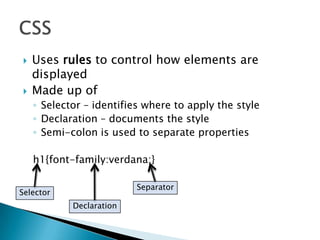
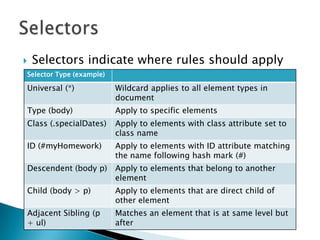
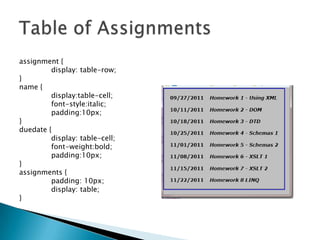
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) allow separation of document content from presentation through rules that control formatting and layout. A single CSS stylesheet can alter the appearance of multiple web pages, and different stylesheets can be used for a single page. CSS uses selectors, declarations, and properties to style elements. Stylesheets can be embedded within HTML documents or linked as external files, and support inheritance of styles. CSS treats elements as boxes and controls properties like margins, borders, padding, and positioning.