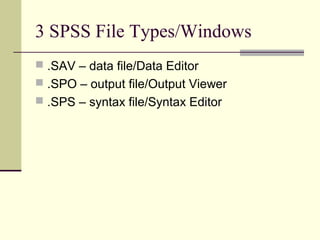
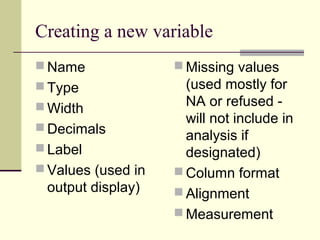
SPSS is a statistical software package used for data management and analysis. It allows users to enter and manipulate data, conduct a wide range of statistical analyses, and generate graphs. SPSS files come in three types: .SAV files contain the data, .SPO files contain output, and .SPS files contain syntax. The data editor interface allows users to view, enter, edit, and sort data. It also enables data manipulation through functions like computing new variables and recoding existing ones. SPSS can be used to produce basic descriptive statistics, frequencies, cross-tabulations, and more advanced analyses like correlations, t-tests, regression and ANOVA. Syntax files allow users to save and re-run analyses.