This document provides an introduction to designing and working with databases in Microsoft Access. It discusses key Access objects like tables, forms, queries, and reports.
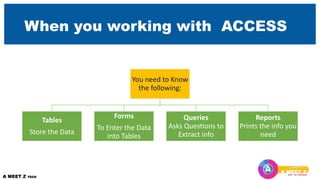
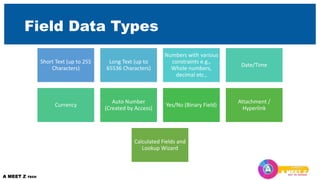
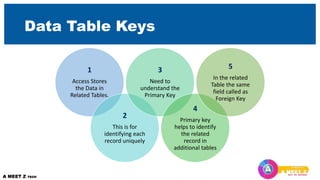
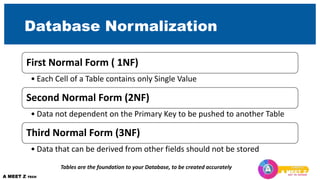
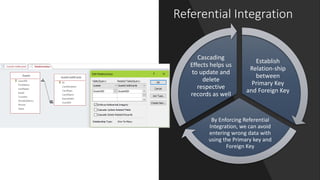
The first section explains the structure of tables and different field data types. It also covers primary and foreign keys. The second section discusses relationships between tables and referential integrity.
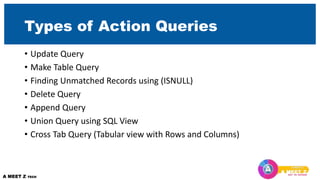
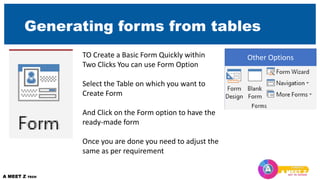
The third section covers organizing records through sorting, filtering, and searching. Later sections provide overviews of creating queries, action queries, forms, and reports. It also introduces macros and automation. The document aims to give an overall understanding of the Access environment and objects for managing data.
















![Ways to create a Query
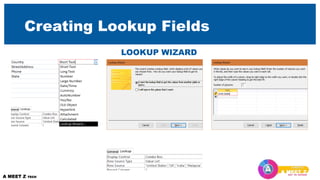
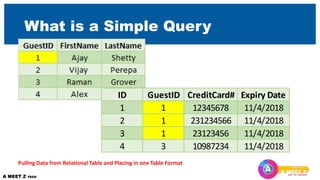
Using Simple Query Wizard
• Pulling required information from two relational tables
• Look at the Relation-ships to understand what you can get from a Query
Building Queries in Designer View
• Sort View using a Specific Field
• Using Show/Hide Option [check box]
• Establishing Constraints
• Using Simple Criteria
• Criterial with Wildcards (* , ?)
• “[abc]*”
• Multiple Query Criteria with AND / OR , BETWEEN Statements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessessentialtraining-framework-190223031809/85/Access-essential-training-framework-25-320.jpg)
![Query in Design View –
using filtering constraints
Sort View using a Specific Field
Using Show/Hide Option [check box]
Establishing Constraints
Using Simple Criteria
Criterial with Wildcards (* , ?)
“[abc]*”
Multiple Query Criteria with AND / OR , BETWEEN Statements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessessentialtraining-framework-190223031809/85/Access-essential-training-framework-27-320.jpg)
![Filtering Data with Math Comparisons
• Comparison Operators
• > Greater Than
• < Less Than
• <> No Equal to
• <= Less than or Equal to
• >= Greater than Equal to
• Majorly used to calculate Value Fields
• Parameter Requests - Like [which alphabet to begin with] & “*”
[which Country would you like to see]
• Building Expressions (Calculated Columns), using Builder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/accessessentialtraining-framework-190223031809/85/Access-essential-training-framework-28-320.jpg)