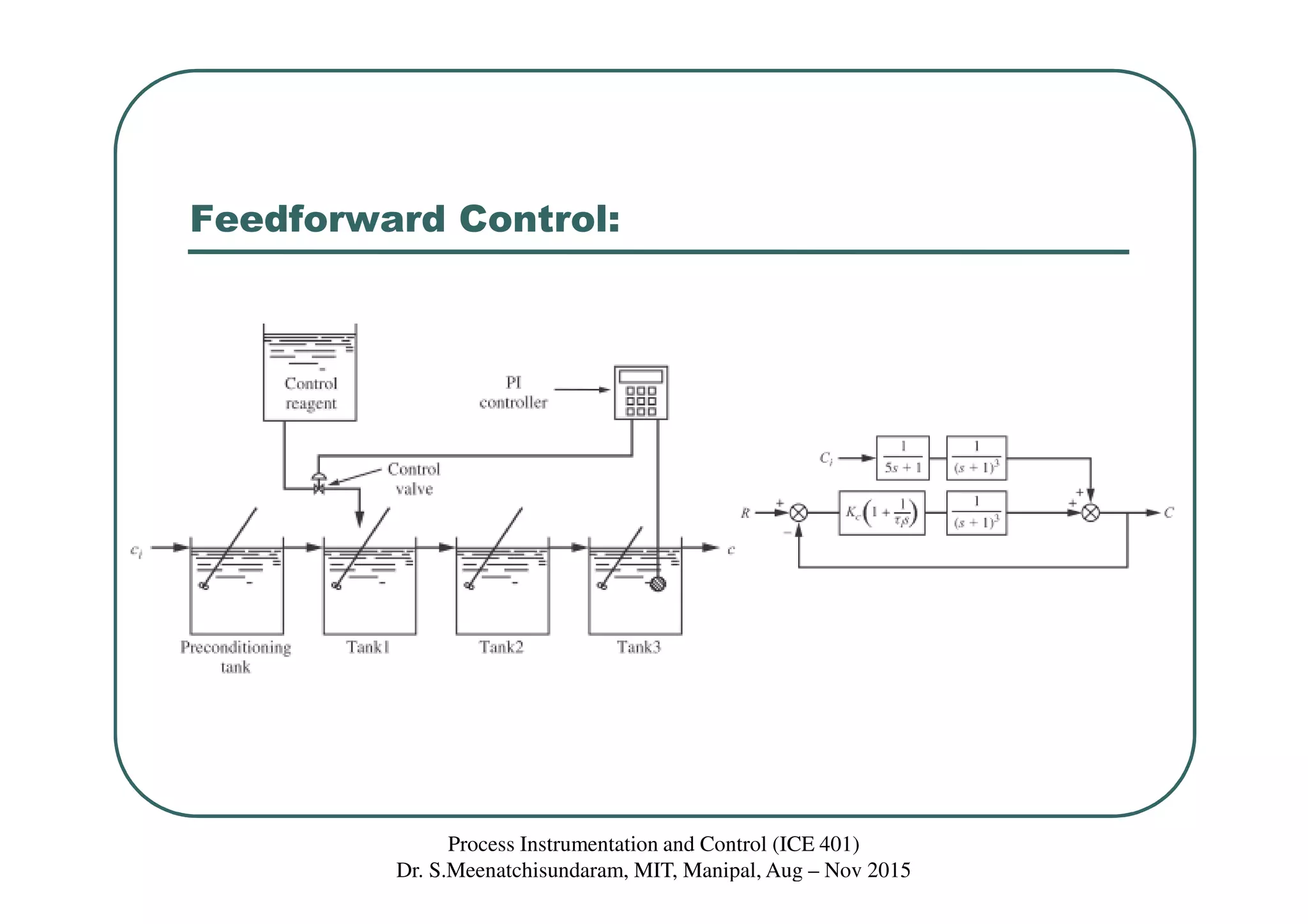
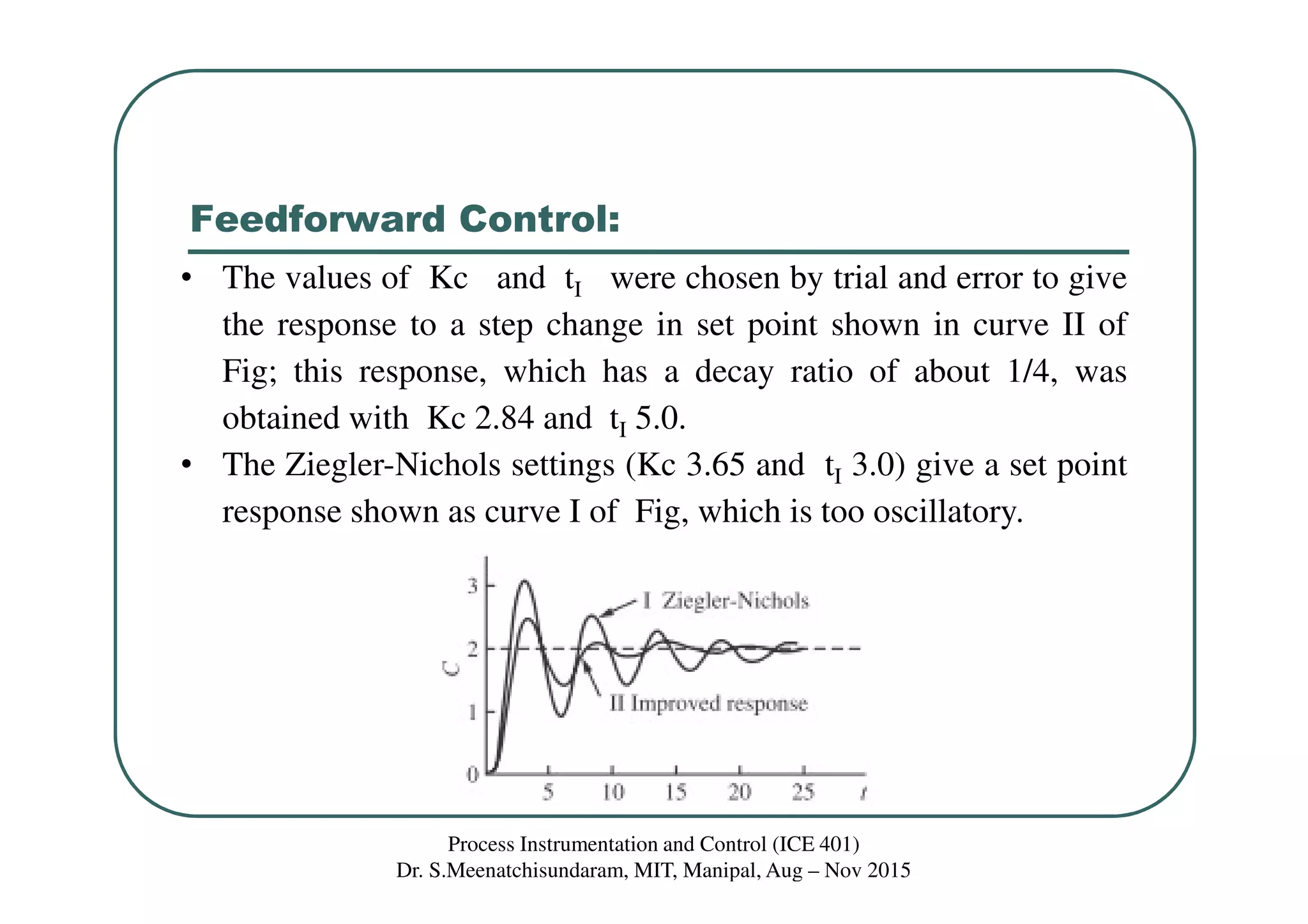
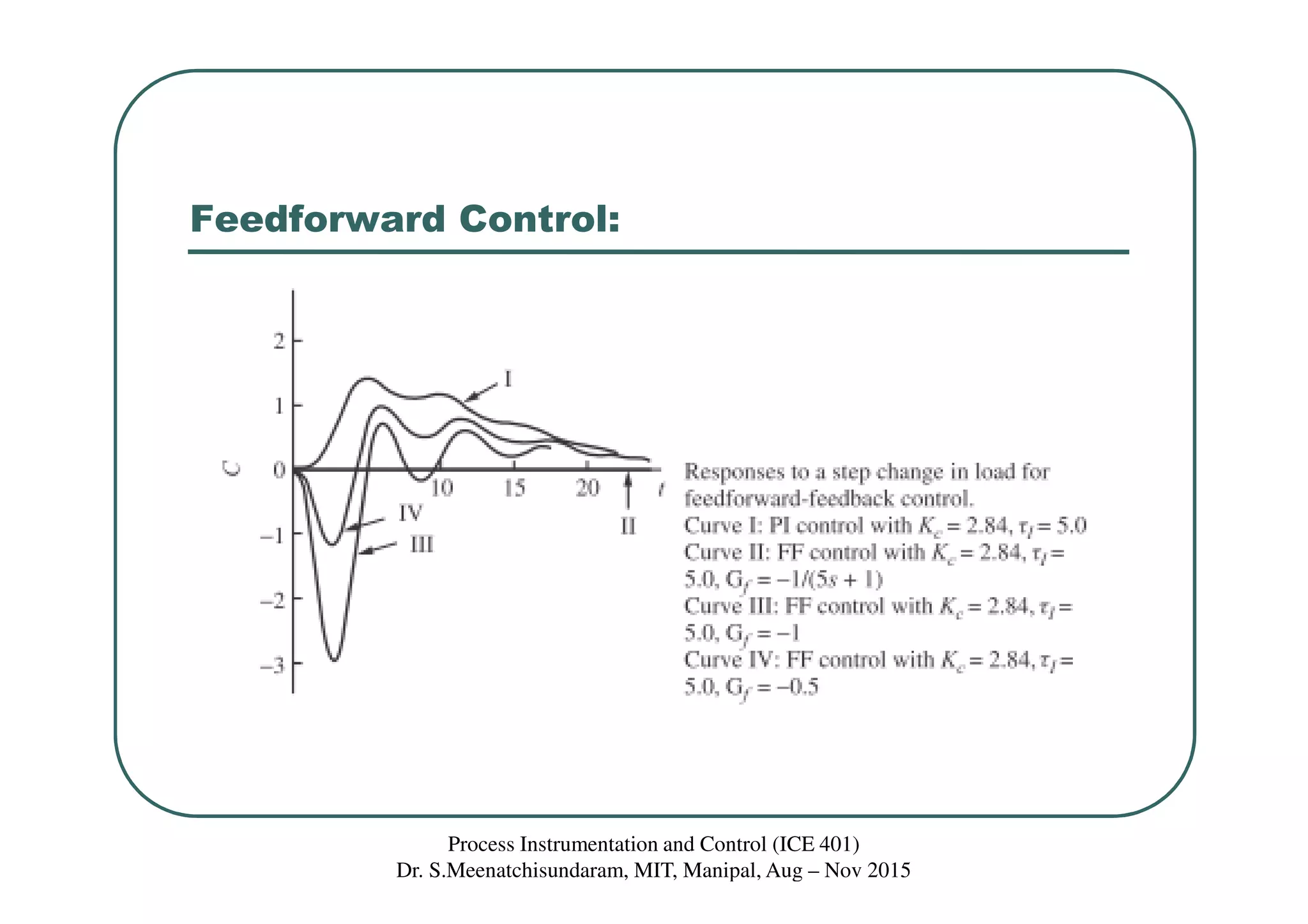
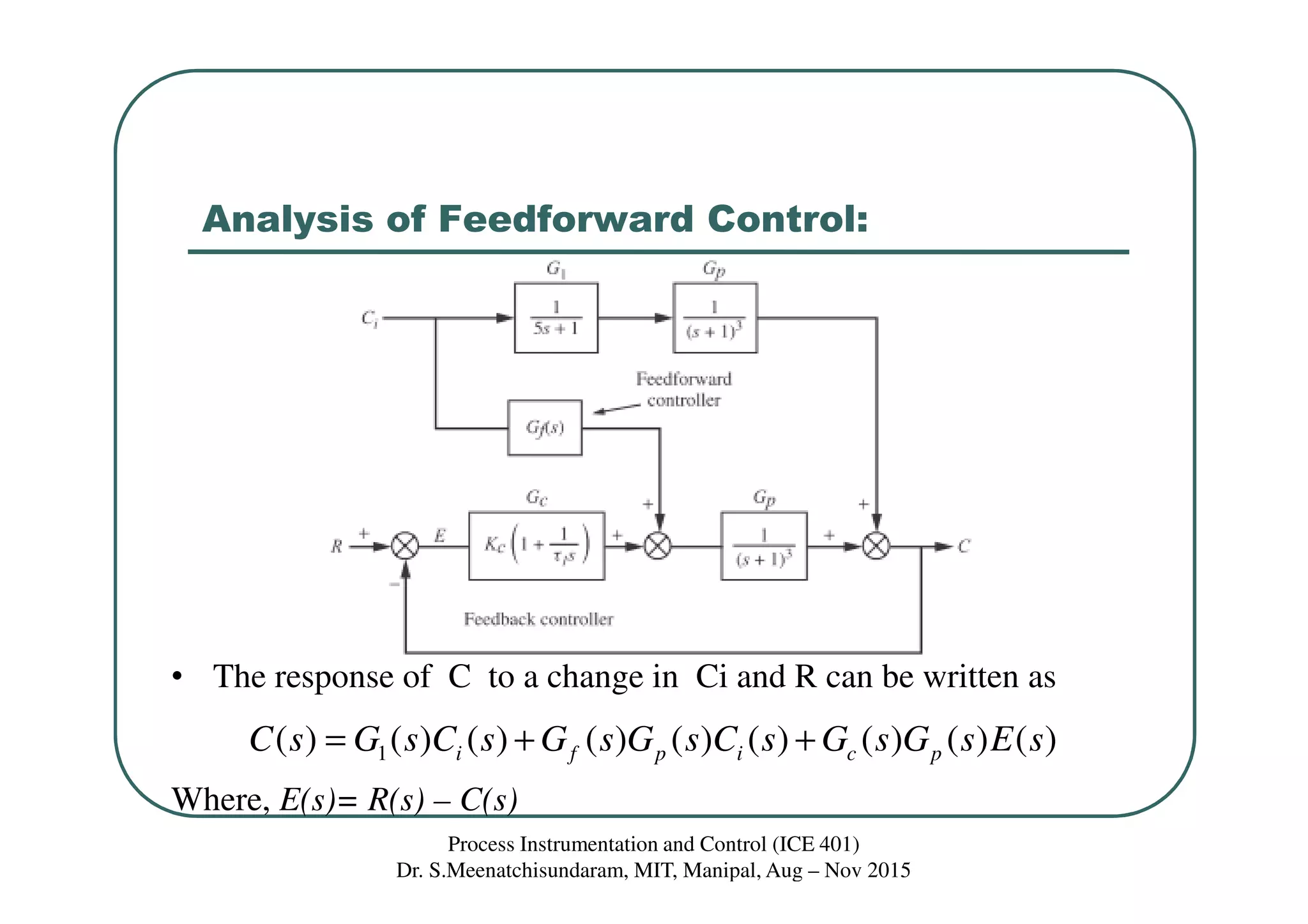
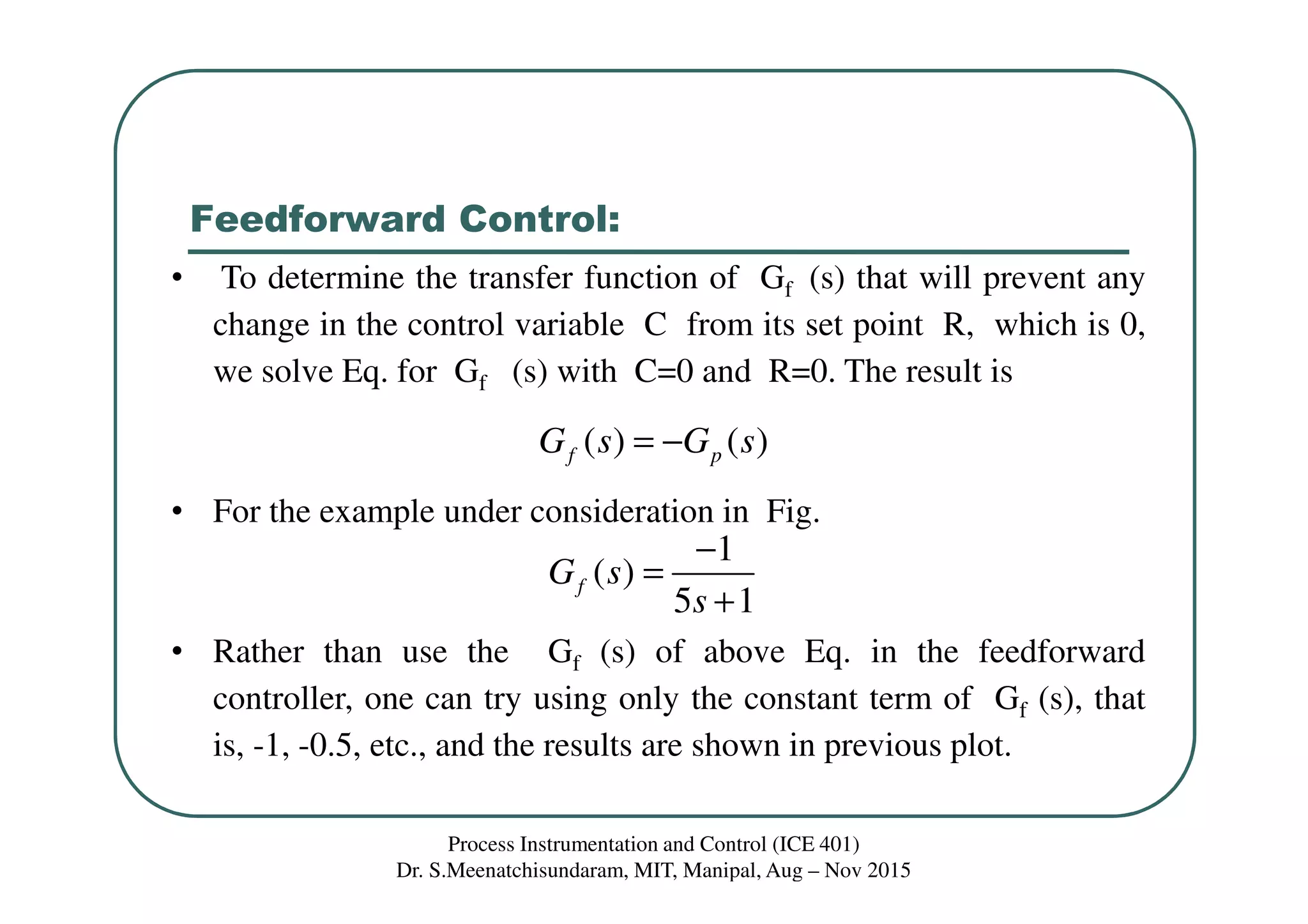
This document discusses feedforward control in a process instrumentation and control system. It describes a three-tank system used to control the concentration of a solute stream. Feedforward control is introduced to improve quality of control for frequent load disturbances. A feedforward controller uses information about disturbances detected at the inlet stream to adjust the control valve and prevent changes in the outlet composition from the setpoint. The document provides equations to model the feedforward control system and discusses using constant terms for the feedforward controller transfer function.