes in various electronic applications, particularly in rectifying AC to DC. Key characteristics, including voltage drops for silicon and germanium, and different rectifier configurations, are also presented.