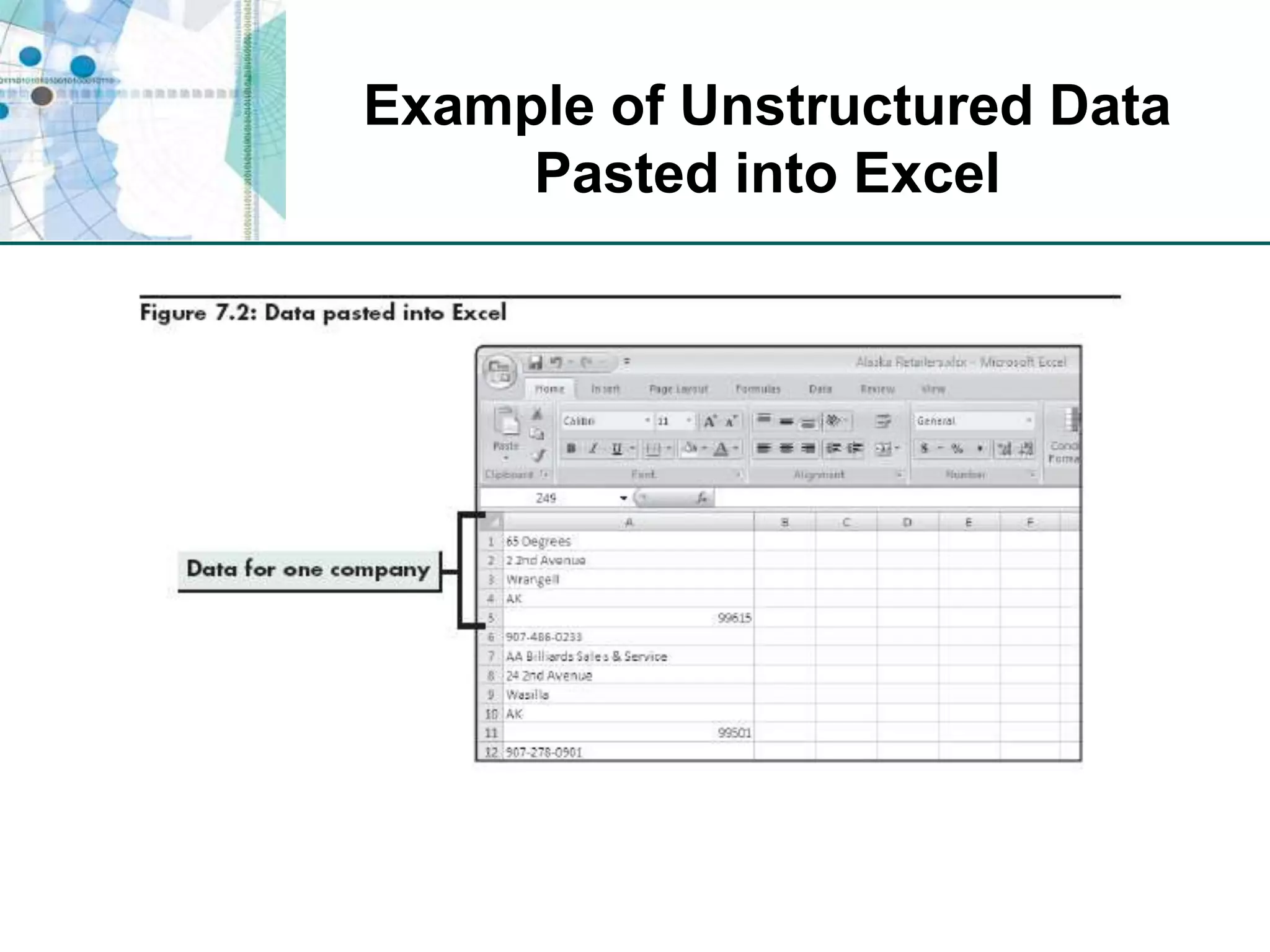
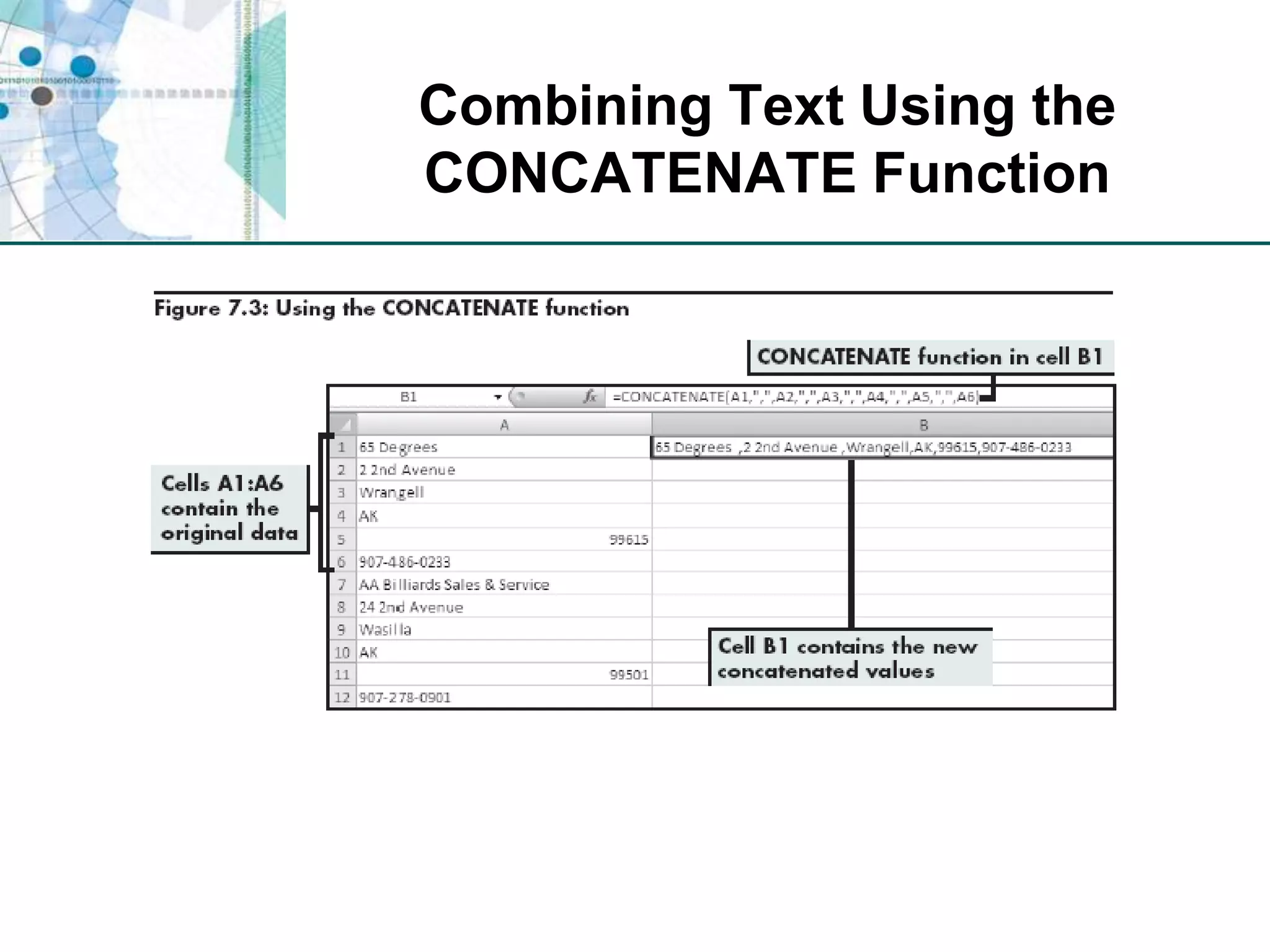
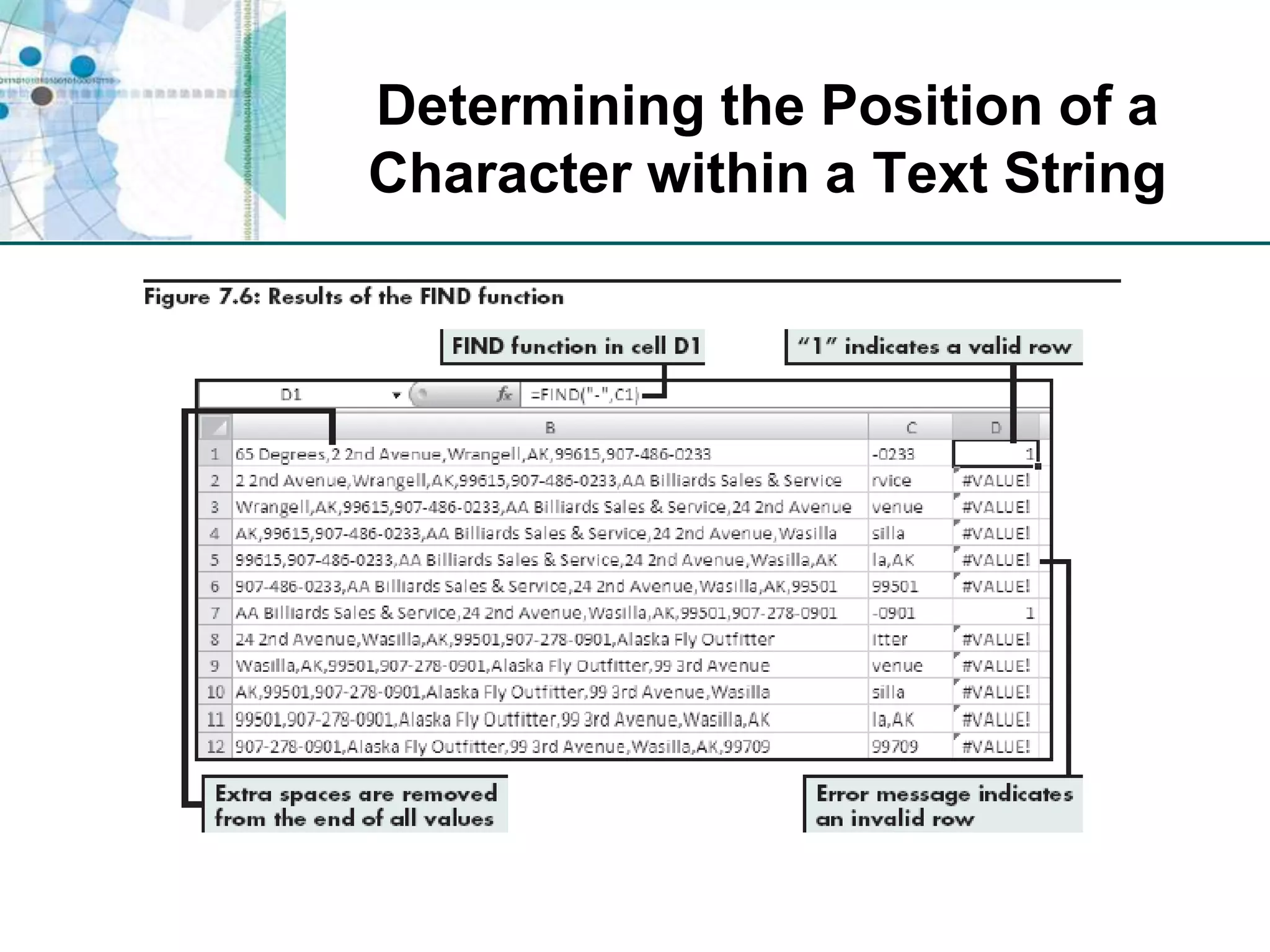
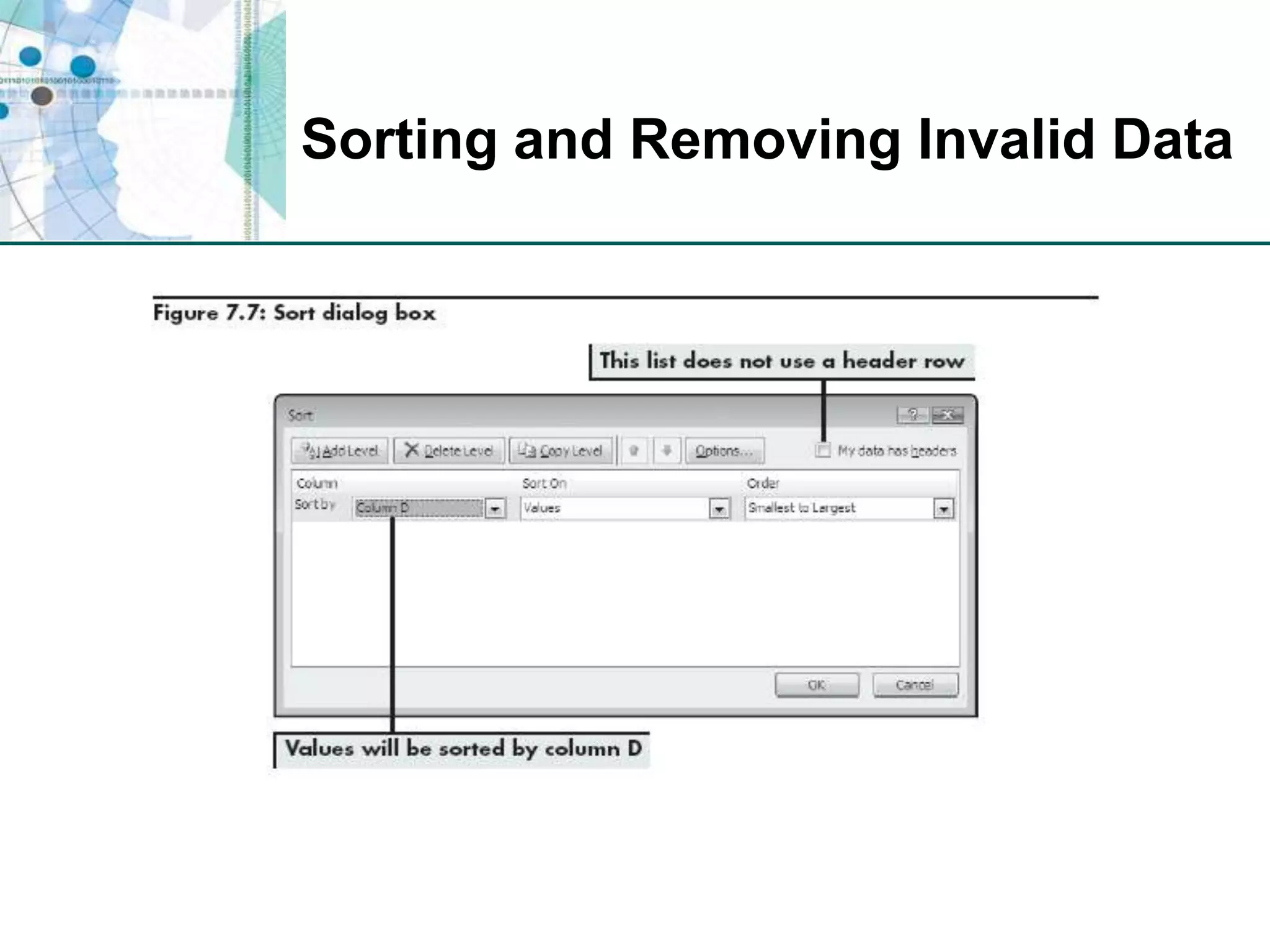
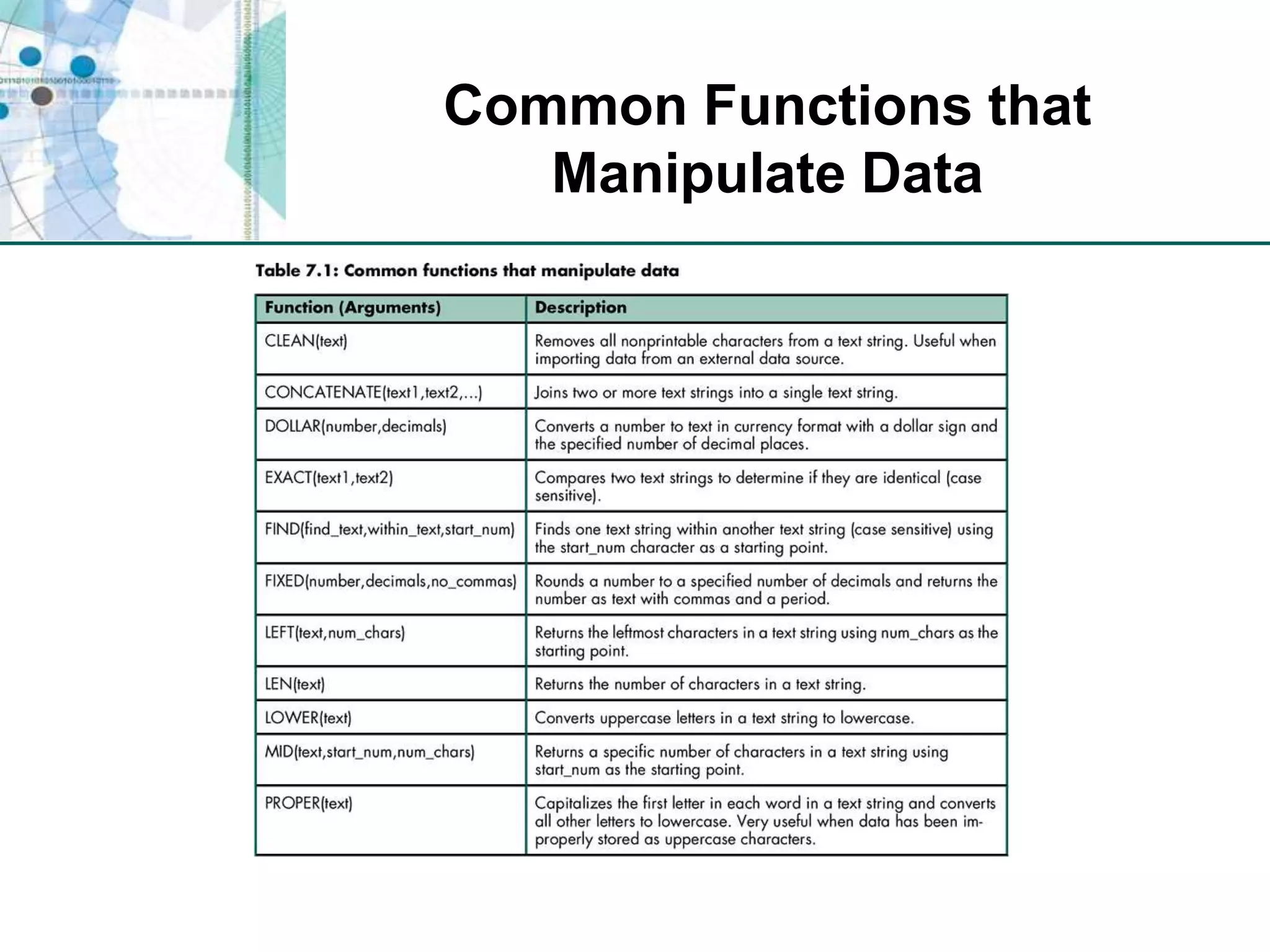
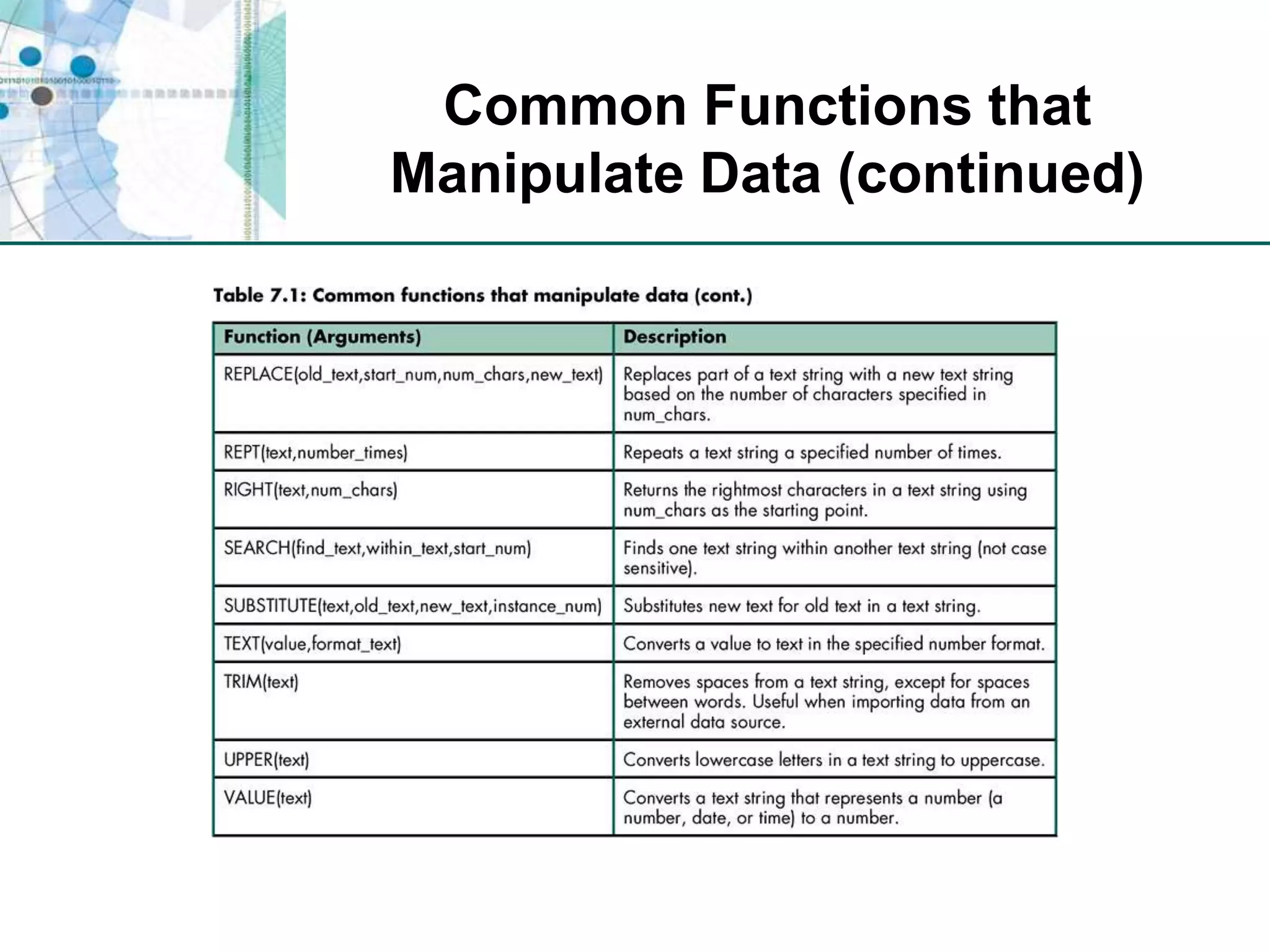
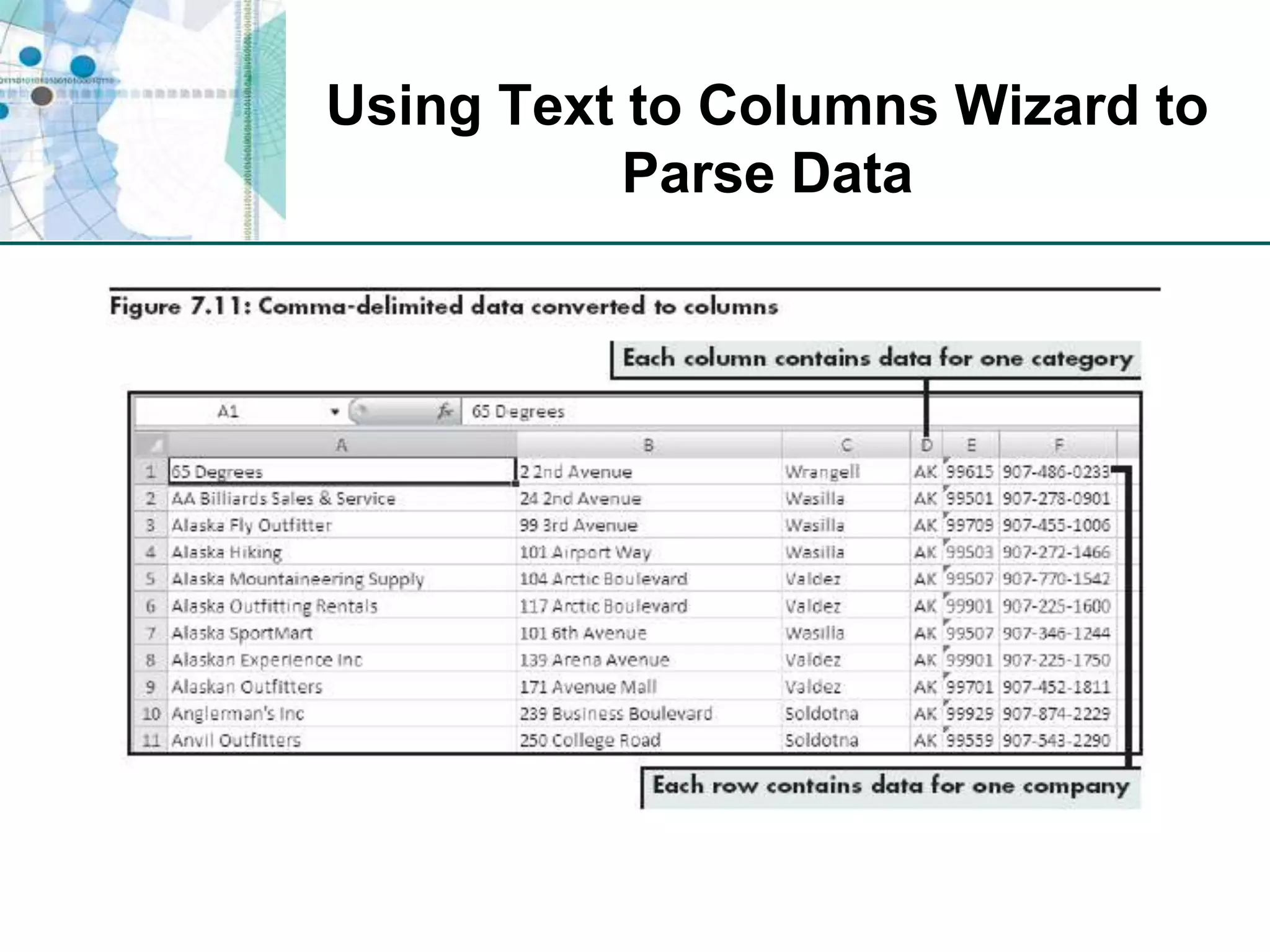
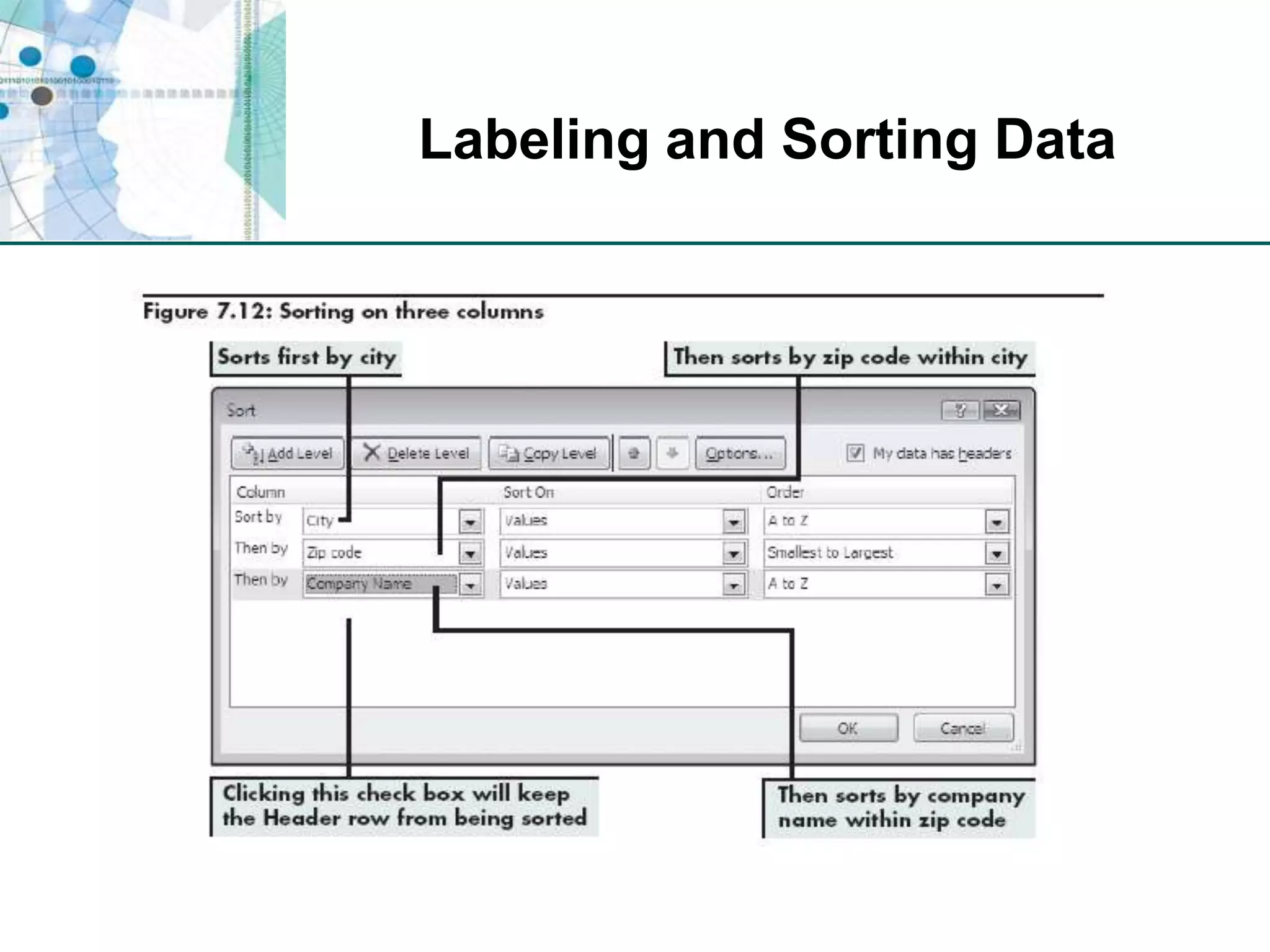
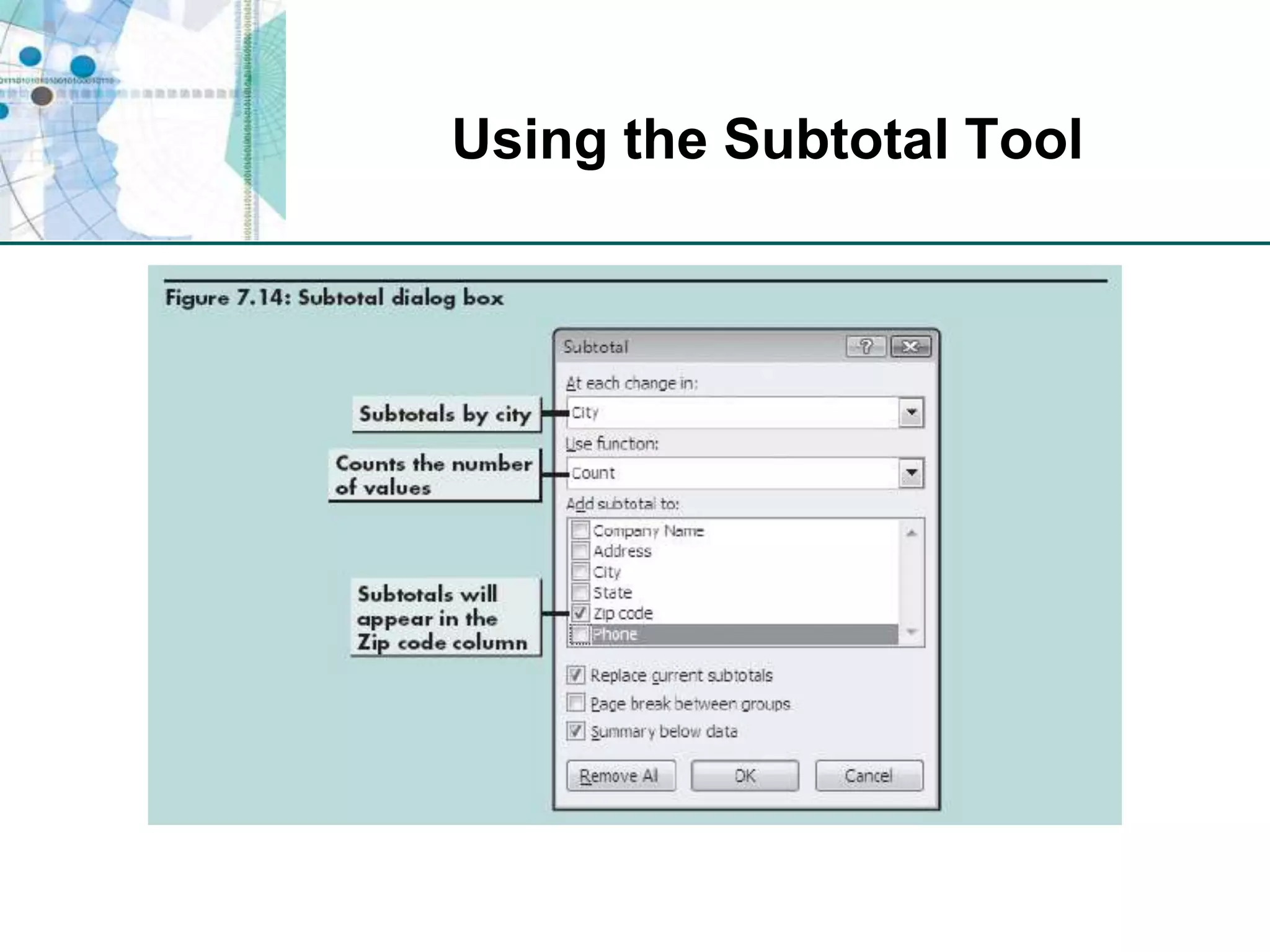
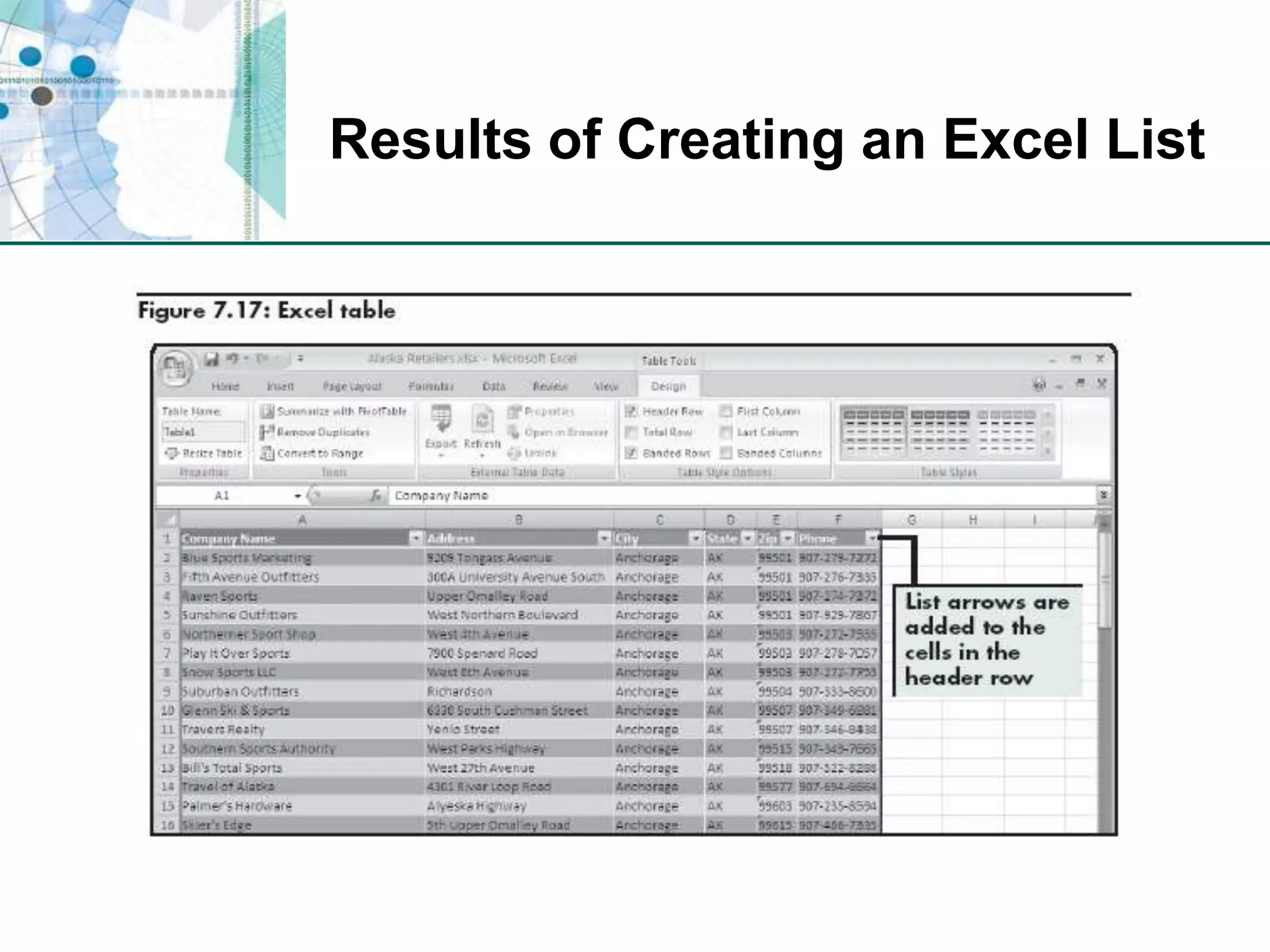
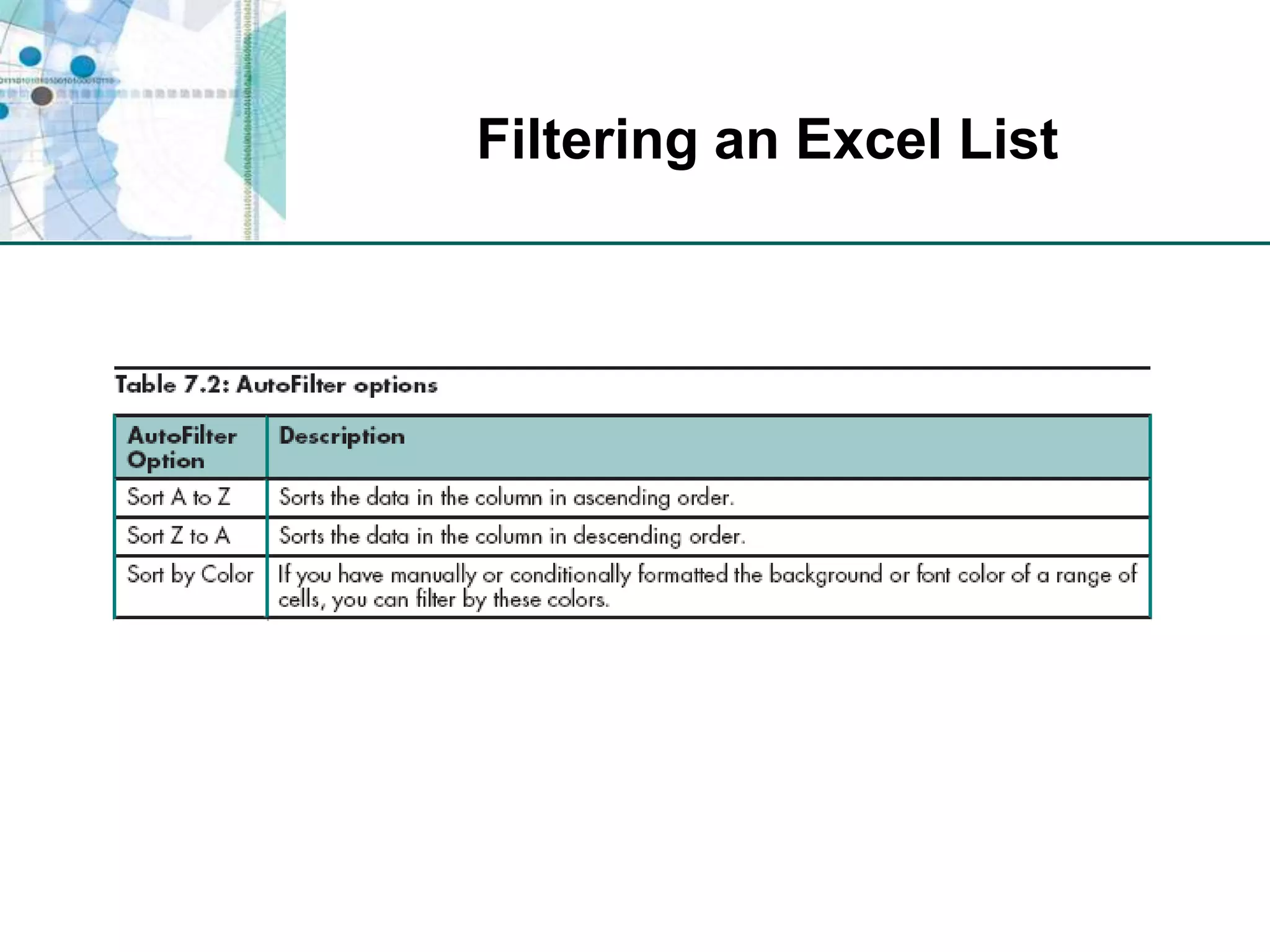
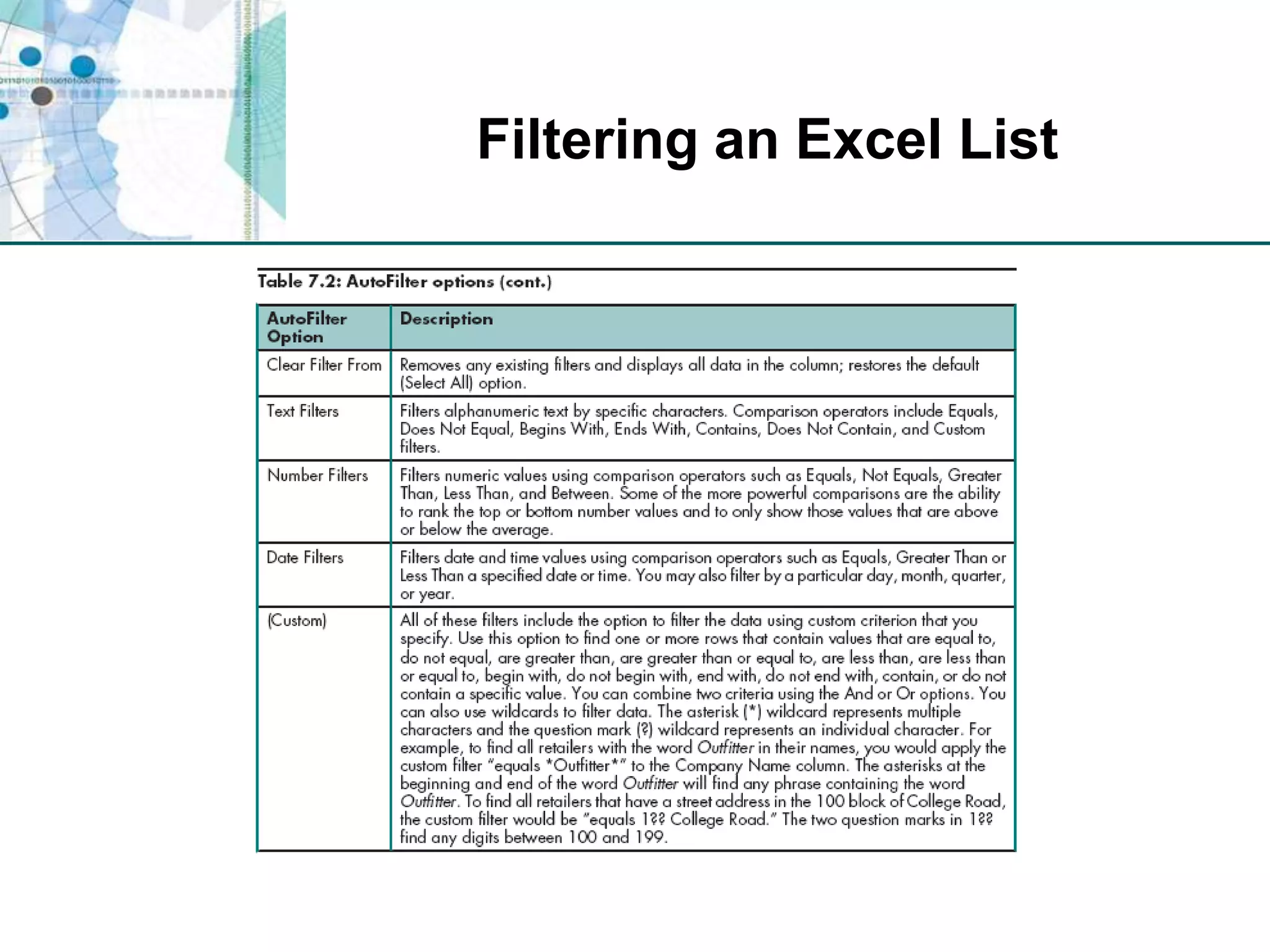
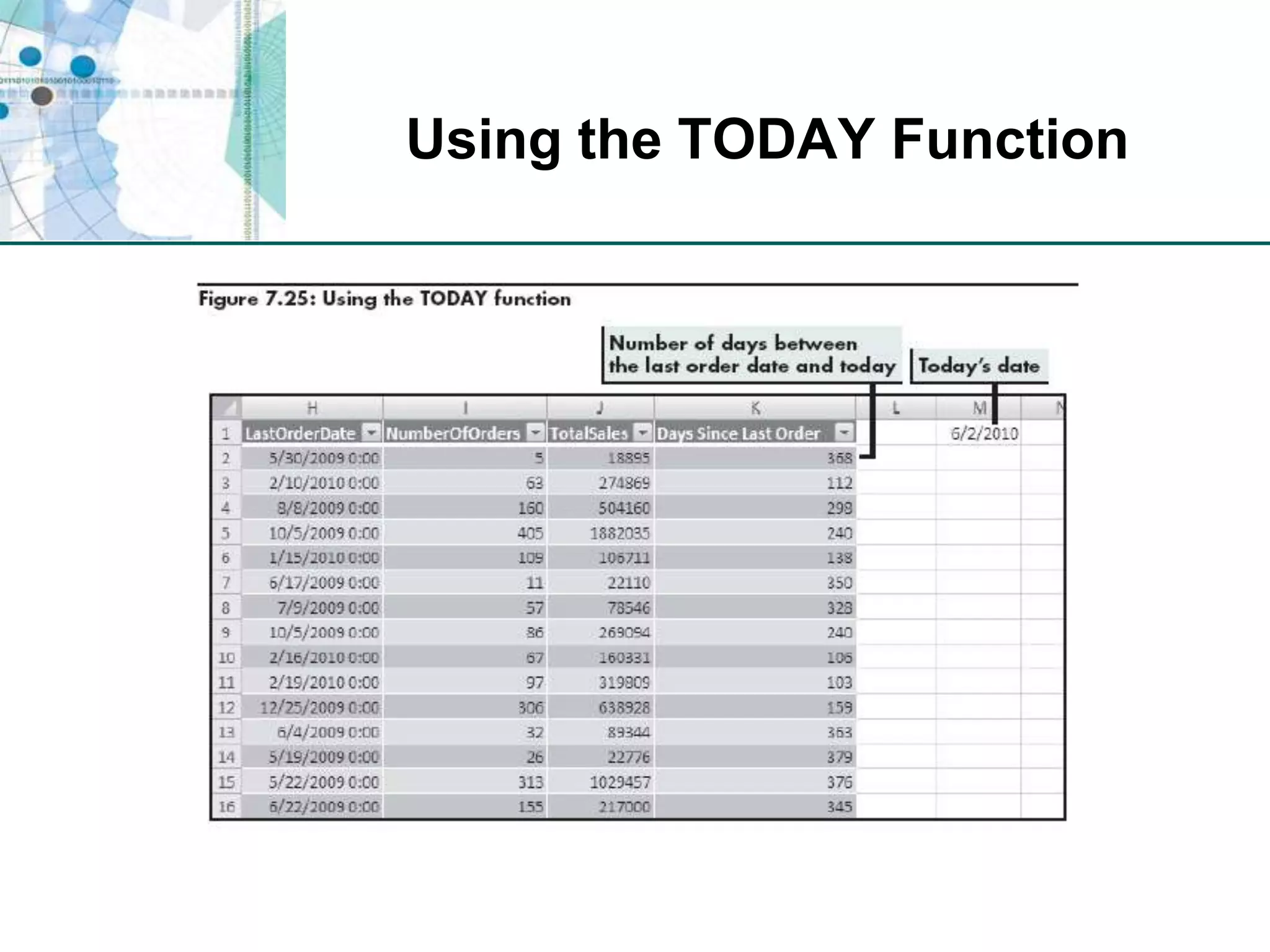
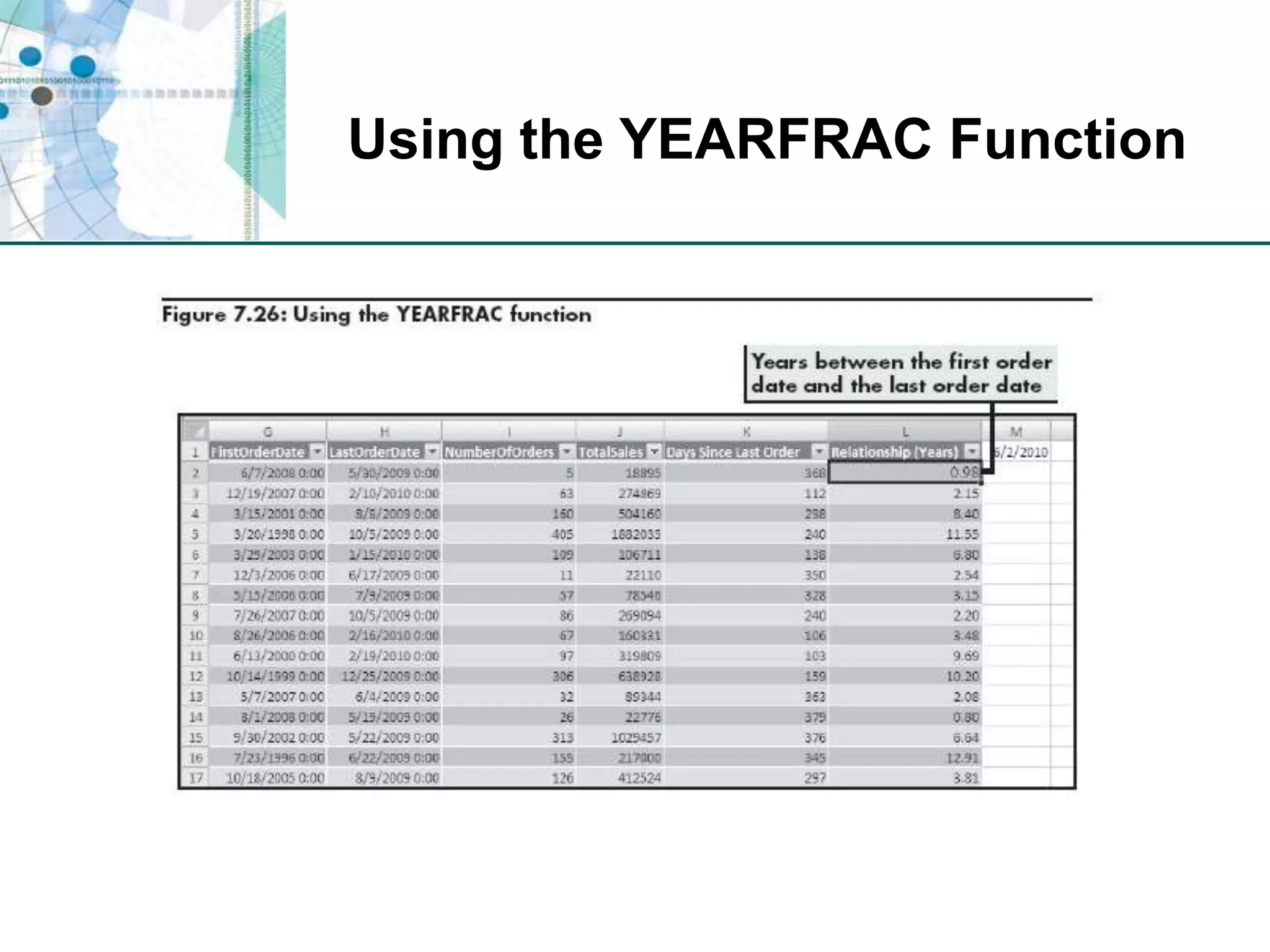
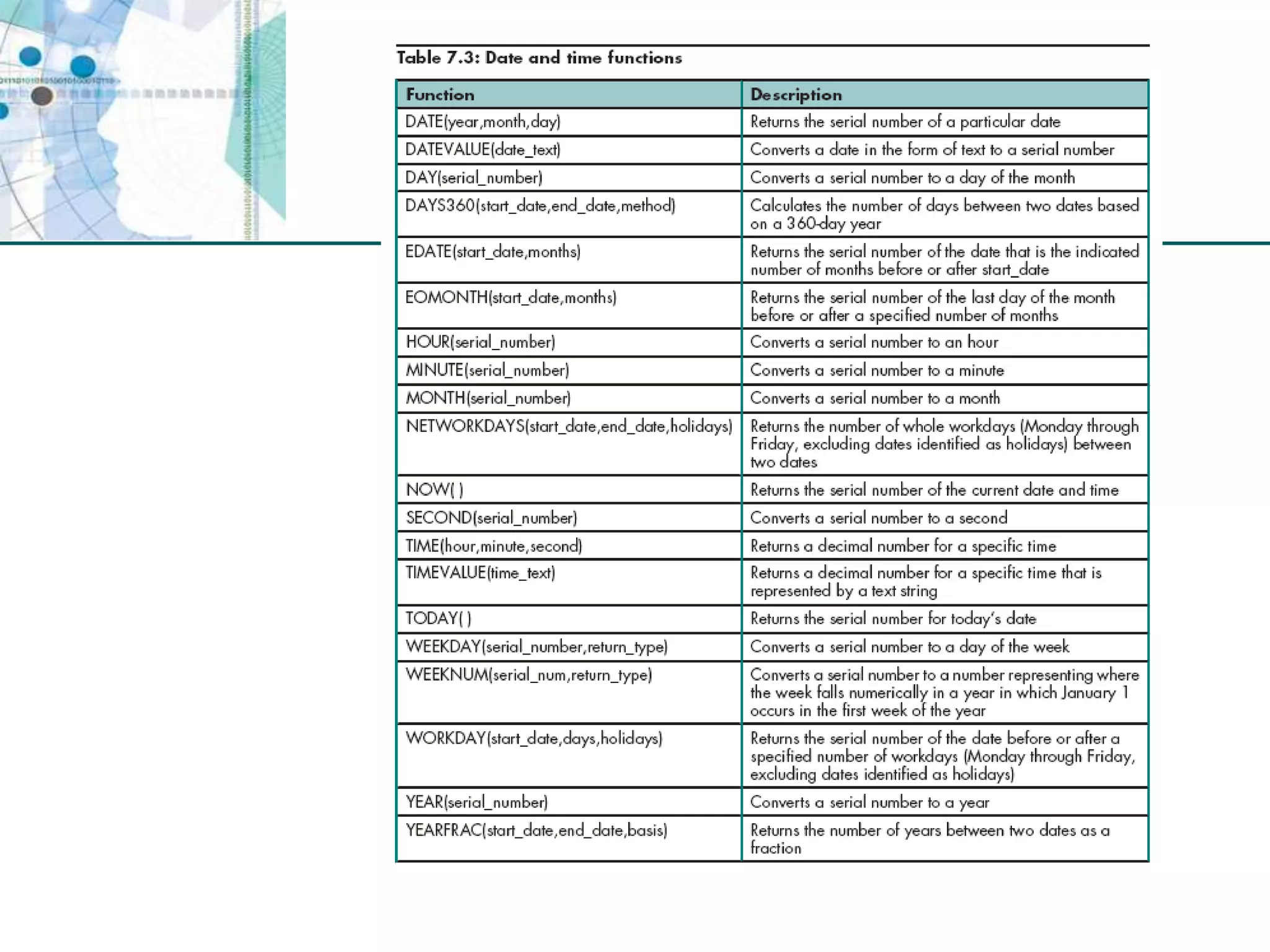
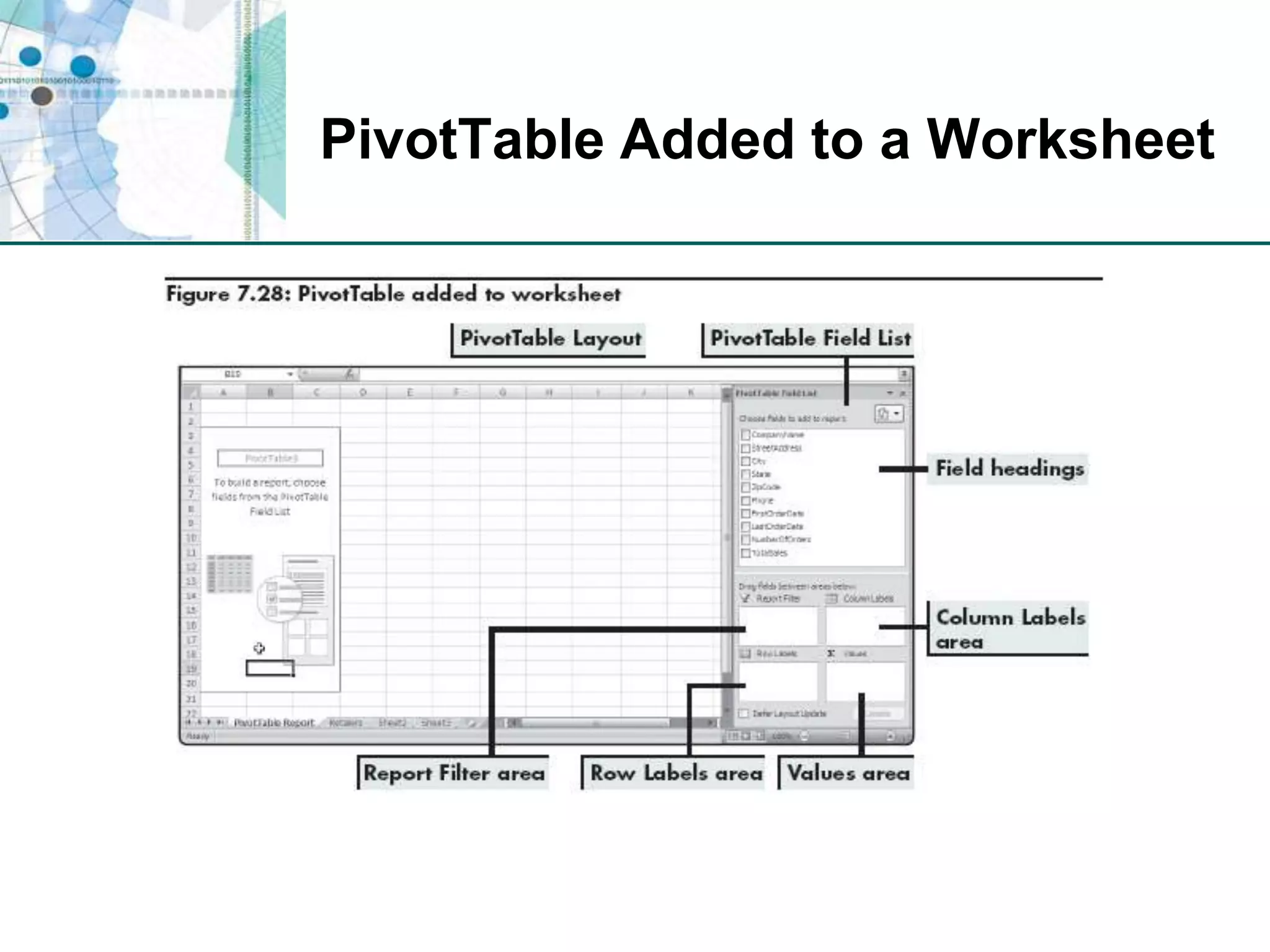
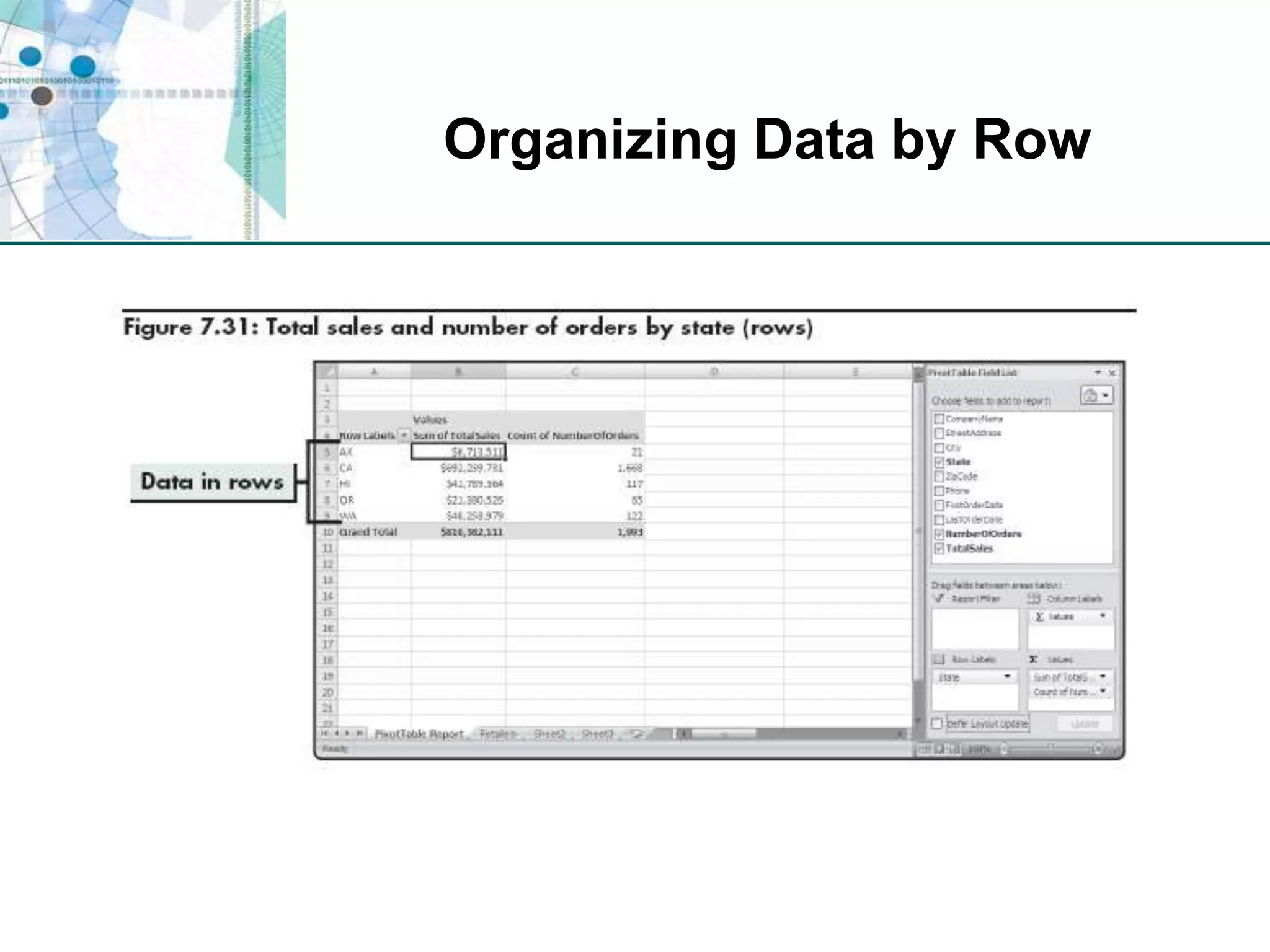
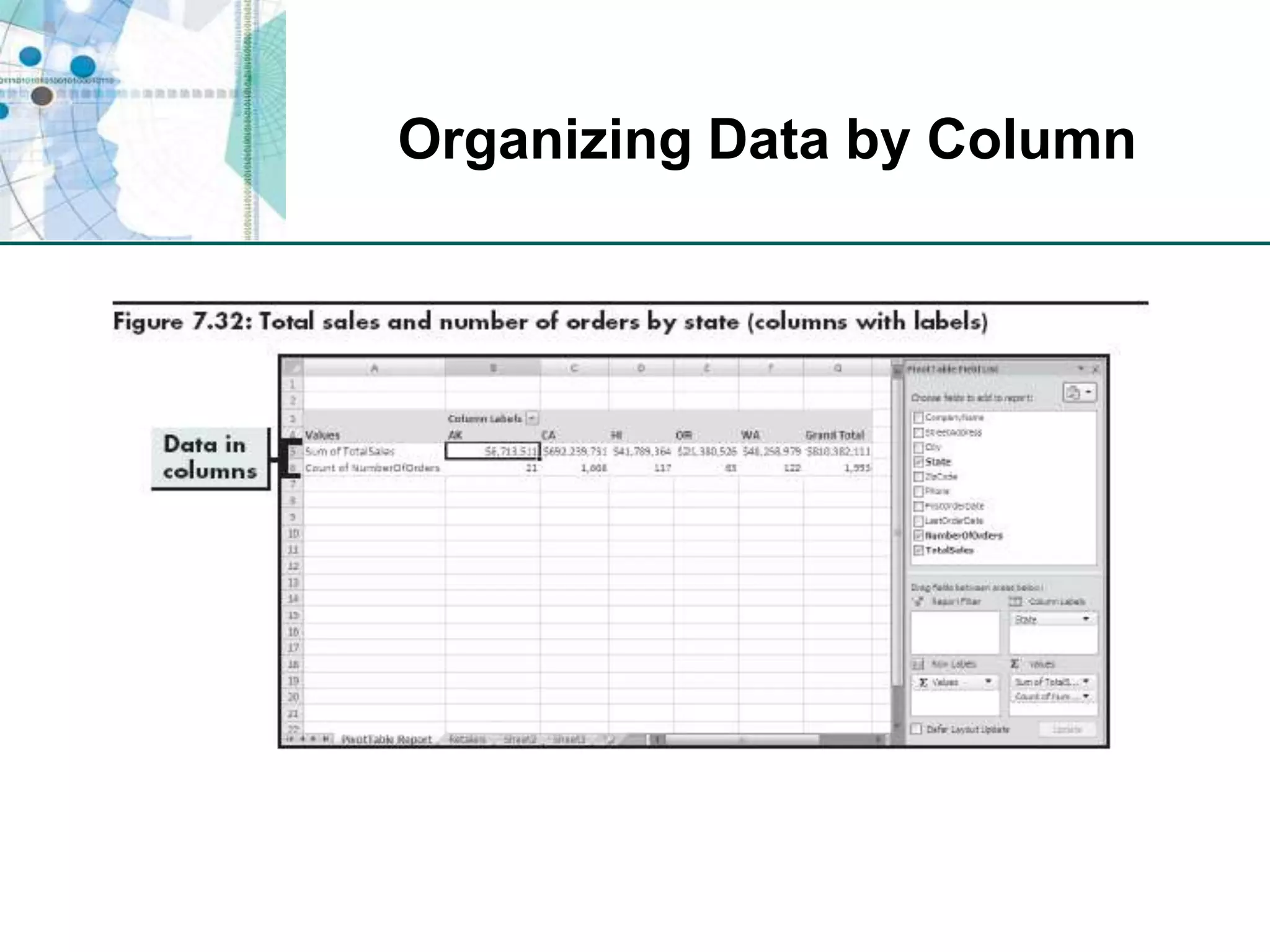
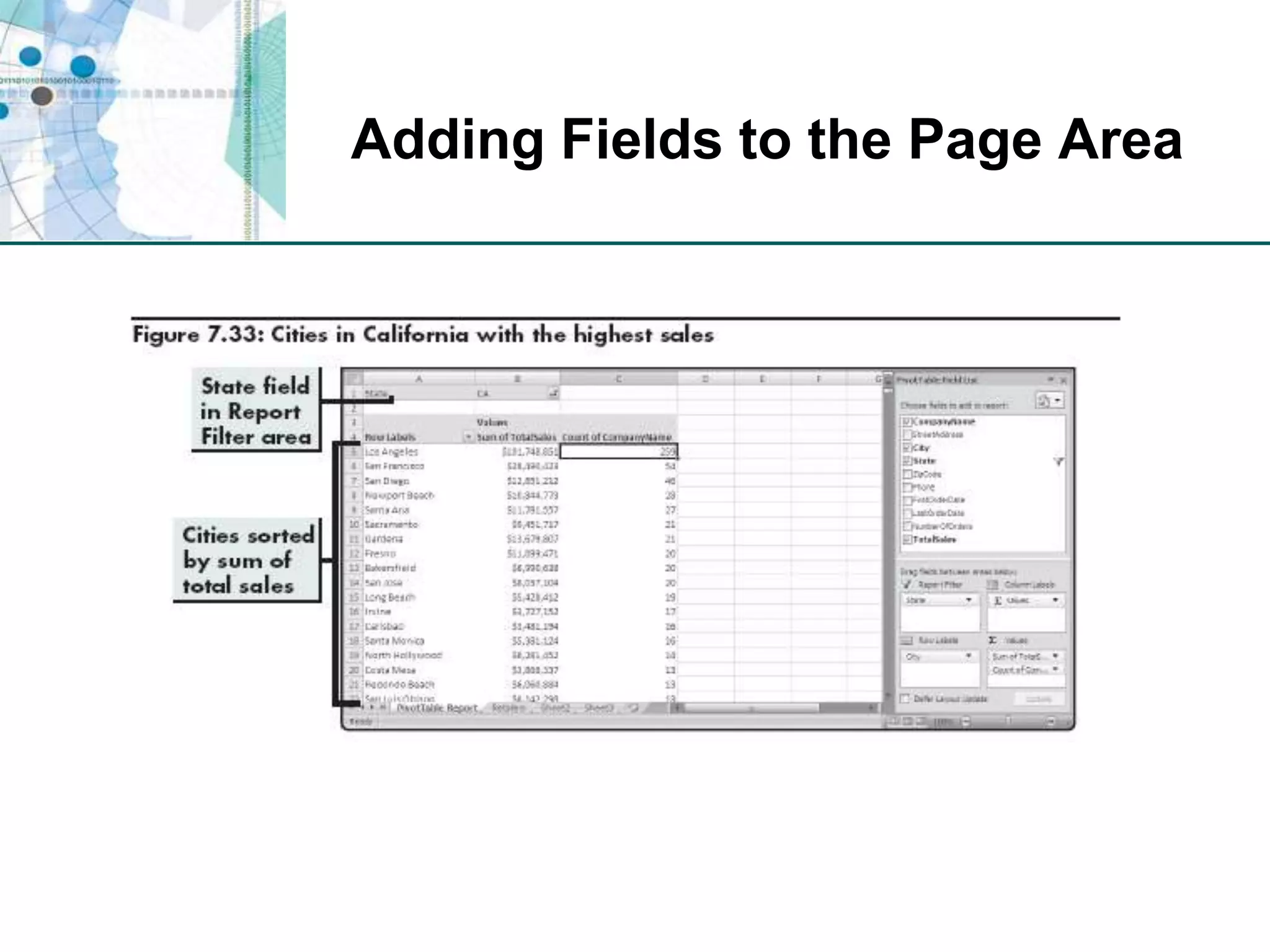
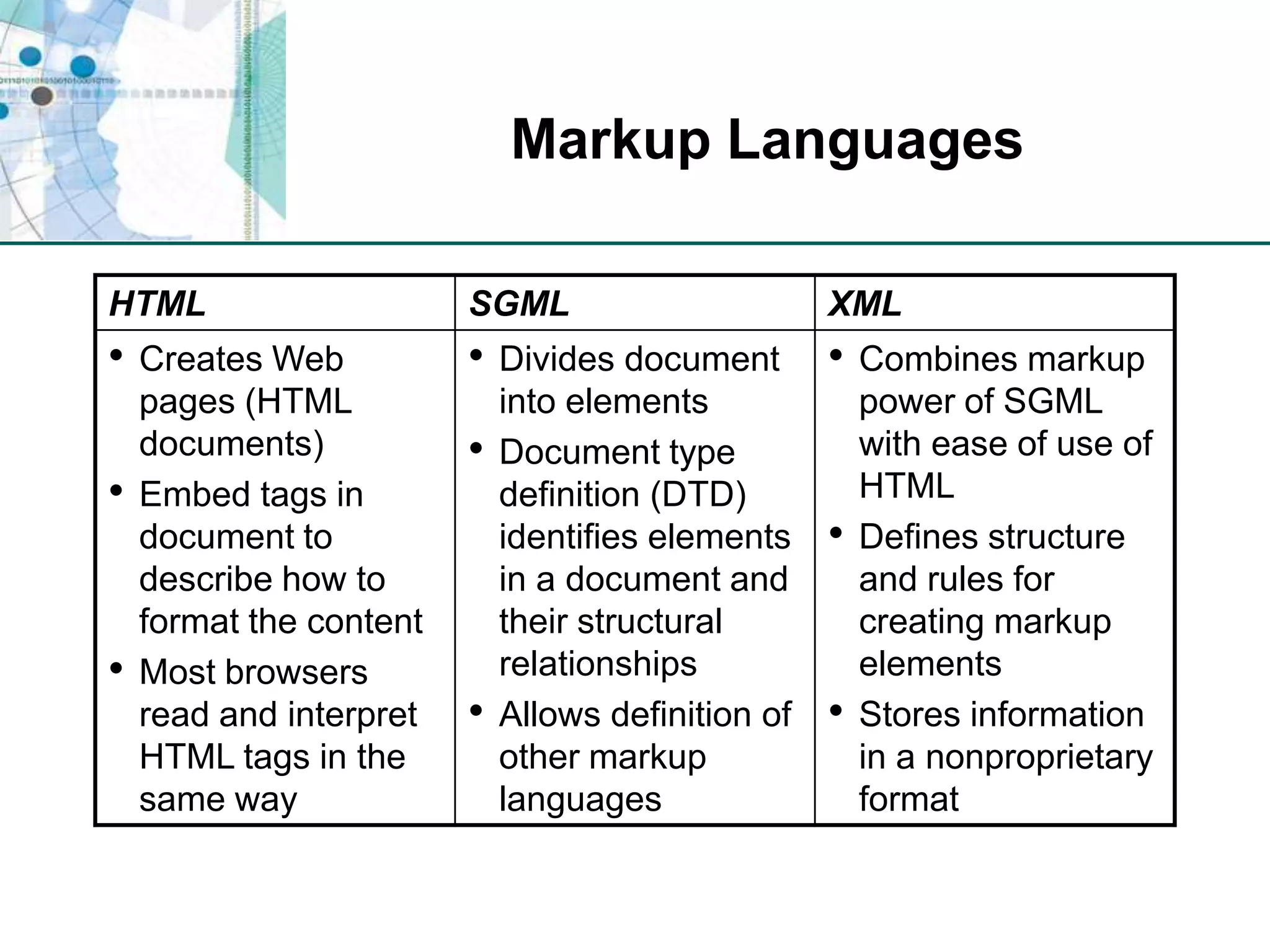
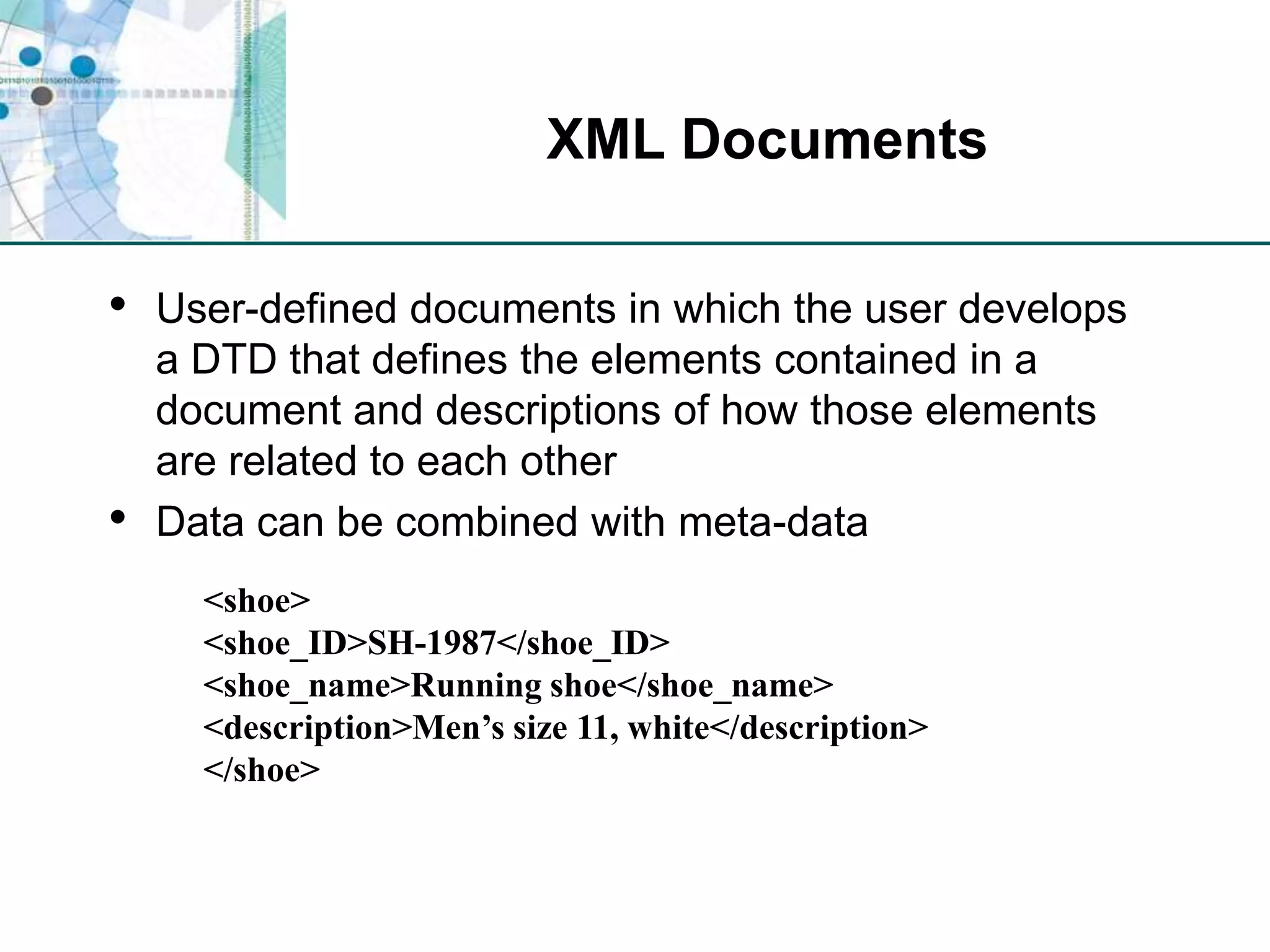
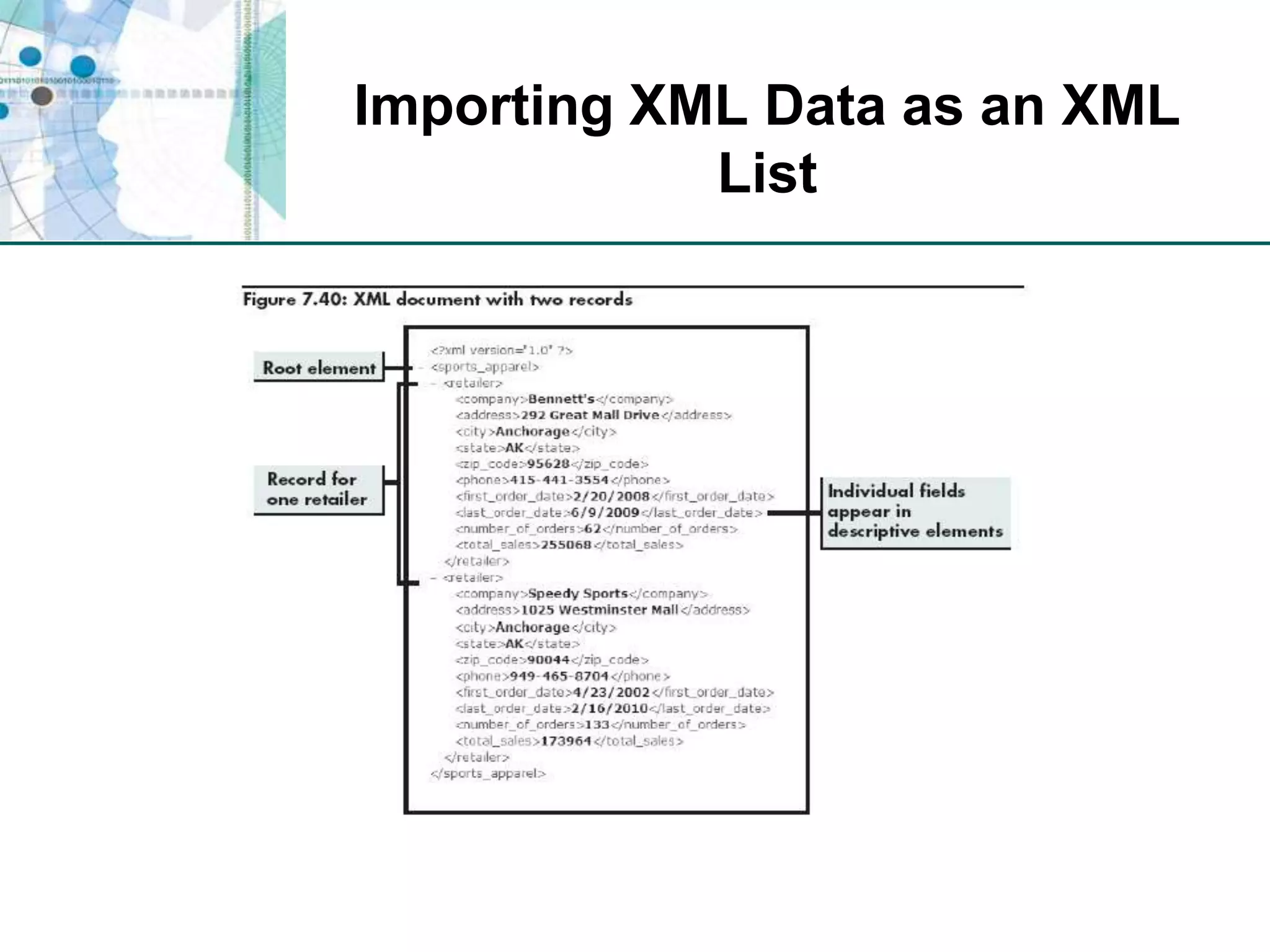
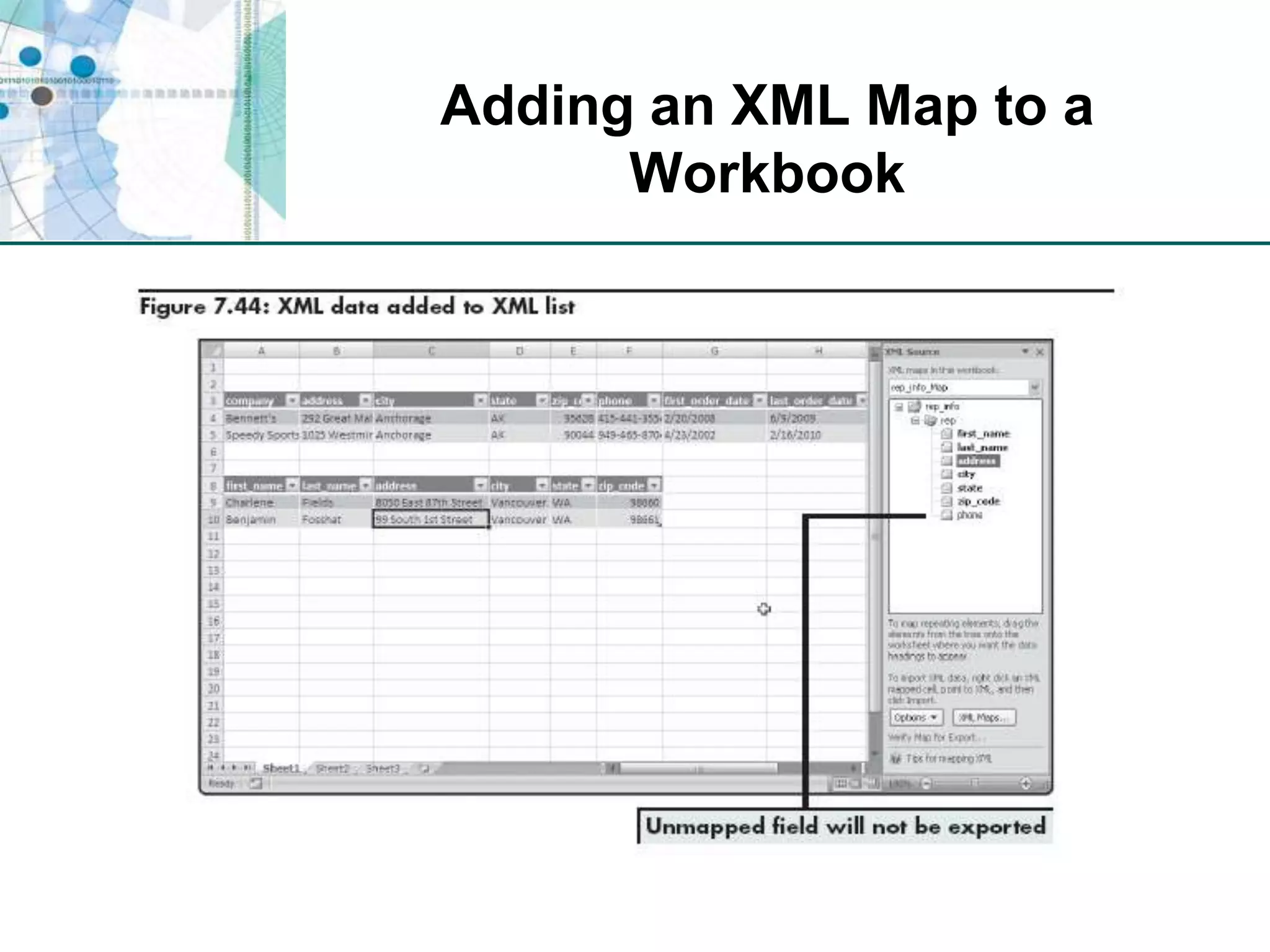
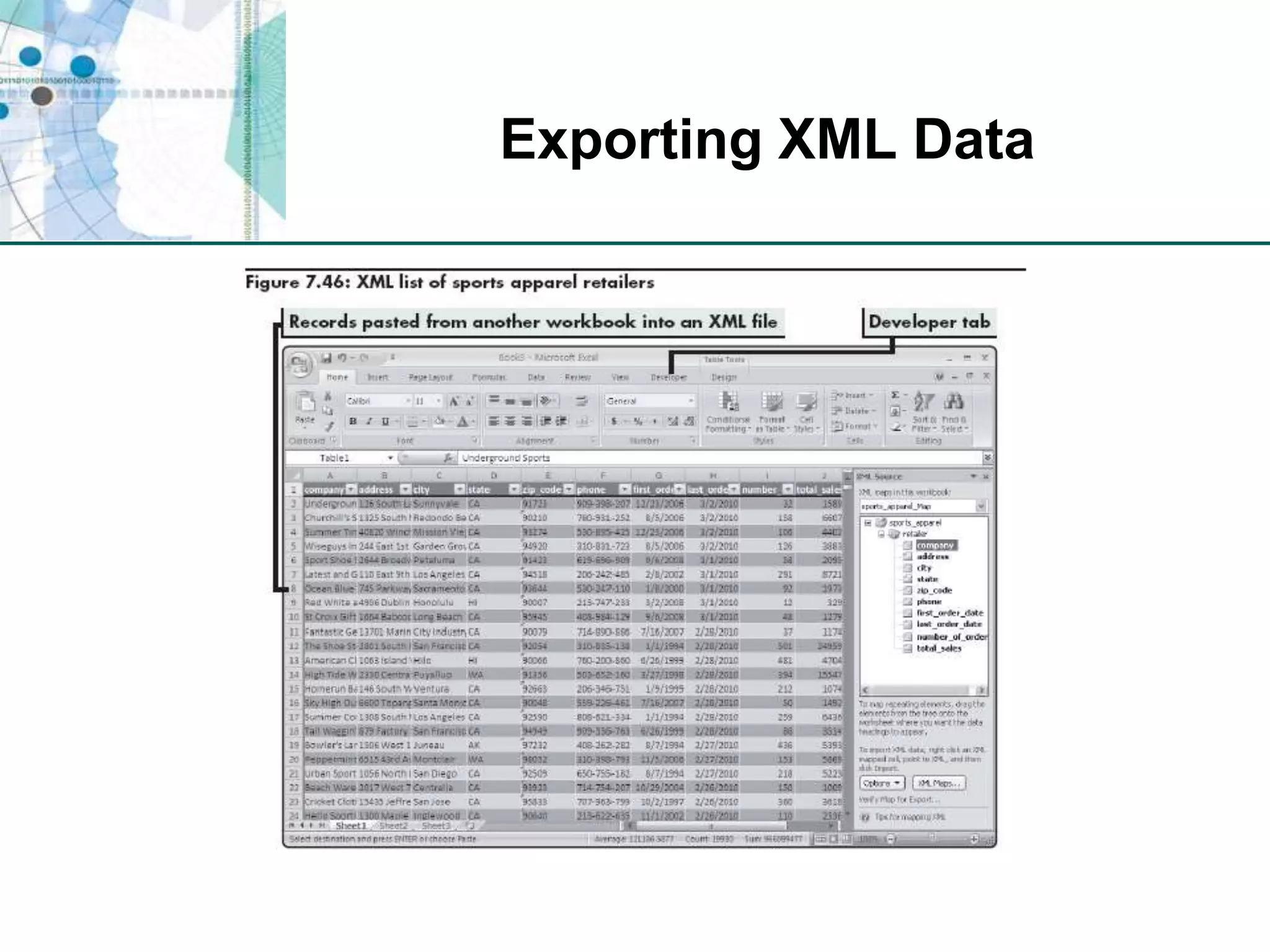
This chapter discusses organizing data for effective analysis in Excel. It covers importing and structuring text data, analyzing data imported from databases using functions like CONCATENATE and YEARFRAC, creating PivotTable reports to summarize data, and importing/exporting XML data using XML maps.