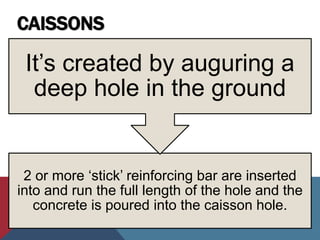
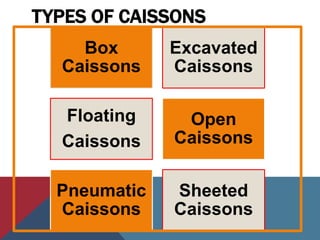
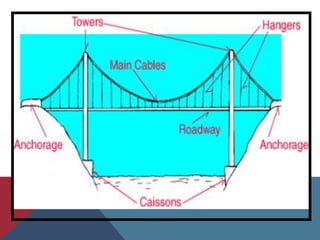
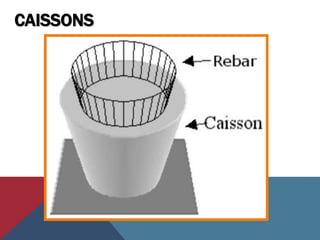
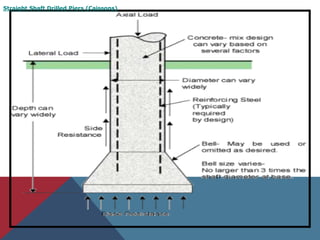
Caissons are prefabricated hollow structures that are sunk into the ground and filled with concrete to form deep foundations. They are commonly used for bridge piers and structures over bodies of water. The process involves sinking a caisson to the desired depth using excavation methods and then filling it with concrete. Caissons carry structural loads through bell-shaped bottoms that spread the load over a wider area of soil or bedrock.