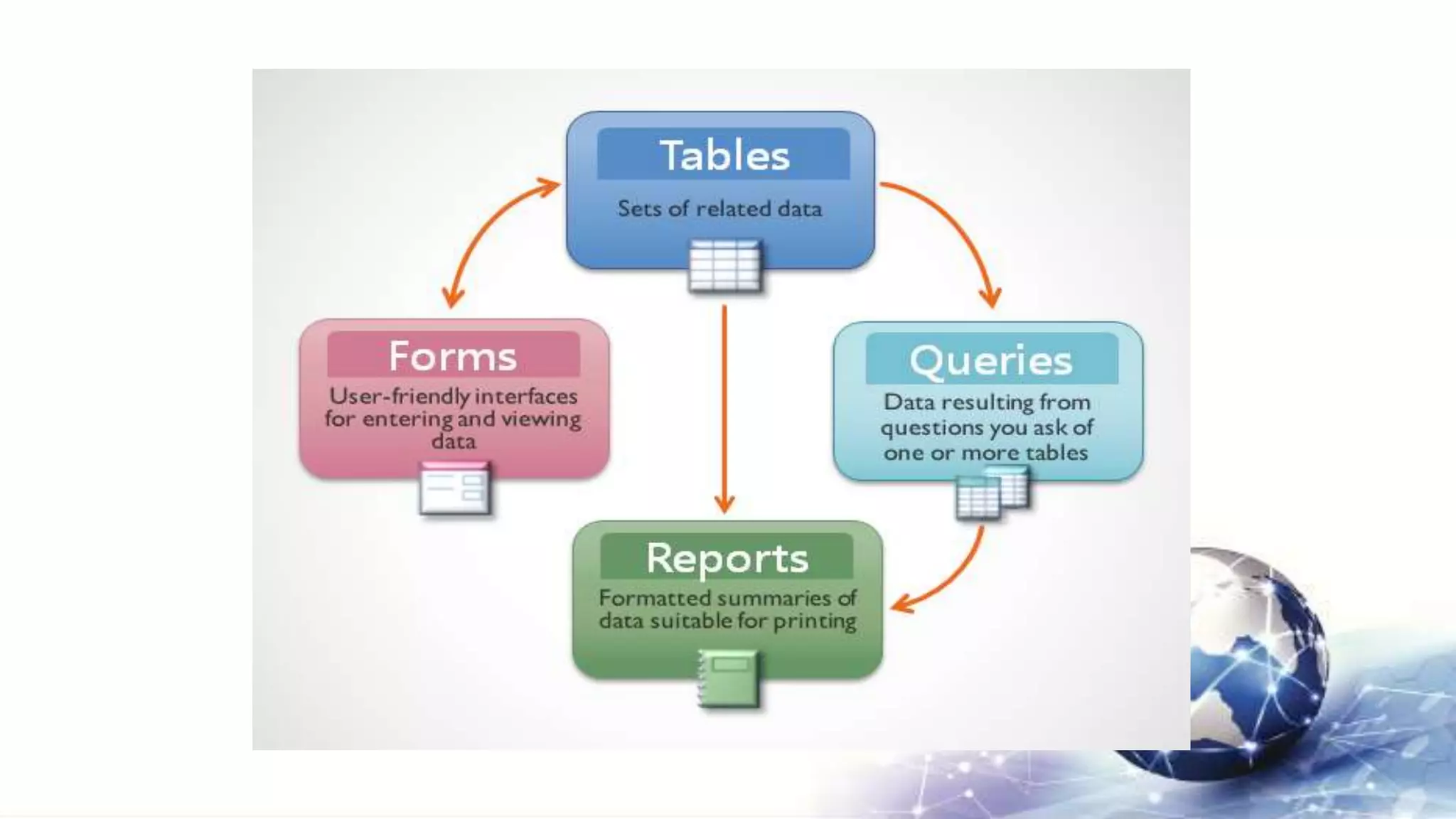
This document provides an introduction to Microsoft Access databases. It defines what a database is and describes the key components of an Access database, including tables, queries, forms and reports. It also outlines common database terminology like records, fields, primary keys and relationships. Database objects in Access are described as well as different data types. The document concludes by covering how to create a new blank Access database.